Pushtoday
MuscleChemistry Registered Member
[h=3]Overview and History of Clomid[/h]Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) belongs to a category and class of drugs known as selective Estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). Selective Estrogen receptor modulators belong to an even broader class of drugs known as anti-estrogens. The other subcategory of drug under the anti-estrogens category is known as aromatase inhibitors (AIs), such as Aromasin (Exemestane) and Arimidex (Anastrozole). AIs and SERMs make up anti-estrogens. Aromatase inhibitors differ greatly from SERMs in their action and how they deal with the issues of estrogen control. The misunderstanding that SERMs, such as Nolvadex and Clomid, serve to lower estrogen levels must first be addressed before delving into any further details.
This is a persistent rumor among the anabolic steroid using community that has begun to erode as of late, but the rumor still persists. SERMs serve to block the action of Estrogen at the receptor sites in breast tissue by occupying the receptor sites in place of Estrogen so that Estrogen itself cannot exert its effects there through receptor site binding. Conversely, SERMs will also act as Estrogens at receptor sites at other cells in other areas of the body (the liver, for example in Nolvadex’s case). SERMs do not lower circulating levels of Estrogen in blood plasma. Aromatase inhibitors serve to do this by eliminating the production of Estrogen through binding to and disabling the aromatase enzyme, which is the enzyme responsible for the conversion (or aromatization) of androgens into Estrogen.
clomid1Clomid was developed and approved for use in the early 1970s for the treatment of female infertility (and later on subsequently expanded to treating male infertility as well). Not too long after its release in the United States, its popularity and use spread internationally where, like Nolvadex, its popularity and rate of use is so massive that it is widely and freely available in the majority of countries and regions across the world under an almost infinite number of brand names as well as generic products. Its popularity and cheap cost make it a very easily attainable compound for both medical use as well as off-label use for the anabolic steroid using community.
Clomid, although it is classified as an anti-Estrogen, is actually utilized for the treatment of female infertility resulting from ovulation failure (anovulatory infertility). Although Clomid is a very close relative to Nolvadex with both belonging to the SERM category of drugs, Clomid in reality operates at a much poorer efficiency compared to Nolvadex in regards to its Estrogen antagonistic activity in breast tissue. This is to say that it is a weaker Estrogen blocker in breast tissue, where Nolvadex is much better suited for this task. Instead, Clomid’s prime application in medicine is that of a non-steroidal ovulatory stimulant for women. Because Clomid is a SERM, like Nolvadex, it exhibits mixed Estrogen agonist and antagonist effects in various tissues of the body. Like Nolvadex, Clomid acts as an Estrogen antagonist in the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, endometrium, vagina, and cervix. This is to say that in these tissues and areas of the body, Clomid serves to mitigate (inhibit or block) the action of Estrogen.
In males as well as females, its Estrogen antagonistic effect on the hypothalamus will trigger a release of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone). These two hormones in men are the signal hormones that signal the testes to begin or increase its production of Testosterone, and this total process is known as the HPTA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis). In females, this same action occurs, except LH and FSH will trigger the release of eggs from from the ovaries (known as follicular rupture), which would lead to increased chances of contraception. This total process in females is known as the HPOA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Ovarian Axis). Much like Nolvadex, Clomid is what would be considered an Estrogen that acts as a ‘fake’ Estrogen in areas of the body, such as breast tissue (so as to block the effects of ‘real’ Estrogen, while it also works as an actual Estrogen in other areas of the body. This is another manner of describing the agonistic/antagonistic nature of Clomid in regards to Estrogen.
For anabolic steroid using athletes and bodybuilders that are for the most part males, Clomid can serve as an effective anti-Estrogen for the purpose of mitigating one particular unwanted side effect of Estrogen as a result of the use of aromatizable anabolic steroids (such as Testosterone, Dianabol, Boldenone, etc.). This particular unwanted side effect is that of gynecomastia, which refers to the development of breast tissue resulting from excess Estrogen levels in body. Because of Clomid’s Estrogen antagonistic effects on the hypothalamus resulting in the increased production of gonadotropins LH and FSH, Clomid can effectively be utilized to increase endogenous Testosterone production in males. This is especially important for anabolic steroid using individuals that wish to restore proper hormonal function during the weeks following the conclusion of an anabolic steroid cycle, a period known as PCT (Post Cycle Therpay). The traditional protocol for such a use is that of a combination of Nolvadex, Clomid, and HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) for the duration of several weeks, and although much better more modern protocols have been developed, this long-standing traditional PCT protocol is still effective. The use of Clomid for this purpose will be covered in further detail under the Clomid doses section of this profile.
All of the tripohenylethylene compounds under the SERM family (Nolvadex, Clomid, and Toremifene) also exhibit Estrogen agonistic effects in the liver, meaning the liver is one such area of the body where SERMs such as Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) will act as an Estrogen rather than block Estrogenic activity there. In studies, this has shown to be a beneficial aspect of SERMs, as Estrogens as well as Estrogen agonists (such as Clomid and Nolvadex) impart a positive effect on cholesterol values through actions in the liver. This is the reason as to why the reduction of Estrogen levels through the use of an aromatase inhibitor (AI) is not always the best decision, as the reduction in Estrogen often results in negatively impacted cholesterol profiles as demonstrated anecdotally as well as in clinical studies.
[h=3]Chemical Characteristics of Clomid[/h]Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) is a non-steroidal selective Estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that possesses both mixed agonistic as well as antagonistic properties in relation to Estrogen in different areas of the body. Clomid belongs to a family of compounds known as triphenylethylene compounds, of which Nolvadex (Tamoxifen Citrate) is also a member of, and a very closely related compound to Clomid.
[h=3]Properties of Clomid[/h]Clomid’s primary use within the medical field is that of a fertility drug in females but also among males as well.
It has already been established that Clomid, being a SERM, does not reduce circulating Estrogen levels in the body, but instead serves to occupy the receptor sites in breast tissue so that Estrogen itself cannot bind to these receptors due to Clomid’s stronger binding strength to it. In layman’s terms, Clomid essentially acts as a ‘fake’ Estrogen that acts as a placeholder at the receptor sites in breast tissue. As a result, Estrogen cannot activate gene transcription in the cells there in order to formulate gynecomastia, and any existing Estrogen that has already bound to receptor sites will essentially be ‘forced’ out of the receptor sites by Clomid which then occupies the receptor site instead. However, it must be noted that Clomid’s action in this area is far weaker and less efficient than its close relative compound Nolvadex, which serves as a better choice for this purpose.
Although Clomid could indeed be utilized by anabolic steroid using individuals that wish to prevent or eliminate and reverse formulating gynecomastia in its early stages, its more effective and promising role is that of an endogenous Testosterone production stimulating compound. This is the primary purpose and function of Clomid among anabolic steroid using athletes and bodybuilders, and is the primary desired effect in this sense. It must be noted, however, that research has also demonstrated various advantages that Nolvadex does possess over Clomid in this sense as well, which will be further covered in the next section of this profile.
As a SERM, Clomid will not serve to block or reduce any other Estrogenic side effects, however, as it serves only to block Estrogenic activity at the breast tissue area (when major Estrogenic side effects are concerned). Clomid does not (nor do any SERMs) serve to reduce bloating, water retention, rising blood pressure (as a result of water retention), or acne formation – these are all side effects resultant from increasing blood plasma Estrogen levels.
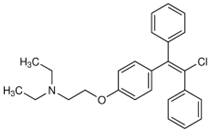 Clomiphene Citrate (AKA Clomid)
Clomiphene Citrate (AKA Clomid)
Chemical Name: 2-(4-(2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-diethyl-ethanamine
Molecular Weight: 406 g/mol or 598.10 g/mol (citrate salt)
Formula: C26H28ClNO
Original Manufacturer:
Half Life: 5 – 7 days (some reports as long as 14 days)
Detection Time: 2 months
Anabolic Rating: N/A Androgenic Rating: N/A
[h=1]Clomid Dosage[/h]
Clomid is the most popular endogenous Testosterone simulating compound among the anabolic steroid using community. This is due in part because of how long it has been on the market, as well as being the very first fertility drug (for both men and women) that anabolic steroid users first took notice of. Despite the fact that Nolvadex has demonstrated an overall better ability to stimulate Testosterone levels in men, Clomid nevertheless remains a staple compound for hormonal recovery during PCT for most anabolic steroid users. The overwhelming majority of PCT protocols will include Clomid and Nolvadex together for an added effect on HPTA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis) recovery during the post-cycle period, although there are some problems and setbacks related to Clomid’s action that will be covered shortly. Clomid doses in comparison to Nolvadex, for example, will normally need to be in the higher range in order for the compound to do its job in the body, as it is not as powerful as its brother compound Nolvadex, and this will be explained shortly.
In terms of Clomid dosages for the purpose of HPTA and endogenous Testosterone restoration, one study has demonstrated that 150mg of Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) administered daily raised endogenous Testosterone levels of 10 healthy males by approximately 150%, while incidentally, 20mg of Nolvadex (Tamoxifen Citrate) daily raised endogenous Testosterone levels by the same amount[1]. It is very evident here that Clomid is very effective for this purpose, but Nolvadex seems to be a more cost-effective choice seeing as though it is more effective than Clomid when compared mg for mg. Nevertheless, Clomid can still be a very valuable compound for hormonal restoration, as Clomid doses of 100mg daily would theoretically raise Testosterone levels to 100% above baseline, and 50mg would raise Testosterone levels to 50% above baseline, etc.
Some further studies have demonstrated Clomid’s effectiveness in the long term, where 178 hypogonadal males also suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED) were administered Clomid dosages for 4 months, and 75% of the test subjects improved while 25% did not – however, all test subjects exhibited significant increases in LH, FSH, and Testosterone production[2]. The study had also noted that with short term administration, only modest increases in sexual function were observed. It is very evident that Clomid can be utilized as an effective treatment for erectile dysfunction in most males, even during the long-term.
Prior to delving into any further details, an important note must be made to the reader:
The use of SERMs or any anti-Estrogens should only be utilized when absolutely required, and should be discontinued as soon as the requirements to use them (such as gynecomastia or insufficient androgen production) have desisted.
Medical Clomid Dosage
Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) is utilized within the medical establishment primarily for the treatment of ovulatory dysfunction (female infertility), which prevents problems for females attempting pregnancy. For this purpose, the prescription Clomid doses land in the range of 50mg per day, and Clomid administration is to only begin 5 days after the menstrual cycle has started. Following this, Clomid doses are to be continued for only 5 days. If an improvement in ovulation is not observed, then prescription Clomid doses are to be increased to 100mg daily for the same 5 day period.
Most of the time, medical professionals will have their patients engage in an average of 6 of these aforementioned cycles, provided the therapy does not work the first several times.
Clomid Dosage During Anabolic Steroid Use
Although Nolvadex is the more potent, better suited, and stronger choice over Clomid for the mitigation of gynecomastia during cycles, Clomid can indeed be utilized for this purpose. Nolvadex, however, should be the first and foremost choice among anabolic steroid users for this purpose, and is normally the only choice among experienced anabolic steroid users.
For the purpose of gynecomastia prevention/reduction during a cycle: Although Clomid doses are not normally utilized for either the prevention of the development of gynecomastia during an anabolic steroid cycle, the Clomid doses are approximately 50 – 100mg daily during an anabolic steroid cycle. Some individuals have found that Clomid’s effectiveness as an Estrogen antagonist in breast tissue is in fact so weak compared to Nolvadex that Clomid doses might require even higher administrations above 100mg daily.
Female Clomid Dosage
Female anabolic steroid users should not have any requirement for the use of Clomid, as breast tissue growth (gynecomastia) is not normally a concern among female athletes, and nor is the issue of insufficient Testosterone production, seeing as though females do not possess a necessary requirement for the same normal physiological levels of Testosterone that males do. Various female anabolic steroid using bodybuilders have been known to utilize Clomid for various purposes leading up to a competition show, but it is highly recommended that females do not engage in this practice due to the fact that Clomid (particularly in pre-menopausal females) presents various serious and very inconvenient side effects.
Clomid Dosage for Increased Endogenous Testosterone Secretion and PCT (Post Cycle Therapy)
The fact that Clomid is an effective HPTA and endogenous Testosterone stimulating agent is well documented and has been covered extensively thus far throughout this profile. The fact that Clomid is less effective at acting as an Estrogen antagonist in breast tissue compared to its effectiveness in restoring hormonal function is the reason as to why it is utilized primarily and exclusively for the latter reason among anabolic steroid users. However, it is still important to note that on a mg for mg basis, Nolvadex is far superior to Clomid. Normally it is because of this that if any individuals still insist on the use of Clomid at all, it should be included as a multi-compound PCT program in which it is also used with Nolvadex and perhaps HCG (many will also include the use of an aromatase inhibitor to mitigate the Estrogenic effects of HCG administration).
The standard Clomid doses for PCT (for the purpose of stimulating the release of GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone), LH, FSH, and ultimately Testosterone) is that of 50 – 100mg daily.
Proper Administration and Timing of Clomid Dosages
There are no special considerations in regards to the administration of Clomid. It can be taken before, during, or after meals. It can also be consumed in the morning or at night time. It is recommended to ingest the full dose all at once as opposed to splitting the Clomid doses up throughout the day, which is largely unnecessary due to its long half-life of 5 – 7 days.
Expectations and Results from Clomid Dosages
Clomid generally serves as an effective endogenous Testosterone production stimulating compound, ideal for proper hormonal recovery following the end of an anabolic steroid cycle. Although it can be used for the treatment or reversal of early development gynecomastia, it is not recommended due to its poor ability at achieving such an effect, where Nolvadex is the preferred agent of the two.
[related-items]
[1] Hormonal effects of an antiestrogen, tamoxifen, in normal and oligospermic men. Vermeulen A, Comhaire F. Fertil Steril. 1978 Mar;29(3):320-7.
[2] Clomiphene increases free testosterone levels in men with both secondary hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction: who does and does not benefit? Guay AT, Jacobson J, Perez JB, Hodge MB, Velasquez E. Int J Impot Res. 2003 Jun;15(3):156-65.
This is a persistent rumor among the anabolic steroid using community that has begun to erode as of late, but the rumor still persists. SERMs serve to block the action of Estrogen at the receptor sites in breast tissue by occupying the receptor sites in place of Estrogen so that Estrogen itself cannot exert its effects there through receptor site binding. Conversely, SERMs will also act as Estrogens at receptor sites at other cells in other areas of the body (the liver, for example in Nolvadex’s case). SERMs do not lower circulating levels of Estrogen in blood plasma. Aromatase inhibitors serve to do this by eliminating the production of Estrogen through binding to and disabling the aromatase enzyme, which is the enzyme responsible for the conversion (or aromatization) of androgens into Estrogen.
clomid1Clomid was developed and approved for use in the early 1970s for the treatment of female infertility (and later on subsequently expanded to treating male infertility as well). Not too long after its release in the United States, its popularity and use spread internationally where, like Nolvadex, its popularity and rate of use is so massive that it is widely and freely available in the majority of countries and regions across the world under an almost infinite number of brand names as well as generic products. Its popularity and cheap cost make it a very easily attainable compound for both medical use as well as off-label use for the anabolic steroid using community.
Clomid, although it is classified as an anti-Estrogen, is actually utilized for the treatment of female infertility resulting from ovulation failure (anovulatory infertility). Although Clomid is a very close relative to Nolvadex with both belonging to the SERM category of drugs, Clomid in reality operates at a much poorer efficiency compared to Nolvadex in regards to its Estrogen antagonistic activity in breast tissue. This is to say that it is a weaker Estrogen blocker in breast tissue, where Nolvadex is much better suited for this task. Instead, Clomid’s prime application in medicine is that of a non-steroidal ovulatory stimulant for women. Because Clomid is a SERM, like Nolvadex, it exhibits mixed Estrogen agonist and antagonist effects in various tissues of the body. Like Nolvadex, Clomid acts as an Estrogen antagonist in the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, endometrium, vagina, and cervix. This is to say that in these tissues and areas of the body, Clomid serves to mitigate (inhibit or block) the action of Estrogen.
In males as well as females, its Estrogen antagonistic effect on the hypothalamus will trigger a release of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone). These two hormones in men are the signal hormones that signal the testes to begin or increase its production of Testosterone, and this total process is known as the HPTA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis). In females, this same action occurs, except LH and FSH will trigger the release of eggs from from the ovaries (known as follicular rupture), which would lead to increased chances of contraception. This total process in females is known as the HPOA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Ovarian Axis). Much like Nolvadex, Clomid is what would be considered an Estrogen that acts as a ‘fake’ Estrogen in areas of the body, such as breast tissue (so as to block the effects of ‘real’ Estrogen, while it also works as an actual Estrogen in other areas of the body. This is another manner of describing the agonistic/antagonistic nature of Clomid in regards to Estrogen.
For anabolic steroid using athletes and bodybuilders that are for the most part males, Clomid can serve as an effective anti-Estrogen for the purpose of mitigating one particular unwanted side effect of Estrogen as a result of the use of aromatizable anabolic steroids (such as Testosterone, Dianabol, Boldenone, etc.). This particular unwanted side effect is that of gynecomastia, which refers to the development of breast tissue resulting from excess Estrogen levels in body. Because of Clomid’s Estrogen antagonistic effects on the hypothalamus resulting in the increased production of gonadotropins LH and FSH, Clomid can effectively be utilized to increase endogenous Testosterone production in males. This is especially important for anabolic steroid using individuals that wish to restore proper hormonal function during the weeks following the conclusion of an anabolic steroid cycle, a period known as PCT (Post Cycle Therpay). The traditional protocol for such a use is that of a combination of Nolvadex, Clomid, and HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) for the duration of several weeks, and although much better more modern protocols have been developed, this long-standing traditional PCT protocol is still effective. The use of Clomid for this purpose will be covered in further detail under the Clomid doses section of this profile.
All of the tripohenylethylene compounds under the SERM family (Nolvadex, Clomid, and Toremifene) also exhibit Estrogen agonistic effects in the liver, meaning the liver is one such area of the body where SERMs such as Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) will act as an Estrogen rather than block Estrogenic activity there. In studies, this has shown to be a beneficial aspect of SERMs, as Estrogens as well as Estrogen agonists (such as Clomid and Nolvadex) impart a positive effect on cholesterol values through actions in the liver. This is the reason as to why the reduction of Estrogen levels through the use of an aromatase inhibitor (AI) is not always the best decision, as the reduction in Estrogen often results in negatively impacted cholesterol profiles as demonstrated anecdotally as well as in clinical studies.
[h=3]Chemical Characteristics of Clomid[/h]Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) is a non-steroidal selective Estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that possesses both mixed agonistic as well as antagonistic properties in relation to Estrogen in different areas of the body. Clomid belongs to a family of compounds known as triphenylethylene compounds, of which Nolvadex (Tamoxifen Citrate) is also a member of, and a very closely related compound to Clomid.
[h=3]Properties of Clomid[/h]Clomid’s primary use within the medical field is that of a fertility drug in females but also among males as well.
It has already been established that Clomid, being a SERM, does not reduce circulating Estrogen levels in the body, but instead serves to occupy the receptor sites in breast tissue so that Estrogen itself cannot bind to these receptors due to Clomid’s stronger binding strength to it. In layman’s terms, Clomid essentially acts as a ‘fake’ Estrogen that acts as a placeholder at the receptor sites in breast tissue. As a result, Estrogen cannot activate gene transcription in the cells there in order to formulate gynecomastia, and any existing Estrogen that has already bound to receptor sites will essentially be ‘forced’ out of the receptor sites by Clomid which then occupies the receptor site instead. However, it must be noted that Clomid’s action in this area is far weaker and less efficient than its close relative compound Nolvadex, which serves as a better choice for this purpose.
Although Clomid could indeed be utilized by anabolic steroid using individuals that wish to prevent or eliminate and reverse formulating gynecomastia in its early stages, its more effective and promising role is that of an endogenous Testosterone production stimulating compound. This is the primary purpose and function of Clomid among anabolic steroid using athletes and bodybuilders, and is the primary desired effect in this sense. It must be noted, however, that research has also demonstrated various advantages that Nolvadex does possess over Clomid in this sense as well, which will be further covered in the next section of this profile.
As a SERM, Clomid will not serve to block or reduce any other Estrogenic side effects, however, as it serves only to block Estrogenic activity at the breast tissue area (when major Estrogenic side effects are concerned). Clomid does not (nor do any SERMs) serve to reduce bloating, water retention, rising blood pressure (as a result of water retention), or acne formation – these are all side effects resultant from increasing blood plasma Estrogen levels.
 Clomiphene Citrate (AKA Clomid)
Clomiphene Citrate (AKA Clomid)Chemical Name: 2-(4-(2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-diethyl-ethanamine
Molecular Weight: 406 g/mol or 598.10 g/mol (citrate salt)
Formula: C26H28ClNO
Original Manufacturer:
Half Life: 5 – 7 days (some reports as long as 14 days)
Detection Time: 2 months
Anabolic Rating: N/A Androgenic Rating: N/A
[h=1]Clomid Dosage[/h]
Clomid is the most popular endogenous Testosterone simulating compound among the anabolic steroid using community. This is due in part because of how long it has been on the market, as well as being the very first fertility drug (for both men and women) that anabolic steroid users first took notice of. Despite the fact that Nolvadex has demonstrated an overall better ability to stimulate Testosterone levels in men, Clomid nevertheless remains a staple compound for hormonal recovery during PCT for most anabolic steroid users. The overwhelming majority of PCT protocols will include Clomid and Nolvadex together for an added effect on HPTA (Hypothalamic Pituitary Testicular Axis) recovery during the post-cycle period, although there are some problems and setbacks related to Clomid’s action that will be covered shortly. Clomid doses in comparison to Nolvadex, for example, will normally need to be in the higher range in order for the compound to do its job in the body, as it is not as powerful as its brother compound Nolvadex, and this will be explained shortly.
In terms of Clomid dosages for the purpose of HPTA and endogenous Testosterone restoration, one study has demonstrated that 150mg of Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) administered daily raised endogenous Testosterone levels of 10 healthy males by approximately 150%, while incidentally, 20mg of Nolvadex (Tamoxifen Citrate) daily raised endogenous Testosterone levels by the same amount[1]. It is very evident here that Clomid is very effective for this purpose, but Nolvadex seems to be a more cost-effective choice seeing as though it is more effective than Clomid when compared mg for mg. Nevertheless, Clomid can still be a very valuable compound for hormonal restoration, as Clomid doses of 100mg daily would theoretically raise Testosterone levels to 100% above baseline, and 50mg would raise Testosterone levels to 50% above baseline, etc.
Some further studies have demonstrated Clomid’s effectiveness in the long term, where 178 hypogonadal males also suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED) were administered Clomid dosages for 4 months, and 75% of the test subjects improved while 25% did not – however, all test subjects exhibited significant increases in LH, FSH, and Testosterone production[2]. The study had also noted that with short term administration, only modest increases in sexual function were observed. It is very evident that Clomid can be utilized as an effective treatment for erectile dysfunction in most males, even during the long-term.
Prior to delving into any further details, an important note must be made to the reader:
The use of SERMs or any anti-Estrogens should only be utilized when absolutely required, and should be discontinued as soon as the requirements to use them (such as gynecomastia or insufficient androgen production) have desisted.
Medical Clomid Dosage
Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) is utilized within the medical establishment primarily for the treatment of ovulatory dysfunction (female infertility), which prevents problems for females attempting pregnancy. For this purpose, the prescription Clomid doses land in the range of 50mg per day, and Clomid administration is to only begin 5 days after the menstrual cycle has started. Following this, Clomid doses are to be continued for only 5 days. If an improvement in ovulation is not observed, then prescription Clomid doses are to be increased to 100mg daily for the same 5 day period.
Most of the time, medical professionals will have their patients engage in an average of 6 of these aforementioned cycles, provided the therapy does not work the first several times.
Clomid Dosage During Anabolic Steroid Use
Although Nolvadex is the more potent, better suited, and stronger choice over Clomid for the mitigation of gynecomastia during cycles, Clomid can indeed be utilized for this purpose. Nolvadex, however, should be the first and foremost choice among anabolic steroid users for this purpose, and is normally the only choice among experienced anabolic steroid users.
For the purpose of gynecomastia prevention/reduction during a cycle: Although Clomid doses are not normally utilized for either the prevention of the development of gynecomastia during an anabolic steroid cycle, the Clomid doses are approximately 50 – 100mg daily during an anabolic steroid cycle. Some individuals have found that Clomid’s effectiveness as an Estrogen antagonist in breast tissue is in fact so weak compared to Nolvadex that Clomid doses might require even higher administrations above 100mg daily.
Female Clomid Dosage
Female anabolic steroid users should not have any requirement for the use of Clomid, as breast tissue growth (gynecomastia) is not normally a concern among female athletes, and nor is the issue of insufficient Testosterone production, seeing as though females do not possess a necessary requirement for the same normal physiological levels of Testosterone that males do. Various female anabolic steroid using bodybuilders have been known to utilize Clomid for various purposes leading up to a competition show, but it is highly recommended that females do not engage in this practice due to the fact that Clomid (particularly in pre-menopausal females) presents various serious and very inconvenient side effects.
Clomid Dosage for Increased Endogenous Testosterone Secretion and PCT (Post Cycle Therapy)
The fact that Clomid is an effective HPTA and endogenous Testosterone stimulating agent is well documented and has been covered extensively thus far throughout this profile. The fact that Clomid is less effective at acting as an Estrogen antagonist in breast tissue compared to its effectiveness in restoring hormonal function is the reason as to why it is utilized primarily and exclusively for the latter reason among anabolic steroid users. However, it is still important to note that on a mg for mg basis, Nolvadex is far superior to Clomid. Normally it is because of this that if any individuals still insist on the use of Clomid at all, it should be included as a multi-compound PCT program in which it is also used with Nolvadex and perhaps HCG (many will also include the use of an aromatase inhibitor to mitigate the Estrogenic effects of HCG administration).
The standard Clomid doses for PCT (for the purpose of stimulating the release of GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone), LH, FSH, and ultimately Testosterone) is that of 50 – 100mg daily.
Proper Administration and Timing of Clomid Dosages
There are no special considerations in regards to the administration of Clomid. It can be taken before, during, or after meals. It can also be consumed in the morning or at night time. It is recommended to ingest the full dose all at once as opposed to splitting the Clomid doses up throughout the day, which is largely unnecessary due to its long half-life of 5 – 7 days.
Expectations and Results from Clomid Dosages
Clomid generally serves as an effective endogenous Testosterone production stimulating compound, ideal for proper hormonal recovery following the end of an anabolic steroid cycle. Although it can be used for the treatment or reversal of early development gynecomastia, it is not recommended due to its poor ability at achieving such an effect, where Nolvadex is the preferred agent of the two.
[related-items]
[1] Hormonal effects of an antiestrogen, tamoxifen, in normal and oligospermic men. Vermeulen A, Comhaire F. Fertil Steril. 1978 Mar;29(3):320-7.
[2] Clomiphene increases free testosterone levels in men with both secondary hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction: who does and does not benefit? Guay AT, Jacobson J, Perez JB, Hodge MB, Velasquez E. Int J Impot Res. 2003 Jun;15(3):156-65.

