Tag: Renegade Row
30-Day Abs Challenge for A Rock-Hard Core
Most decent fitness information revolves around building good long-term diet and workout habits. This makes a lot of sense, as fitness and health should be life-long pursuits. Sadly, you cannot store fitness, and your strength and conditioning will soon decline if you stop working out or eating healthily.
There is a reason that ex-athletes often look so out of shape – they stopped training.
So, in most cases, long-term consistency will always beat short-term fitness fixes. That said, there is a time and a place for workouts and diets that are only meant to last a few weeks. Things like 30-day push-up challenges or 14-day diets can help restore lost momentum and bust through plateaus.
Short-term workout challenges and diets can also test and develop your willpower and intestinal fortitude, or guts. You’ll undoubtedly feel a sense of satisfaction on reaching the end of one of these challenges, which can be a reward in its own right.
This 30-day abs challenge will give you a hard, strong core and could even take you a few steps closer to developing a shredded six-pack.
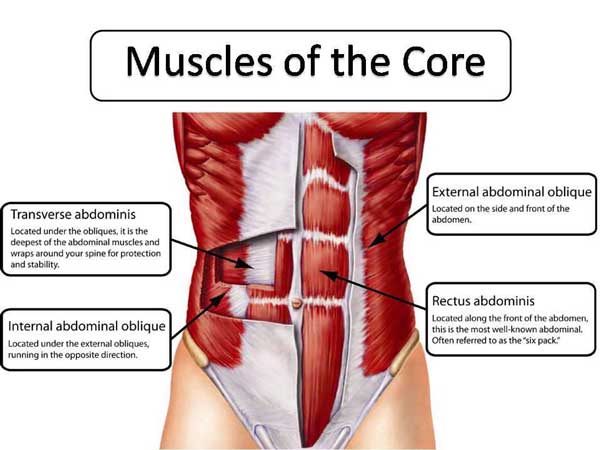
Abs Anatomy Basics
So, what muscles will you be working during this 30-day abs challenge? Rather than focus just on those at the front of your abdomen, this workout is designed to work all the muscles that encircle your waist and make up your core:
Rectus abdominis – located at the front of your abdomen, this is your six-pack muscle, although you’ll need to be pretty lean to see it. The functions of your rectus abdominis are flexion and lateral flexion of your spine. It also plays a part in compressing your abdominal contents.
Obliques – there are two sets of oblique muscles: internal and external. They work together to laterally flex and rotate your spine. The obliques are basically your waist muscles.
Transverse abdominis – encircling your midsection like a weightlifting belt, the TVA compresses your abdominal contents to produce intra-abdominal pressure, or IAP for short. This pressure helps stabilize your lumbar spine from within.
Erector spinae – the erector spinae is a group of three muscles that run up either side of your back. Together they extend and stabilize your lower and upper spine.
30-Day Abs Challenge – Program Overview
This is an abs specialization program. That means you’ll be working your abs more frequently than usual and with more volume and intensity than you’re probably used to. However, you won’t be training your abs every day, which could lead to injury and overtraining. Instead, you’ll be hitting your abs four days a week for one month straight.
It’s up to you on which days you train, but it’s generally best to avoid doing all your abs workouts in a row. We don’t want you to work your abs Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday.
Instead, separate at least a few of your abs workouts with a different form of training or a rest day. For example:
Monday – Abs Workout
Tuesday – Cardio/Strength Training
Wednesday – Abs Workout
Thursday – Abs Workout
Friday – Cardio/Strength Training
Saturday – Abs Workout
Sunday – Rest
Each workout contains four exercises so that you work all your core muscles equally. Each week involves different, more demanding exercises to ensure your core strength increases over the coming 30 days. The workouts themselves are also progressive, and the volume/intensity builds up over the course of the month.
In terms of equipment, you don’t need much to complete this 30-day abs challenge. In fact, you can do this challenge at home with a few items of basic workout gear.
However, you will need:
Exercise mat
Ab wheel or a barbell and weight plates
Resistance bands
Stability ball
Pull-up bar/captain’s chair
Medicine ball or dumbbell/kettlebell
Finally, this 30-day workout challenge is not designed for beginners. Instead, it’s aimed at intermediate or advanced exercisers looking to take their core conditioning to a new, higher level. Beginners should follow a less intense workout plan that focuses on building basic core strength.
30-Day Abs Challenge – Week One
Week one of our 30-day abs challenge starts with some fairly basic exercises and a moderate level of volume and intensity. Think of this as your warm-up week. Do three sets of each exercise, resting 60-90 seconds between efforts. However, regarding reps, continue each set until the target muscles start to fatigue. The reps quoted in the chart below are for guidance only.
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
RKC plank
3
20-30 seconds
60-90 seconds
2
Stability ball crunch
3
15-20
60-90 seconds
3
Reverse crunch
3
15-20
60-90 seconds
4
Side plank
3
15-20
60-90 seconds
1 – RKC Plank
Unlike regular planks, RKC (Russian kettlebell challenge) planks are designed to fatigue your abs as fast as possible. Brace and contract your core as hard as you can; seek failure, and don’t wait for failure to come to you! If you feel that you can go for more than 30 seconds, you weren’t bracing hard enough.
Steps:
Lie on the floor and rest on your elbows and forearms. Clasp your hands together if you wish. Brace your core and pull your shoulders back and down.
Lift your hips up so your body is straight. Contract your hands, arms, chest, shoulders, legs, and glutes.
Without holding your breath, contract your core as hard as possible.
Hold for as long as you can but, if you can do more than 30 seconds, you weren’t bracing hard enough.
Tips:
Rest your elbows on a folded mat for comfort.
Imagine you are trying to drag your toes toward your elbows to maximally engage your abs.
Do not hold your breath, as doing so can cause your blood pressure to rise.
2 – Stability ball crunch
While floor crunches are fine, they have a short range of motion, so they’re too easy for fitter, more experienced exercisers. Using a stability ball makes crunches much more challenging, especially now your abs are tired from the RKC planks.
Steps:
Sit on your stability ball. Walk your feet forward and lean back until the ball fills the curve of your lower back. Place your hands on your temples and brace your abs.
Press your lower back into the ball, curve your spine, and lift your upper back up to form a C shape.
Lean back, get a good stretch in your abs, and repeat.
Tips:
Make this exercise harder by holding a weight behind your head or across your chest.
Exhale as you lift your shoulders to maximally engage your abs.
Pause at the top of each rep for a more effective workout.
3 – Reverse Crunch
There is no such thing as upper abs vs. lower abs. Instead, your rectus abdominis is one long, flat muscle. That said, it is possible to use your abs to lift your shoulders or lift your hips by engaging different groups of muscle fibers. Reverse crunches tend to emphasize the lower fibers of the rectus abdominis, but the upper fibers are working, too.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs bent and feet in the air. Place your hands on the floor next to your hips.
Press your lower back into the floor and lift your hips off the floor. Pull your knees toward your shoulders.
Lower your hips and legs back down and repeat.
Tips:
Avoid pressing with your arms, which takes work away from the target muscles.
Exhale as you lift your legs to increase abs engagement.
Pause at the top of each rep to make this exercise more challenging and effective.
4 – Side plank
Where regular planks emphasize your rectus abdominis, side planks hit your obliques more. Most people find side planks harder than front planks, which makes sense given that the obliques are much smaller than the rectus abdominis muscle.
Steps:
Lie on your side so your body is straight and your hips and shoulders are square. Rest on your lowermost forearm and elbow. Brace your core.
Lift your hips and then hold them up for the required duration.
On completion, lower your hips to the floor, roll over, and repeat on the opposite side.
Tips:
Do not hold your breath, as doing so can cause your blood pressure to increase.
Lift your uppermost leg to make this exercise more challenging.
You can also do side planks with your supporting arm straight, like this:
30-Day Abs Challenge – Week Two
Week two of our 30-day abs challenge builds on what you achieved in week one. The exercises are slightly more difficult, so you should be ready to work a little harder. Your interset rest periods are also a little shorter. As before, reps are quoted for illustrative purposes only. Do as many reps as it takes to fatigue the target muscles.
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Stability ball stir the pot
3
15-20
45-75 seconds
2
Serratus crunch
3
15-20
45-75 seconds
3
Hanging knee raises
3
15-20
45-75 seconds
4
Russian twist
3
15-20
45-75 seconds
1 – Stability ball stir the pot
Planks on a stable surface are fine, but you’re probably ready for a more challenging abs workout. Stability ball stir the pot is a much more dynamic and challenging way to do planks. This is an exercise you’ll love to hate!
Steps:
Place your forearms on a stability ball and then walk your feet out and back so your body and legs are straight. Brace your core.
Without dropping your hips, make small circles with your arms, alternating between clockwise and counterclockwise.
Keep your body extended and your core braced throughout.
Tips:
The larger the ball, the less challenging this exercise becomes.
Make larger circles to increase instability and make this exercise harder.
Move your feet further apart to make stir the pots a little easier.
2 – Serratus crunch
The serratus crunch is so-called because, as well as working your rectus abdominis, it also hits your serratus anterior muscles. While not strictly part of your core, these small but visually impressive muscles can add a lot to your appearance. Needless to say, this exercise also overloads your abs.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs bent and feet flat on the floor. Hold a weight in your hands (medicine ball, dumbbell, kettlebell) and extend your arms so they’re vertical. Press your lower back into the floor.
Contract your abs and lift your head and shoulders off the floor. Reach up with your arms as if you’re trying to touch the ceiling.
Lie back down and repeat.
Tips:
Exhale as you lift your shoulders to fully engage your abs.
You can also do this exercise with your legs raised.
Don’t go too heavy too soon; this exercise works best when you focus on the movement rather than the load.
3 – Hanging knee raises
Like reverse crunches from last week’s program, hanging knee raises target the lower fibers of your rectus abdominis. However, lifting the entire weight of your legs makes this exercise much more challenging. On the downside, you will need a pull-up bar or captain’s chair to do this exercise.
Steps:
Hang from your pull-up bar with your arms straight. Alternatively, rest on your elbows on a captain’s chair station. Brace your abs.
Without using momentum to help you raise your legs, bend your knees and lift them up until they’re higher than your hips.
Lower your legs under control and repeat.
Tips:
Use lifting chalk or wrist straps if your grip fails before your abs.
Do not swing your knees up. Instead, move slowly and deliberately to keep the tension on your abs.
Too easy? Clamp a dumbbell between your feet to make this exercise more demanding:
4 – Russian Twist
It’s not really clear why Russian twists are so-called because they don’t have anything to do with Russia. Regardless, they’re a challenging and effective oblique and rectus abdominis exercise that most people love and hate in equal measure.
Steps:
Sit on the floor with your legs bent and feet flat.
Lean back until your body is inclined to about 45 degrees.
Extend your arms out in front of you at shoulder height.
Rotate your upper body as far as possible to the left and right. Do not lean back or lift your torso; keep the angle the same.
Continue for the specified number of reps.
Tips:
Hold a dumbbell or kettlebell to make this exercise more challenging.
Anchor your feet if necessary.
Maintain a neutral spine throughout. Do not round your lower back.
30-Day Abs Challenge – Week Three
Week three sees an increase in training volume as you progress from doing three sets of each exercise to four. There is also a slight increase in exercise difficulty. Don’t worry – you can handle it. And congratulations on reaching the halfway stage of this four-week challenge!
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Ab wheel rollout
4
15-20
45-75 seconds
2
Bicycle crunch
4
15-20
45-75 seconds
3
Straight leg lifts
4
15-20
45-75 seconds
4
Resistance band Pallof press
4
15-20
45-75 seconds
1 – Ab wheel rollout
Ab wheel rollouts are a sort of moving plank. With this exercise, you extend your arms out in front of you to create a long lever which puts a lot of tension through your abs. This is a challenging core exercise, but after two weeks of intense core training, you are ready for it!
Steps:
Kneel down and place your ab wheel on the floor in front of your knees. Hold the handle with an overhand grip, arms straight, and core braced.
Push the ab roller away from you and lower your body toward the floor. Take care not to hyperextend your spine.
Use your abs and lats to pull the roller back to your legs and repeat.
Tips:
Shorten your range of motion if you feel this exercise in your lower back.
Kneel on a folded exercise mat or foam pad for comfort.
You can also do this exercise from standing. However, this is MUCH more demanding:
2 – Bicycle crunch
The bicycle crunch is a tough but popular abs exercise. It involves all your significant core muscles, as well as your hip flexors. Done slowly and through a full range of motion, this exercise will challenge even the strongest exerciser.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs straight and your hands on your temples. Press your lower back into the floor and lift your feet a few inches off the floor. Keep them up for the duration of your set.
Lift your head and shoulders and bend one leg. Twist and touch one knee to the opposite elbow.
Return to the starting position and then repeat on the opposite side.
Continue alternating for the duration of your set.
Tips:
Start with legs bent and feet on the floor to make this exercise more manageable.
Take care not to pull on your neck, which could lead to injury.
Try to touch the outside of your elbow to the outside of your knee to hit your obliques harder.
3 – Straight leg lifts
Straight leg lifts are a low-tech but high-effect abs exercise. Like hanging knee raises, they target the lower fibers of your abs and hip flexors. Doing straight leg raises after bicycle crunches will be a special kind of core-training hell!
Steps:
Lie down and press your lower back into the floor. Lift your feet a few inches off the floor. Rest your arms on the floor next to your hips.
Without using your arms for assistance, raise your legs up until they’re vertical.
Lower your legs down until your feet are a few inches above the floor and repeat.
Tips:
Keep your lower back pressed into the floor throughout. Do NOT allow your back to arch.
If necessary, place your hands under your butt to help keep your back flat.
Bend your legs to shorten the lever and make this exercise easier. You can also try raising one leg at a time.
4 – Resistance band Pallof press
The Pallof press is an anti-core exercise, meaning it works your muscles without involving any movement. Don’t let this put you off; the Pallof press is still a great way to work your abs, especially your obliques.
Steps:
Attach a resistance band to a chest-high anchor.
Grip the end of the band and stand sideways onto your anchor point. Hold your hands in front of your chest.
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent.
Extend your arms in front of you, noting how the tension on your core increases. Do NOT allow your torso to twist.
Bring your arms back in and repeat.
Do the same number of reps on both sides.
Tips:
Stand further away from your anchor point to put more tension on the band and make this exercise harder.
You can also do this exercise with a cable machine.
You can also do this exercise in a half-kneeling position for variety:
30-Day Abs Challenge – Week Four
Week four is graduation week, and we’re going to finish strong! As well as introducing another four new core exercises, you’ll also get shorter rests between sets, turning the intensity up to the max. Keep pushing hard all the way to the end, and keep reminding yourself it’s the final week of workouts.
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Renegade row
4
15-20
30-60 seconds
2
V-sit
4
15-20
30-60 seconds
3
Flutter kick
4
15-20
30-60 seconds
4
Saxon side bend
4
15-20
30-60 seconds
1 – Renegade row
Renegade rows were invented by NFL strength and conditioning expert John Davies. It is a plank variation that also involves an anti-rotation element. It’s a challenging exercise, so don’t go too heavy too soon!
Steps:
Adopt the push-up position with a dumbbell in each hand. Your arms, legs, and body should be straight. Brace your core, and pull your shoulders down and back.
Keeping your body tight and still, bend one arm and row the dumbbell off the floor and into your lower ribs.
Place the dumbbell back on the floor, swap sides, and repeat.
Alternate arms for the duration of your set.
Tips:
Use hex-shaped dumbbells if available, as they tend to be more stable.
You can also do this exercise with kettlebells.
Bend your legs and rest on your knees to make this exercise easier.
2 – V-sit
The V-sit is an old-school abs strength and conditioning exercise. This is a tough move, but after three weeks of prep work, you’re ready for it. The V-sit is so-called because your body makes a V-shape at the midpoint of each rep.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs straight and arms above your head. Press your lower back into the floor and brace your abs.
Lift your legs and upper body simultaneously and reach up toward your toes. At this point, you should be balancing on your butt, body making a V-shape.
Lie back down and repeat.
Tips:
Place a folded matt under your lower back for comfort.
Make this exercise harder by holding a medicine ball and touching it to your feet.
Bend your legs and pull your knees into your chest to make this exercise easier.
3 – Flutter kick
Flutter kicks are a favorite abs exercise in the military. You’ll often see this exercise done by Navy SEALs, usually as they lie on a beach with waves breaking over them. Part punishment, part core strengthener, this challenging exercise will hammer the lower fibers of your rectus abdominis.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs straight, hands together, and under your butt.
Press your lower back into the floor and lift your feet a few inches off the floor.
Lift your head and shoulders a few inches off the floor.
Keeping your legs straight, kick your legs up and down like you are swimming. Four kicks equal one rep.
Continue for the prescribed number of reps.
Tips:
Stop your set if your lower back starts to lift off the floor.
The slower the tempo, the more challenging this exercise becomes.
Bend your knees slightly to shorten the levers and make this exercise easier.
4 – Saxon side bend
Saxon sidebands are named after old-school strongman and bodybuilder Arthur Saxon. Performing with his brothers, Saxon was known for his incredible feats of strength, which included lifting horses and pressing several times his body weight overhead. The Saxon side bend was one of his favorite abs exercises.
Steps:
Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent. Brace your core.
Raise and hold a weight (dumbbell, medicine ball) overhead.
Keeping your arms extended, lean to the left and then to the right for the prescribed number of reps. Only lean sideways, and not forward or backward.
Tips:
Take care not to twist your shoulders or hips.
Bend your arms and lower the weight to your head to make this exercise a little easier.
Because of the long levers involved, this is a challenging exercise, so don’t go too heavy too soon.
FAQs
Do you have a question about our 30-day abs challenge or core training in general? No sweat Boba Fett, because we’ve got the answers!
1. Will this challenge give me a six-pack?
Getting a six-pack is as much about your diet as it is your workout program. This 30-day abs challenge will definitely strengthen and harden your abs, but you won’t be able to see them unless you carve your body fat down to under ten percent for men and less than 15 percent for women.
Because of this, it’s often said that abs are built in the kitchen, although the saying should really be that abs are revealed in the kitchen.
Getting leaner invariably means eating less and exercising more to create a calorie deficit, so your body has no option but to burn stored body fat for fuel.
Read more about eating for ripped abs here.
2. Can I change the exercises in the 30-day abs challenge workouts?
If there are any exercises that you cannot do or that cause pain, feel free to do something else instead. However, try and use similar exercises so that you stay true to the spirit of the program. For example, you could do cable crunches instead of stability ball crunches, as they are basically the same movement. However, sit-ups and hanging leg raises are too dissimilar to be interchangeable.
If you are thinking of changing an exercise because you find it hard – don’t! This is a CHALLENGE, and it’s the hard exercises that will deliver the best results. Even if you can only do a few reps, stick with the hard moves. Your efforts will be rewarded in the end.
3. XYZ exercise hurts my back – what should I do?
If any of the exercises cause back pain, you should stop immediately and revisit your technique. Make sure you are doing the movement correctly. If it still causes pain, replace that exercise with something similar that doesn’t cause you problems. While exercise is good for everybody’s body, some movements may not suit your body type or fitness level.
4. How do I know if I’ve done enough reps?
One of the reasons that prescribing a rep range for a workout is so hard is that we have no way of knowing how strong you are. For some, 15 reps of leg raises will be too easy, but for others, it’ll be way too hard. If we tell you how many reps to do, we’d just be guessing.
So, instead, do as many reps as you can, stopping 2-3 short of failure. At this point, you should feel your muscles working (love that burn!), and your movements will probably noticeably slow down.
Push yourself close to failure, and your muscles will respond by getting stronger. But stop too soon, and your workout won’t be as effective as it could have been.
That said, try to do more reps workout by workout. This is called progressive overload, which is one of the cornerstones of effective training.
5. Will doing abs exercises help me lose belly fat?
Many people believe that doing exercises for a particular body part will melt fat from that area. This is called spot reduction. Unfortunately, there is no evidence to suggest that spot reduction happens, so it’s probably best to forget about this much-loved myth. The same is true for “sweating off fat” – that’s impossible, too.
Your body stores and burns fat globally, i.e., all over. While exercising, healthy eating and a calorie deficit will force your body to burn fat for fuel, you cannot influence from where that fat will come. It MAY be your abs, but it could also be your arms, butt, or chest.
So, while you can lose belly fat, we cannot guarantee that abs exercises will help give you a slimmer stomach. Forget about spot reduction, and focus on your entire body for the best fat-loss results.
30-Day Abs Challenge – Closing Thoughts
Sometimes, the best way past a fitness plateau is to smash through it! Sticking with your regular workout program is not the answer. Instead, you need to push the volume and intensity up a notch and get Hulk-mad, going beyond your normal limits.
This 30-day abs challenge might not give you a six-pack, but after four weeks, your core will be harder and stronger than ever before. Dial in your diet, and, who knows, you may even start to see your abs.
And the best part? You can do these workouts at home, so it’s virtually excuse-free.
So, what are you waiting for? Get started today!

The Best Anti-Core Exercises for Increased Lumbar Stability
When most people talk about core training or working out in general, they tend to mean exercises that involve movement. For the core, that means things like crunches, sit-ups, hanging leg raises, Russian twists, side bends, etc.
These exercises usually feature a concentric or shortening phase followed by an eccentric or lengthening phase. After all, what goes up, must come down, right?
However, in many instances, the core muscles work isometrically, generating force without changing length. They contract to prevent unwanted movement, which is what the term core stability means.
Training to prevent movement might seem kinda odd. Still, it’s actually critical for various sports and activities in and out of the gym. For example, squats and deadlifts require incredible levels of static core stability, as do overhead barbell presses, push-ups, and barbell curls.
Fitness experts call these static core strengtheners anti-core exercises. The anti refers to how the core muscles work to prevent movement rather than cause it.
Whether you are training for improved aesthetics, better performance, weight loss, or health, anti-core exercises deserve a place in your workouts. If nothing else, preventing unwanted movement of your lumbar spine could help stop lower back injuries.
In this article, we reveal the best anti-core exercises.
Core Anatomy Basics
Core is the collective term for the muscles that encircle your midsection. Some fitness folk also like to include other muscles in the core, such as the glutes and lats, but that just confuses matters. So, for the purposes of this article, the core is the muscles in and around the abdominal region.
The primary muscles that make up the core are:
Rectus abdominis
Located on the front of your abdomen, the rectus abdominis is the large, flat muscle that, when you are lean, has that unique six-pack appearance. The rectus abdominis is responsible for the flexion of your spine and also contributes to lateral flexion.
In anti-core terms, the rectus abdominus prevents extension and lateral flexion of the spine.
Obliques
The obliques are essentially your waist muscles. There are two sets of obliques on each side of your abdomen – internal and external. They work together to rotate and laterally flex your spine.
In anti-core terms, the obliques prevent rotation as well as initiating it.
Transverse abdominis
Known as the TVA for short, this muscle surrounds your abdominal contents like a corset or weightlifting belt. It contracts inward to increase intra-abdominal pressure, stabilizing your spine from within.
If prizes were being given for the most critical anti-core muscle, the TVA would be a shoo-in for the gold medal!
Erector spinae
Erector spinae is a group of muscles that run up either side of your spine, including the
iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis, each of which can be subdivided into three further sections. The erector spinae are responsible for extending your spine as well as lateral flexion.
In anti-core terms, the erector spinae prevents flexion and lateral flexion.
Movements of the spine
The spine is a column of 33 individual bones called vertebrae. It’s divided into five sections:
Cervical spine – your neck – made up of 7 vertebrae
Thoracic spine – your upper back – made up of 12 vertebrae
Lumbar spine – your lower back – made up of 5 vertebrae
Sacrum – part of your pelvis – made up of 5 immovable/fused vertebrae
Coccyx – your “tailbone” – made up of 4 immovable/fused vertebrae
The cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs, which are sections of tough fibrous cartilage. These discs absorb shock and compress to allow movement.
Speaking of which, the spine is capable of four main movements:
Flexion, i.e., bending forward
Extension, i.e., bending backward
Lateral flexion, i.e., bending sideways
Rotation, i.e., twisting
Movements can also be combined, e.g., flexion with rotation during a twisting crunch.
As such, there are four groups of anti-core exercises, each one designed to prevent one (or more) of these movements. For example, anti-extension exercises emphasize the rectus abdominis, while anti-rotation exercises emphasize the obliques. However, all anti-core exercises involve the transverse abdominis.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Anti-Core Exercises
Not sure if you need to include anti-core exercises in your workouts? Consider these benefits and then decide!
Very functional
Functional training is a very misused term. Many people confuse functional training with technically demanding exercises involving a lot of balance, e.g., squats on a stability ball or curls while slacklining. While these are impressive feats, they’re not examples of real functional training.
In contrast, functional training means doing exercises that have a carry-over to your life outside of the gym, i.e., they improve how you function.
Anti-core exercises train your midsection in a very functional way. People often have to use their core muscles this way during their daily lives, in the gym, or on the sports field. Anti-core exercises will have a significant carry-over to your everyday life.
Spine-friendly
Like any joint, the spine is prone to wear and tear. If you do a lot of crunches, sit-ups, Russian twists, etc., you can cause stress to both the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, and these structures can become worn and damaged.
By their very nature, anti-core exercises involve no movement, so there will much less stress on your vertebrae, spinous ligaments, or discs. In fact, anti-core exercises should not cause lower back stress or pain of any sort – done correctly, of course!
Easy to learn
With no movements to think about, most anti-core exercises are very straightforward and easy to learn. You just have to keep still and prevent movement. That’s not to say these exercises are easy – far from it. However, from a technical performance perspective, the learning curve for most anti-core exercises is pretty short.
While anti-core exercises are mostly beneficial and safe, there are also a few drawbacks to consider:
Usually done for time instead of reps
Many anti-core exercises are held for a predetermined time, e.g., 30 seconds. This means you’ll need to use a timer or be able to see a clock with a second hand. Also, some people prefer to pump out reps, and keeping still may be less appealing.
Elevated blood pressure
Isometric anti-core exercises can cause a short-term increase in blood pressure (1). This is because the muscles are contracted, which reduces blood flow. This should be no issue for people with healthy blood pressure but could be problematic for anyone with hypertension.
This problem can be reduced by never holding your breath during anti-core exercises. Breath-holding can have a significant effect on blood pressure.
Speak to your doctor if you have high blood pressure before doing any of the exercises in this article.
Five Best Anti-Flexion Core Exercises
Anti-flexion exercises emphasize your erector spinae muscles. These exercises are good for improving your posture and protecting your lower back from pain and injuries.
1. Back extension hold
Anti-flexion exercises don’t come much simpler than the back extension hold. Done for time, this exercise teaches you to use your back muscles to resist the pull of gravity. Back extension holds are an excellent stepping stone onto more demanding exercises and is ideal for beginners.
Steps:
Mount your back extension machine (45-degree or horizontal) and get into the mid-point of the exercise so your body is straight. Brace your core and engage your glutes and hamstrings.
Without holding your breath, maintain your position for as long as possible.
Yes, all that shaking is perfectly normal.
Relax, rest a moment, and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Erector spinae, core, gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Benefits:
Very easy to learn.
Very accessible as most gyms have a back-extension machine.
Easy to progress/regress by altering the time of each hold.
Tips:
Work up to holding for 2-3 minutes per rep.
Make this exercise harder by holding a weight to your chest or using resistance bands.
Keep your knees slightly bent throughout for comfort and safety.
2. Cobra Superman hold
No back-extension machine? No problem! You can work on your anti-flexion strength with this straightforward floor exercise. On the downside, it can be a little uncomfortable, so make sure you use a mat to avoid any unnecessary pain.
Steps:
Lie on the floor on your front and place your hands on your temples.
Lift your head, chest, arms, legs, and feet a few inches off the floor so you’re balancing on your abdomen and hips only.
Hold this position for as long as possible.
Muscles targeted:
Erector spinae, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, core, trapezius, rhomboids, deltoids.
Benefits:
An ideal exercise for home workouts.
No equipment required.
Good for improving spine mobility.
Tips:
Place a folded mat under your hips for comfort.
Take care not to hyperextend your spine.
Do not hold your breath.
3. Dual kettlebell front rack carry
While stationary exercises like back extension and Superman/cobra holds are effective, they don’t teach you to stabilize your spine during movement. As such, they’re good preparatory exercises but also need to be progressed. Dual kettlebell front rack carries train you to resist flexion while moving your legs, so they’re much more functional.
Steps:
Rack and hold two kettlebells on your shoulders. Pull your shoulders down and back, and brace your core. Look straight ahead.
Keeping your torso upright, walk around your training area until you start to tire.
Lower the weights to the floor, rest, and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Erector spinae, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, core, trapezius, rhomboids, deltoids.
Benefits:
A highly functional exercise.
Good for integrating your core with your upper and lower body.
An excellent general strength and conditioning exercise.
Tips:
Use dumbbells instead of kettlebells if preferred.
Use gym chalk to stop your hands from slipping.
Use one weight only to add anti-lateral flexion to this exercise.
4. Romanian deadlift
While most people do RDLs to strengthen their glutes and hamstrings, it’s actually a very effective anti-flexion exercise. However, you need to be able to resist flexion in isolation first, e.g., with back extension holds, before attempting this exercise.
Steps:
Hold a barbell with an overhand, shoulder-width grip. Stand with your feet between shoulder and hip-width apart, knees slightly bent.
Brace your core and pull your shoulders down and back.
Hinging from your hips, lean forward and lower the bar down the fronts of your legs. Do NOT round your lower back.
Drive your hips forward, stand up straight, and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Erector spinae, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, core, trapezius, rhomboids, deltoids, forearms.
Benefits:
An excellent exercise for your entire posterior chain.
Easy to scale by adding or subtracting weight.
A proven way to learn how to hip hinge, which is a prerequisite for many more demanding exercises, such as kettlebell swings and power cleans.
Tips:
Remove your shoes to keep your heels on the floor and your weight toward the back of your feet.
Use chalk or lifting straps to reinforce your grip.
Keep your chest up and your lower back slightly but tightly arched throughout.
Related: Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs) Guide
5. Deadlift
The barbell deadlift is one of the best bang-for-your-buck exercises you can do. Working a large percentage of the muscles in your body, deadlifts have the potential to build muscle size and strength like no other. However, the key to a good deadlift is keeping your spine extended, which is what also makes them an excellent anti-flexion exercise.
Steps:
Place a loaded barbell on the floor. Ideally, the bar should be about mid-shin height.
Stand with your toes under the bar, feet between shoulder and hip-width apart.
Bend down and hold the barbell with an overhand or mixed shoulder-width grip.
Straighten your arms, drop your hips, and lift your chest. Brace your core and pull your shoulders back and down.
Drive your feet into the floor and stand up, ensuring your hips don’t rise faster than the bar.
Push your hips back, bend your legs, and lower the weight back to the floor.
Allow it to settle for a couple of seconds, reset your core and grip, and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Erector spinae, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, quadriceps, core, trapezius, rhomboids, deltoids, forearms.
Benefits:
One of the most productive barbell exercises you can do.
Teaches you how to lift heavy objects off the floor safely.
A very time-efficient exercise that trains multiple muscle groups at the same time.
Tips:
Place your barbell on blocks or in a power rack if you tend to round your back when deadlifting from the floor.
Do NOT bounce the bar off the floor. Instead, allow the weight to “go dead” between reps for safety and best results.
Experiment with an overhand and mixed grip to see which you prefer.
Related: 9 Weeks to a Bigger Deadlift Program
Five Best Anti-Extension Core Exercises
Anti-extension exercises target your rectus abdominis. Working on your anti-extension strength will lessen the likelihood of hyperextending your spine during athletic and everyday activities.
1. Plank
The plank is the original anti-extension core exercise. With roots in yoga and Pilates, this exercise has been around for centuries. However, despite being so common, many people do this exercise incorrectly. Don’t be one of them!
Steps:
Kneel down and rest your forearms on the floor. Your elbows should be under your shoulders, lower arms parallel. Brace your core and pull your shoulders back and down.
Walk your feet out and back to form a straight line with your shoulders and hips.
Hold this position for the required duration. However, do not hold your breath.
Muscles targeted:
Rectus abdominus, core, hip flexors.
Benefits:
No equipment required.
An excellent preparatory exercise for more advanced movements.
An easy exercise to progress or regress.
Tips:
Try to increase muscle tension instead of holding for excessively long durations.
Bend your legs and rest on your knees to make this exercise easier.
Rest your forearms on a stability ball to make this exercise more challenging.
Related: Plank Progressions and Variations for Stronger Abs
2. Dead bug
Dead bugs teach you to resist extension while moving your arms and legs, which is how your core muscles often have to work in nature. This is a highly functional anti-core move that’s suitable for all levels of exerciser.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs bent and arms extended up toward the ceiling. Brace your core and press your lower back into the floor.
Extend your left arm and right leg and lower them to the floor. Keep your lower back pressed down.
Return to the starting position and repeat on the opposite side.
Continue alternating arms/legs for the duration of your set.
Muscles targeted:
Rectus abdominus, core, hip flexors.
Benefits:
A very lower back-friendly exercise.
A very functional anti-extension core exercise.
No equipment required, so ideal for home workouts.
Tips:
Make this exercise easier by only lowering your arms OR legs.
Make it more challenging by lowering both arms and legs together.
Increase the intensity of this exercise by holding dumbbells or a medicine ball.
3. Overhead Pallof press
The Pallof press was invented by Bostonian physical therapist John Pallof. Unlike many anti-core exercises, this one uses weights to overload your muscles. As such, it can be progressed just like any other strength-training exercise, i.e., by increasing the load. Unlike the traditional anti-rotation Pallof press, this is an anti-extension exercise.
Steps:
Attach a rope handle to a high pulley. Grab the handle and then turn your back to the cable machine. Hold your hands at shoulder height. Brace your core and adopt a split stance for balance.
Without leaning forward or backward, raise your arms above your head. Note how the tension on your core increases as you extend your arms.
Lower your hands back to your shoulders and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Rectus abdominis, core, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, deltoids.
Benefits:
Can be made as easy or as challenging as required by adjusting the weight.
Teaches you how to integrate your upper and lower body with your core.
A good exercise for improving shoulder mobility and stability.
Tips:
The narrower/closer your feet are, the more challenging this exercise becomes.
You can also do this exercise with a resistance band.
Experiment with different height cables to see what works best for you.
4. Rollout
Rollouts are like a moving plank. As you extend your arms, the tension on your core increases dramatically, and you’ll have to work harder to prevent lumbar spine extension. Rollouts also provide an intense lat workout. An ab roller is an excellent investment!
Steps:
Kneel down and hold your roller with an overhand grip. Place the roller on the floor in front of your knees. Brace your core and pull your shoulders back and down.
Push the roller out in front of you and lower your chest and abdomen down to the floor. Do not allow your lower back to extend.
Using your abs and lats, pull the roller back up to your legs.
That’s one rep – keep going!
Muscles targeted:
Rectus abdominus, core, latissimus dorsi, triceps.
Benefits:
A low-tech exercise that’s ideal for home workouts.
Can be modified to suit most levels of exerciser.
A challenging, effective anti-extension core exercise.
Tips:
Do this exercise from standing for a more intense workout.
Don’t extend your arms so far to make this exercise less challenging.
No ab roller? No problem! You can also do this exercise with a barbell.
Related: Rollouts: Benefits, Technique, And Alternatives
5. Extended plank
Planks are an excellent exercise. However, if you can do them for over a minute or two, they probably aren’t challenging enough to increase core strength. This variation takes your hands and feet further apart to make them much more demanding.
Steps:
Firstly, lie on your back with your arms stretched out to the side. Make marks on the floor with your fingertips to determine your “wingspan.”
Next, place your feet on one mark and your hands on the other. This is your extended plank position.
Brace your core and hold the extended plank position for as long as possible, taking care not to hyperextend your lumber spine or hold your breath.
Muscles targeted:
Rectus abdominus, core, hip flexors.
Benefits:
No equipment required.
A much more challenging way to do planks.
An excellent anti-extension move for advanced exercisers.
Tips:
Shorten the distance between markers if you cannot do this exercise correctly, or you can feel it in your lower back.
Ensure your hands are dry and won’t slip to avoid accidentally face-planting the floor.
This is a very challenging core exercise, so proceed with caution.
Five Best Anti-Lateral Flexion Core Exercises
Anti-lateral flexion exercises strengthen your obliques, rectus abdominis, and erector spinae muscles, albeit one side at a time. Improving your ability to resist lateral flexion will ensure you can keep your torso upright when dealing with unilateral or unbalanced loads.
1. Side plank
The side plank is an excellent introduction to anti-lateral flexion exercises. It’s a little harder than front planks but just as simple to learn. This exercise is popular in group workout classes for a reason!
Steps:
Lie on your side and rest on your forearm. Your body and legs should be straight. Brace your core.
Lift your hips off the floor and hold them up for the required duration.
Lower your hips back to the floor, roll over, and repeat on the opposite side.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, erector spinae, deltoids.
Benefits:
No equipment required, so ideal for home workouts.
Easy to learn and master, so perfect for novice exercisers.
An excellent preparatory exercise for more demanding anti-lateral flexion movements.
Tips:
Rest your elbow on a folded exercise mat or foam pad for comfort.
Bend your legs to make this exercise easier.
You can also do this exercise with your supporting arm extended:
2. Single-arm farmer’s walk
Exercises don’t come much more functional than the single-arm farmer’s walk. However, despite its simplicity, this exercise can be extremely challenging. All you need is a single dumbbell, kettlebell, or heavy bag, so this exercise is ideal for home workouts.
Steps:
Hold a heavy weight in one hand, arm by your side. Brace your core and make sure your hips and shoulders are level.
Without leaning sideways, go for a walk around your training area.
On completion, lower the weight to the floor, swap hands, and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, erector spinae, forearms.
Benefits:
A highly functional core.
Can be modified for all levels of strength by increasing or reducing the weight.
An excellent way to develop a stronger, more enduring grip.
Tips:
Chalk your hands or use lifting straps to reinforce your grip if necessary.
Walk in zigzags to destabilize the weight and make this exercise more demanding.
Take care not to lean sideways or shrug your shoulders during this exercise.
3. Single-arm waiter’s walk
The single-arm waiter’s walk is similar to the farmer’s walk, but the weight is held overhead and not down by your side. This increases the stability demand of this exercise. Take care not to go too heavy too soon with this exercise; it’s harder than it looks!
Steps:
Lift and hold a single dumbbell or kettlebell overhead. Brace your core and engage your shoulders and upper back to stabilize the load.
Without leaning sideways, go for a walk around your training area.
On completion, lower the weight to the floor, swap sides, and repeat.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, erector spinae, deltoids.
Benefits:
A challenging and effective anti-lateral flexion exercise.
Builds stronger, more stable shoulders.
Can be modified for all levels of strength by increasing or reducing the weight.
Tips:
Chalk your hands or use lifting straps to reinforce your grip if necessary.
Walk in zigzags to destabilize the weight and make this exercise more demanding.
Take care not to lean sideways or shrug your shoulders during this exercise.
4. Single-arm overhead press
Overhead presses are great for building bigger shoulders and triceps. However, when you switch from using both arms to just one, they become an excellent ant-lateral flexion exercise. Requiring just one weight, this anti-core move is ideal for home workouts.
Steps:
Hold a dumbbell or kettlebell in one hand at shoulder height. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and brace your core. Make sure your hips and shoulders are level.
Without leaning sideways, press your weight up and overhead to arm’s length.
Lower the weight back to your shoulder and repeat.
Switch hands and do the same number of reps with your other arm.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, erector spinae, deltoids.
Benefits:
A very functional upper-body and core exercise.
An excellent way to identify and fix left-to-right strength imbalances.
A very accessible, practical exercise.
Tips:
Do this exercise in front of a mirror to ensure you’re keeping your shoulders level.
Use less weight than you would for a two-handed overhead press.
You can also do this exercise with a barbell, which is an exercise called the javelin press:
5. Suitcase deadlift
The suitcase deadlift is so-called because it’s the same technique you’d use to pick up a single bag at the airport. This awesome exercise teaches you how to maintain a neutral and stable spine while generating force with your legs.
Steps:
Place a kettlebell or dumbbell on the floor and then stand sideways on to it. The handle should run parallel to your feet.
Squat down and grab the handle with a neutral or palms-in grip.
Pull your shoulders down and back, brace your core, and look straight ahead.
Drive your feet into the floor and stand up straight, taking care not to lean sideways.
Lower the weight back to the flood and repeat.
Turn around and do the same number of reps on the opposite side.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, erector spinae, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, forearms.
Benefits:
A high degree of crossover with activities outside of the gym.
An effective and functional anti-lateral flexion exercise.
An excellent deadlift assistance exercise.
Tips:
Use gym chalk or lifting straps to stop your hands from slipping.
Do this exercise in front of a mirror to ensure your torso, hips, and shoulders are straight.
Experiment with your stance width to see what works best for you.
Five Best Anti-Rotation Core Exercises
Anti-rotation exercises target your obliques. Having stronger obliques will help you prevent unwanted twisting during activities like running, kicking, and throwing. Anti-rotation is especially important during contralateral activities where you use one arm and the opposite leg, e.g., running.
1. Bird-dogs
Bird-dogs are one of the most basic anti-rotation exercises around. Ideal for beginners, this exercise teaches you how to stabilize your core as you move your arms and legs. Bird-dogs are also an excellent muscle activation exercise and are perfect for warm-ups.
Steps:
Kneel on all fours with your shoulders over your hands and your hips over your knees.
Brace your core and set your shoulders down and back.
Keeping your hips and shoulders level, extend your right arm and left leg.
Lower them back to the floor and repeat.
On completion of your set, swap sides and do the same number of reps with the opposite arm and leg. Or, if preferred, you can use an alternating arm and leg action.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominis, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, deltoids, erector spinae.
Benefits:
An excellent exercise for lower back pain sufferers.
A great movement for beginners.
No equipment required, so ideal for home workouts.
Tips:
Kneel on a folded exercise mat for comfort.
Use ankle/wrist weights to make this exercise more challenging.
You can also do this exercise in a high plank position like this:
2. Pallof press
The Pallof press is one of the most widely-performed anti-rotation core exercises. Popular with almost every type of exerciser, it’s safe to say that this move delivers. If you’ve never done Pallof presses before, you are in for a treat, but if you’re already doing them, you should definitely continue!
Steps:
Attach a D-shaped handle to a cable machine set to mid-chest height.
Stand side-on to the pulley and hold the handle on both hands. Your feet should be about shoulder-width apart, with your knees slightly bent. Brace your core.
Pull your hands into your chest and step away from the machine to load the cable.
Without moving your hips or shoulders, extend your arms out in front of you. Feel how the tension on your muscles increases as you straighten your arms.
Bend your arms and return your hands to your chest.
Repeat for the required number of reps and then switch sides.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominis, erector spinae, pectoralis major, deltoids, triceps,
Benefits:
An ideal exercise for beginners.
A very spine-friendly anti-core exercise.
Very scalable – just adjust the load to reflect your current strength.
Tips:
You can also do this exercise with a resistance band.
Vary the height of your arms to work your core from different angles.
Try doing Pallof presses in a half-kneeling position for variety, like this:
3. Single-leg Romanian deadlift
While regular Romanian deadlifts are an excellent anti-flexion exercise, switching to one leg/one arm means you’ll also have to work hard to prevent twisting. This exercise is also great for improving balance and stability and is ideal for runners and other athletes.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together and a dumbbell or kettlebell in your left hand. Shift your weight over onto your right foot. Brace your core and pull your shoulders back and down.
Hinge forward from your hips and lower the weight down the front of your leg. Extend your left leg out behind you for balance.
Stand back up and repeat.
Rest a moment and then do the same number of reps on the opposite leg, remembering to switch hands, too.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, rectus abdominis, erector spinae.
Benefits:
A time-efficient way to train your core and lower body simultaneously.
An excellent exercise for better balance and coordination.
Easier on your lower back than two-legged Romanian deadlifts.
Tips:
Rest your non-working foot lightly on the floor for balance if needed, i.e., B-stance or kickstand RDLs.
Try holding the weight in the same hand rather than the opposite hand. This is considerably more demanding.
Do this exercise next to a wall or handrail for balance if required.
Related: Why the Single Leg Romanian Deadlift Deserves to Be the Hero of Your Workout
4. Renegade row
Renegade rows are among the most challenging anti-rotation exercises, even with light to moderate weights. However, if you’ve mastered Pallof presses and can do bird-dogs in your sleep, this is the exercise you’ve been waiting for!
Steps:
With a dumbbell in each hand, squat down, and place them on the floor.
Walk your feet out into the push-up position. Brace your core and tense your legs.
Bend one arm and row your dumbbell up and into your lower ribs.
Lower the weight back to the floor, switch arms, and repeat.
Alternate arms for the required number of reps.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, latissimus dorsi, biceps, triceps, deltoids, erector spinae.
Benefits:
A total core exercise that teaches you to stabilize your core as you move your arms and legs.
A time-efficient conditioning exercise that burns lots of calories.
A challenging movement that’s ideal for intermediate and advanced exercisers.
Tips:
Wear a weighted vest to make this exercise even harder.
Use hexagonal dumbbells for increased stability and safety.
Combine renegade rows with push-ups for a complete upper-body and core workout:
Related: Renegade Rows Guide
5. Single-arm cable chest press
While the single-arm chest press is not an especially good exercise for your pecs, it is an excellent anti-rotation core exercise. It teaches you how to integrate your core with your upper and lower body.
Steps:
Attach a D-shaped handle to a chest-high cable machine. Hold the handle and turn your back on the machine so the cable runs outside your arm. Adopt a split stance for balance. Brace your core.
Keeping your hips and shoulders stationary, push your arm forward and out to full extension.
Bend your arm, bring the handle back to your chest, and repeat.
Switch sides and do the same number of reps with the other arm.
Muscles targeted:
Obliques, rectus abdominus, pectoralis major, deltoids, triceps, erector spinae.
Benefits:
A very lower back-friendly anti-rotation exercise.
Infinitely scalable by increasing or reducing the weight.
Suitable for beginner, intermediate, and advanced exercisers.
Tips:
Press up at an incline to change the feel of this exercise.
Do this exercise with your feet together to challenge your core and balance more.
Do this exercise with a resistance band or in a half-kneeling position:
Anti-Core Exercises – FAQs
Do you have a question about anti-core exercises? No problem, because we’ve got the answers!
1. How many reps and sets should I do?
There is no magic number of reps you should use to train your core. You will make progress whether you do 10 or 30 reps per set. That said, lower reps are generally more time-efficient, so it’s worth choosing exercises that are demanding enough to fatigue your muscles relatively quickly, e.g., between 12-20. Wherever possible, avoid very high-rep sets, e.g., 50.
In terms of sets, 3-5 should be sufficient for most people. If you can do more, the chances are that you a) aren’t getting close enough to failure or b) are resting too long between efforts.
2. How often should I do anti-core exercises?
It’s generally accepted that it takes 48-72 hours for a muscle or muscle group to recover from a workout. As such, you should aim to do anti-core exercises 2-3 times per week on non-consecutive days, e.g., Monday and Thursday, or Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. This provides a good balance between work and recovery.
Training your core more often, i.e., daily, won’t necessarily produce better results, and could even lead to overtraining.
3. Will anti-core exercises give me a six-pack?
While doing anti-core exercises will develop your six-pack muscle (the rectus abdominis) and other critical core muscles, you won’t be able to see them until your body fat percentage is low enough. This usually means under ten percent for men and 15 percent for women.
It’s true what they say – six-pack abs are made in the kitchen, and your diet will determine if your abs and core muscles are visible.
4. Are anti-core exercises safe?
Because they involve minimal movement, most anti-core exercises are very safe. As long as you brace and stabilize your spine correctly, there should be very little stress on your intervertebral discs or spinous ligaments, so many are even okay for folk who suffer from back pain.
That said, exercises that involve additional movements, e.g., suitcase deadlifts and single-arm overhead presses, are somewhat riskier than static exercises like planks and side planks.
However, if performed correctly and with appropriate loads, there is a very low risk of injury with most anti-core exercises.
5. Do I have to do anti-core exercises – aren’t regular core exercises enough?
While all core exercises are beneficial, anti-core exercises are often more functional. That’s because you often need to use these muscles to prevent unwanted movement of your lumbar spine, e.g., during deadlifts, push-ups, and overhead presses.
If your core is strong, you may not need to do a lot of anti-core training. However, if your lumbar spine lacks the stability it needs, then anti-core exercises are a must.
Wrapping Up
Whether you’re training for performance, aesthetics, or health, your workouts should include anti-core exercises. Anti-core exercises teach you how to stabilize your lumbar spine, which will protect you from lower back injury.
A more stable spine will also let you do more reps with heavier loads, making the rest of your workout more effective.
With 20 anti-core exercises to choose from, you have more than enough options to keep you busy and progressing for years to come. Include anti-core exercises in all your midsection workouts for best results.
References:
Hanson P, Nagle F. Isometric Exercise: Cardiovascular Responses in Normal and Cardiac Populations. Cardiol Clin. 1987 May;5(2):157-70. PMID: 2884033. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2884033
The 10 Best Middle Back Exercises for Strength, Mass, and Better Posture
Take a look at most bodybuilding back workouts, and you’ll see an abundance of lat pulldown and pull-up exercises. That’s good news because these vertical pulling exercises are responsible for building upper back width.In fact, if you want a classic torso V-taper, pull-ups and pulldowns are all but compulsory.However, if you want a back that wide AND thick, you need more than vertical pulls. You need to include horizontal pulling exercises in your workouts, too. These hit your middle back more than your lats.A strong middle back will add a lot to your physique, increase your strength in the big lifts – even the bench press – and improve your posture. For these reasons, the best back workouts usually include as many horizontal pulling exercises as they do vertical.In this article, we reveal the best exercises for building up this critical muscle group. Middle Back Anatomy and Functions While you don’t need to be an expert in anatomy to build an impressive physique, knowing a little about the muscles of the human body can help you choose the best exercises for your workouts.When talking about the middle back, we’re actually referring to the muscles located across and between your scapulae or shoulder blades.These muscles are (1):Rhomboids The rhomboids connect your scapulae to your thoracic spine. There are two rhomboids: major (largest) and minor (smallest). They come as a pair – left and right. The rhomboids are not large muscles, but they are powerful and play an important part in the shape of your upper back and how it functions. For example, they play a vital role in stabilizing your shoulder blades and keeping them pressed flat against your ribcage.Trapezius Known as the traps for short, this is the large kite-shaped muscle of your upper back. It goes from the base of your skull down to the middle part of your spine and spans out toward your shoulders.The trapezius is made up of three sets of fibers – upper, middle, and lower. Each set of fibers has a different function.The upper traps pull your shoulders upward in a movement called elevation of the shoulder girdle. In contrast, the lower traps pull your shoulders downward, which is a movement called depression of the shoulder girdle.However, it’s the mid-traps that work with the rhomboids and are the main topic of this article. The mid-traps, working in conjunction with your rhomboids, pull your shoulder back and together in a movement called shoulder girdle retraction.Posterior deltoidsThe posterior or rear deltoids are NOT part of your middle back, but it’s almost impossible to train your mid-traps and rhomboids without working the muscles at the back of your shoulders. The rear delts are involved in horizontal shoulder extension and external rotation, which are two movements that happen during many mid-back exercises.As such, if you are training your middle back, you are probably working your posterior deltoids, too. This is no bad thing because a weak upper back is usually accompanied by underdeveloped rear deltoids.So, your mid back is actually two muscles working together – the mid-traps and rhomboids. When these muscles contract, they pull your shoulders together. This movement is a necessary part of many exercises, including rows, deadlifts, and even bench presses. It’s also important for your posture. Why is Your Middle Back Weak? Many people, including hardcore exercisers, have a weak upper back. This often manifests as poor posture, a rounded upper back during deadlifts or difficulty fully engaging the mid-traps and rhomboids. Poor bench press performance is often caused by an underdeveloped middle back.Common causes of upper back weakness include:Prolonged sittingSitting for a long time, especially if you hunch over a keyboard or screen, can stretch and weaken your upper back. As most people are habitual slouchers, it’s no wonder that so many people have a weak upper back.Not doing enough upper back trainingMonday is national chest training day, but when is national back training day? A lot of lifters spend far more time training their chests than they do their back, which makes muscle imbalances and weaknesses all but unavoidable.Read also: How to do the middle back stretch.Doing too many of the wrong back exercises and not enough of the right onesMost back exercises fall into one of two groups – vertical pulls or horizontal pulls. Ideally, you should do an equal amount of both types of exercise. But, if your middle back is weak, you should do more horizontal pulling than vertical pulling. Many back workouts involve too much vertical pulling, and that leaves the middle back underdeveloped.A poor mind-muscle connection It’s almost impossible to develop a muscle if you can’t feel it working. This is called your mind-muscle connection. Some people “lose touch” with their muscles and cannot feel them working or control them properly. So, even if you’re doing the right exercises, they may not produce the results you want.A good mind-muscle connection means you can control your muscles at will, and every exercise you perform will become much more effective (2).The good news is that you can fix your mind-muscle connection – find out how here.The 10 Best Middle Back Exercises Do you want to develop an impressive middle back but aren’t sure where to start? These are the ten best exercises for your mid-traps and rhomboids!1. Bent-over barbell row The bent-over barbell row is a somewhat controversial exercise, with some coaches saying that it’s best avoided. However, done with good form and not too much weight, the bent-over barbell row is an excellent middle-back exercise and can be performed safely by most people.Barbell Bent Over RowSteps:Grip and hold a barbell with an overhand, wider-than-shoulder-width grip. Pull your shoulders down and back, brace your core and bend your knees slightly.Hinge forward from the hips and lean over until your upper body is almost parallel to the floor. Let your arms hang straight down from your shoulders.Without using your legs or back, bend your arms and row the bar up and into your chest. Pull your shoulders back and keep your elbows level with your shoulders.Extend your arms and repeat.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae.Benefits:An excellent total back builder.A very accessible exercise – all you need is a barbell and weights.Small changes to the angle of your back will change the feel and effect of this exercise.Tips:Keep your lower back arched throughout to protect your spine and maximize middle back engagement.Lead with your elbows and pull the bar to your chest to emphasize the mid-traps and rhomboids.Keep your wrists straight throughout.2. Seal row If bent-over rows bother your lower back, or you prefer to work your upper body in isolation from your legs, then seal row is the exercise for you. You’ll need a tall bench for this mid-back builder, but in return, you’ll be able to push your mid-back to the limit without having to worry about your lower back at all.Steps:Place a flat bench on blocks or stacks to bumper plates so that your hands are a few inches away from the floor when you lie down on it.Lie face down on the bench and grip a barbell or dumbbells. Pull your shoulders down and back.Bend your arms and pull the bar up and into the bench level with your abdomen.Extend your arms, lower the weight, and repeat.You can also do this exercise on a slightly angled bench to hit your lower traps a little more, i.e., incline seal rows.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps, latissimus dorsi.Benefits:A very back-friendly exercise.Can be done using a barbell or dumbbells as preferred.An effective way to target your middle back.Tips:Shrug your shoulder back at the start of each rep to fully engage your middle back.Lead with your elbows to maximize mid-back engagement.Use dumbbells to increase your range of motion.3. Seated chest-supported cable row The great thing about cable exercises is that they let you keep your muscles under near-constant tension, so you get a better workout in less time. This lower-back-friendly exercise is a very effective middle-back movement. It is ideal for beginner and advanced lifters alike.Steps:Attach a rope handle to a low cable. Alternatively, you can use D-shaped handles on an extended strap.Adjust an incline bench to about 70 degrees and place it in front of the cable machine, with the back of the bench facing the pulley.Sit on the bench with your chest against the backrest. Grip the handles and extend your arms.Pull your shoulders down and back, and brace your core.Bend your arms and pull the handles in toward your lower ribs. Lead with your elbows, keep your wrists straight, and squeeze your shoulders together to maximize upper-back engagement.Smoothly extend your arms, let your shoulders shrug forward to stretch your middle back, retract your shoulders again, and repeat.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps, latissimus dorsi.Benefits:No lower back strain to worry about.Your back muscles are under near-constant tension.Cable machine exercises are ideal for drop sets.Tips:Adjust the angle of the bench to hit different parts of your mid-back. The more inclined the bench, the more lower trap and lat engagement there will be. An upright bench focuses more on your mid-traps and rhomboids.Keep your wrists straight and lead with your elbows.Shrug your shoulders back and together to maximize mid-back engagement.4. Pendlay row Pendlay rows are named after legendary powerlifting and weightlifting coach Glen Pendlay. Also known as dead-stop rows, this barbell exercise is popular with Olympic weightlifters, who often use it to fix any upper and mid-back weakness. The dead stop between reps means you should be able to perform this exercise with moderate to heavy weights in relative comfort.Steps:Start with your barbell on the floor. Stand with your feet about hip to shoulder-width apart, toes under the bar.Bend your knees slightly, hinge forward from the hips, and bend over until your upper body is parallel to the floor.Grab the barbell with an overhand, slightly wider than shoulder-width grip. Tuck your chin in and lengthen your neck; do not lift your head to look forward or allow your lower back to round.Brace your core, draw your shoulders down and back, and pull the bar up into your abdomen. Keep your upper arms tucked in close to your sides. Your upper body should remain stationary throughout.Lower the barbell back down the floor and let it settle, reset your core, and repeat.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae. Benefits:A convenient exercise, as most gyms have a suitable barbell.Provides a brief pause between reps so you can reset your grip and core, do more reps, or use a heavier-than-usual weight.An excellent exercise for powerlifters, weightlifters, and strongman competitors.Tips:You can also do this exercise using dumbbells instead of a barbell.Raise the weight on blocks if you cannot maintain a neutral spine.Use lifting straps if you are training with heavy weights.5. Horizontal row You don’t need to use weights to train your middle back. In fact, there are a couple of great bodyweight exercises that are every bit as effective. Horizontal rows, also known as inverted rows, body rows, and Australian pull-ups, are a very convenient way to train your middle back without gym equipment.Steps:Set a bar to about waist height. Make sure the bar will not move. You can use a barbell in a squat rack or a Smith machine.Sit on the floor beneath the bar and hold it with an overhand, slightly wider than shoulder-width grip.Lean back so your arms are straight, brace your core, and pull your shoulders down and back.Lift your hips, so your weight is supported on your heels and hands only. Make sure your body is straight – from your heels to your shoulders.Keeping your body properly aligned, bend your arms and pull your chest up to the bar. Keep your wrists straight and focus on leading with your elbows. Squeeze your shoulders together at the top of the rep.Slowly and smoothly extend your elbows and return to the starting position, keeping your body straight the whole time.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps, latissimus dorsi.Benefits:No equipment required, so ideal for home exercisers.Easy to scale by raising or lowering the height of the bar.Very lower back friendly.Tips:Use a suspension trainer or gymnastic rings for variety.Bend your legs and put your feet flat on the floor for an easier workout.Rest a weight plate on your hips for a more intense workout.6. Renegade row The renegade row is a combination middle back and core exercise. You can even combine it with push-ups to make it a total upper body builder. Be warned; this exercise is more strenuous than it looks, so don’t go too heavy too soon!Renegade RowsSteps:Hold a dumbbell in each hand. You can also use kettlebells. Squat down and place the weights on the floor, so they’re roughly shoulder-width apart.Brace your abs and walk your feet out and back into the push-up position. Your body should form a straight line. Keep your wrists straight, and do not allow them to collapse.Move your feet out so that they are wider than shoulder-width apart to increase balance and stability. Look straight down at the floor to ensure your neck is neutral.Keeping one arm straight, bend the other arm and row the weight up and into your lower ribs. Do NOT allow your hips or shoulders to twist.Lower the weight back to the floor, swap sides, and repeat. Alternate arms for the duration of your set, keeping your core braced throughout.You can also do this exercise with your legs bent and knees resting on the floor to take pressure off your core.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps, latissimus dorsi, core.Benefits:Works well with light dumbbells.A very comprehensive upper-body exercise.Great for home exercisers, as so little equipment is required.Tips:Use hex-shaped dumbbells if available, as they’re more stable and less likely to roll.Wear a weighted vest to make this exercise harder.Do a push-up between rows to develop your chest as well as your back.7. Dumbbell rear delt row The dumbbell rear delt row does more than work your posterior deltoids; it also hits your mid-traps and rhomboids. The great thing about this exercise is that you don’t need a lot of weight to do it, so it’s ideal for home exercisers and anyone without access to heavy dumbbells.Steps:Sit on the end of an exercise bench with a dumbbell in each hand. Hinge forward from the hips and lower your chest toward your legs. Let your arms hang down from your shoulders. Rotate your wrists so that your hands are in the pronated or palms-down position.Leading with your elbows, pull the weights up and out so your upper arms are perpendicular to your upper body. Keep your wrists straight, and pull your shoulders down and back.Extend your arms and repeat.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps.Benefits:Very little strain on your lower back.This exercise works well with light dumbbells.An accessible exercise that’s suitable for home and gym use.Tips:Use a chair if no bench is available.You can also do this exercise standing and by leaning over.Think about driving your elbows back to maximize middle-back engagement.8. Band pull-aparts The band pull-apart is arguably the most convenient way to train your middle back at home. This is a hugely effective posture exercise, and everyone who lifts weights should do band pull-aparts a few times per week. Do this exercise between sets of bench presses or during your upper body warm-ups. Alternatively, do sets of pull-aparts to break up long periods of sitting.Steps:Hold your resistance band with an overhand, shoulder-width grip. Raise your arms in front of you so your hands are roughly level with your shoulders. Pull your shoulders down and back.Open your arms and stretch the band out across your chest.Return to the starting position and repeat.You can work your rhomboids from different angles by changing the angle of your arms and stretching the band diagonally across your chest, not just horizontally.Muscles targeted:Primary: Mid-traps, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: N/A.Benefits:A very shoulder-friendly exercise.You can do band pull-aparts anywhere and at any time.One of the best posture exercises around.Tips: Do this exercise seated or standing as preferred.Try to accumulate 100 reps every day to fix your posture and keep your shoulders healthy.Include band pull-aparts in all your upper body warm-ups to activate and engage your upper back.9. Face pulls Face pulls are so-called because, when you do them, you look like you are going to stick your thumbs in your ears and waggle your fingers like a rude kid! Don’t let this peculiar name or image put you off; the face pull is an excellent mid-back exercise. It’s also fantastic for your posterior deltoids.Cable Face PullsSteps:Attach a rope handle to a cable pulley set to about chest height.Stand with your feet hip-width apart and grab both sides of the handle using a neutral grip. Place one foot in front of the other for balance if necessary.Keeping your elbows level with your shoulders, bend your arms and pull the rope toward your face, contracting your rear deltoids as you pull the ends of the handle apart.Straighten your arms and repeat for the desired number of reps.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: Biceps.Benefits:A very lower back and shoulder-friendly exercise.Very accessible, as most gyms have a suitable cable machine.Perfect for intensity-boosting drop sets.Tips:Imagine you are trying to poke your thumbs in your ears to maximize upper back engagement.Use a resistance band if you don’t have access to a cable machine.Pull the ends of the handles apart as well as back to work your back even more effectively.10. Reverse pec deck fly Reverse pec deck flys are often viewed as a read deltoid exercise, but they’re much more than that. They’re also a very effective way to target your middle back. With no weights to balance, this exercise leaves you free to focus on pushing your mid-traps and rhomboids to their limit. They’re also an excellent exercise for intensity-boosting drop sets.Steps:Sit on the pec deck machine with your chest against the pad. Reach out and grab the handles. Extend, but do not fully straighten your arms. Your hands should be level with or just below your shoulders.Open your arms and draw the handles out and back until your arms form a T-shape with your body.Return to the starting position, stopping just short of letting the weights touch down, and repeat.Muscles targeted:Primary: Middle trapezius, rhomboids, posterior deltoids.Secondary: N/A.Benefits:No need to stabilize your upper body – the machine does it for you.An excellent exercise for beginners.Very lower back friendly.Tips:Experiment with a neutral and pronated grip to see which one you prefer.Lift your chest and pull your shoulders down and back to maximize mid-trap and rhomboid engagement.On reaching failure, lower the weight by 15-20% and crank out a few more reps to increase the intensity of your workouts.Frequently Asked QuestionsDo you have a question about middle-back training or back workouts in general? No sweat because we’ve got the answers!1. What is the best way to bring my mid-back up to the same level as my lats, shoulders, and chest?If your mid-back is weak, you must prioritize it in your workouts. Train your mid-traps and rhomboids twice per week, e.g., Monday and Thursday, and work them first in your back workouts, i.e., before your lats. Also, consider doing less lat training to give your mid-back a chance to “catch up.”Also, become more mid-back-aware, and pull your shoulders down and back during almost every other exercise you perform, even your arms and legs. This will help strengthen that all-important mind-muscle connection.Once you are happy with your middle back development, maintain it by doing an equal amount of horizontal pulling and pushing training. In other words, for every set of chest training, do a set of rows or similar.2. I can’t feel my middle back working – is this normal?A lack of sensation on your middle back is common and normal, and suggests that you have a weak mind-muscle connection. The good news is that this is relatively easy to fix, although it will take a while to reconnect your brain and back.Ways to do this include:Training your middle back more often.Practicing pulling your shoulders back and together several times a day, especially before training.Adding mid-rep pauses to rows and other mid-back exercises.Doing your reps more slowly and with less weight so you can emphasize retraction.In time, you should notice that you can feel your muscle back working more, indicating your mind-muscle connection is getting stronger.3. What sets and reps should I use for my middle back workouts?Your rep range is goal and exercise-dependent. To build strength, you must lift heavy weights for low reps, i.e., 1-5. Of course, such heavy loads are not practical for some middle-back exercises, such as horizontal rows or band pull-aparts.To build muscle, you can use light to moderate weights and do anywhere from 6-35 reps per set.Generally, the lower end of the scale is best for compound exercises. In contrast, the higher end is more suitable for isolation or single-joint movements.When training for hypertrophy or muscle growth, ensure that you take your sets to within 1-3 reps of failure. Easier sets will not trigger much muscle growth.4. How many times a week should I train my middle back?Twice a week is an excellent place to start for most people. This provides a good balance between work and recovery.For example, you could train your back on Monday and Thursday, leaving plenty of time for the rest of your body and recovery. One workout per week probably won’t be enough to produce good results, but will probably be sufficient to maintain muscle mass and strength.5. How many sets should I do per week for my middle back?The accepted number of sets per muscle group per week is 10-20. Beginners and older exercisers should do 10-14, while younger and more advanced exercisers can work up to 15-20. However, more sets will not necessarily produce better results.These sets should be evenly spread over your workouts. For example, if you want to do 15 sets for your back per week, you could do three workouts, each consisting of five sets for the target muscle.6. Why isn’t my mid-back growing?Your body will respond to your workouts unless you are doing something wrong. Common reasons for not achieving muscle growth include:Failing to consume enough protein – you need between 0.7 to 1.0 grams per pound of body weight.Not training hard enough – you must train to within 1-3 reps of failure.Not training often enough – once a week or less won’t cut it!Skipping too many workouts – even the best middle back exercises and workouts will not work if you don’t do them. You MUST be consistent.Training too hard, long, or often – your body has a limited capacity for recovery. If you work out hard seven days a week, your muscles won’t have the time or energy needed for growth.Not getting enough sleep – your muscles do most of their growing when you’re sleeping. So, you need 6-8 hours per night, and not just at weekends!It’s not been long enough – it takes time for your body to start responding to your workouts. If you’ve only been training for a few weeks, you probably won’t see many changes yet. So be patient and stick with it.7. Got a good mid-back workout for me to try?Sure do! Do this workout twice a week on non-consecutive days, e.g., Tuesday and Friday. But, before you begin, spend a few minutes warming up by doing some light cardio followed by dynamic mobility and flexibility exercises for your shoulders, elbows, and upper back.#Exercise SetsRepsRecovery1Pendlay rows44-63 minutes2Seal row36-82 minutes3Reverse pec deck fly310-1290 seconds4Face pulls212-1560 seconds5Band pull-apart215-2060 secondsMiddle Back Exercises – Final Thoughts It’s easy to neglect your middle back. After all, you can’t see it, so there is less of an incentive to train it. However, the mid-traps and rhomboids play a crucial role in your posture, shoulder stability, and upper back thickness. If you want to look and perform at your best, you MUST train your middle back as hard and as often as you train your lats, chest, and deltoids.Use the exercises and tips in this article to build a mid-back you can be proud of.More Back Exercises:References: 1. KenHub: Back Muscle Anatomy https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21632-back-muscles2. PubMed: Importance of Mind-Muscle Connection During Progressive Resistance Training https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26700744/

Performing Renegade Rows: The Dynamic Tool Your Training Is Missing
Why You Should Be Using The Renegade Row
Due to its ability to efficiently target multiple muscle groups at one time, the renegade row is one of the greatest dynamic resistance exercises in existence.
The exercise holds much value regardless of whether you are new to strength training or if you have been attending the gym for years.
In addition, there are a number of renegade row variations that can be utilized in order to bring about specific adaptations and advance you towards achieving your health and fitness goals.
As you may be aware, all rowing movements tend to develop the muscles of the upper back and the lats. While the renegade row certainly works these muscles, it requires engagement from many more.
The exercise demands a large degree of stabilization work which comes predominantly from the core. Working the core in this manner will improve midline stability and coordination.
This article will not only detail how exactly to perform the renegade row but will also cover the benefits, common mistakes and variations that are associated with the exercise.
Renegade Row Muscles Worked and Technique
As mentioned, the renegade row requires engagement from a vast array of muscles both to stabilize and drive the movement.
In terms of stabilization, all the muscles which isometrically contract during a plank must do likewise during the renegade row – this includes the glutes, core, and legs (1).
The muscles that are primarily responsible for the rowing movement are the lats, traps, rhomboids, and biceps (2).
Use the following 4 coaching points in order to successfully complete the renegade row and build full-body strength and stability.
1) Set a Solid Base
In preparation for the renegade row, it is imperative that you first set yourself up in a solid and stable position, otherwise, the movement will quickly break down.
Place the dumbbells on the floor so that when you get in the plank position, the shoulders are directly above them weights.
Assume an extended plank position and ensure that the feet are placed anywhere between hip and shoulder-width. The distance you go with is really dependent on what feels best.
If you want to really challenge your stability, go with a narrower stance whereas if you want to increase stability select a slightly wider stance.
If you are new to the renegade row, it is recommended to start with a wider stance initially. As you improve, bring the feet in a fraction to increase the difficulty of the exercise.
2) Engage the Core
Before driving the dumbbells from the floor, engage all the muscles of the core and squeeze the glutes tightly. In addition, drive the heels into the floor as best as possible to keep you grounded.
Bracing the body in this manner will hold you in a straight line as you row and have a positive impact on movement efficiency.
To assist in the bracing process, gradually work your way up the body squeezing the muscles as you go. Set the ankles first, then the knees, hips, core and then finally, the upper body.
3) Nailing the Row
The next step is to powerfully pull one of the dumbbells into the body. It’s really important that the movement is akin to a standard dumbbell row.
Therefore, when pulling the dumbbell, look to keep the shoulder locked down (prevent it from rising upward), tuck the elbow into the side of the body and pull far enough so that elbow moves beyond the level of the back.
A useful tip that may facilitate a great row is to visualize pulling the starter cord of a lawnmower as this is exact movement pattern you want to replicate.
4) Controlling the Eccentric Phase
After completing the concentric part of the exercise (pulling the dumbbell off the floor and into the body), it is imperative that the eccentric (or lowering) phase is well controlled.
While maintaining a full-body brace, gradually lower the dumbbell back down to the floor – this will keep the tension on the muscle for a longer period of time.
Swinging the dumbbell or allowing gravity to take over will not only fail to activate the muscles efficiently but may move you out of a stable position.
If the weight is too heavy, it is likely that this will occur. If this happens to you, consider reducing the overall weight to allow for proper execution of the exercise.
Renegade Row Benefits
Adding the renegade row into your training program can bring about a vast number of benefits. However, there are 3 primary benefits that are associated with this movement.
1) Midline Stability Improvements
Performing a row while in the extended plank position will fire up all core musculature in order to prevent rotation from occurring.
Many joints must be stabilized which therefore requires a powerful isometric contraction from multiple muscle groups to fight the compulsion to rotate the trunk.
Over time, regularly practicing the renegade row will increase core strength and therefore enhance midline stability and total body control.
Improving these aspects can have such a positive impact, not only on athletic performance and injury risk (3) but also more generally in day-to-day life.
2) Building Upper Back and Lat Size
One of the more evident benefits of the renegade rows is the impact that it has on back health. As reflected on earlier, the row is an excellent upper back and lat developer.
Therefore, adding the renegade row into your training program can lead to an increase in both the upper back and lats strength and size.
Adding in extra pulling exercise, such as the renegade row, into your program will increase the number of pulling exercises completed and boost overall training volume.
This is significant as there is a direct relationship between training volume and muscle hypertrophy (4). The greater the volume, the greater the rate of muscle growth.
3) Exercise Adaptability
Finally, this exercise can easily be scaled or adapted to align with your needs and training goals. With the renegade row, it is possible to scale the weight, movement patterns, and implements.
Another great benefit of the renegade row is that it does not require a lot of equipment or extreme weight in order to execute. This makes it an excellent dynamic training tool for practically any workout.
Renegade Row Common Mistakes
There are two very common mistakes to be aware of and avoid when performing the renegade row.
Typically, these errors creep in as a result of one of two things. Either using too much weight or setting up incorrectly prior to starting the exercise.
1) Rotating the Trunk
As discussed, the greatest benefits associated with this exercise will come about through resisting rotation.
Often rotation will occur when too much weight is being used. The body will utilize rotation and move out of the plank position in order to assist the drive of the dumbbell.
Take a moment to remind yourself that both the shoulders and hips should stay neutrally aligned and parallel to the floor throughout the duration of the exercise.
If you find that you are rotating in order to bring the dumbbell up, simply lower the dumbbell weight to allow you to control the movement to a greater degree.
2) Lifting the Feet Off The Floor
One of the most challenging components of the renegade row is keeping the feet grounded while rowing.
Finding a stance that allows you to maintain ground contact throughout is imperative. This may mean experimenting a little with your stance to find what works best for you.
If you find that the feet lift from the floor or move excessively, adjust your stance and consider reducing the weight once again.
Renegade Row Variations
For those who are looking to advance their training or challenge themselves, there are a number of effectual renegade row progressions.
Here are 3 of the best renegade row variations to allow you to further develop full-body strength and stability.
1) Renegade Row with Push-Up
A very simple yet effective variation is to add a push up after completing your rows. To complete one full repetition, row both sides individually and then perform one full push-up.
2) Kettlebell Renegade Row
This variation is for those who are experienced and consider themselves to be at an advanced stage.
Because kettlebells are less stable than dumbbells, this exercise will provide a real challenge in terms of both trunk and shoulder stability.
3) Feet Elevated Renegade Row
Elevating the feet removes 2 points of floor contact which will cause you to feel less stable and increase the difficulty of the exercise.
As a result, the core and hip musculature will be forced to work even harder to hold the body in the correct position.
Final Word
There is no denying that the renegade row is a highly demanding exercise and therefore care must be taken when performing it.
However, when executed correctly, the exercise has the ability to build a strong upper back, lats, and core as well as improving midline stability and movement.
For more news and updates, follow Generation Iron on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
References:
1-Youdas, James W.; Coleman, Kendra C.; Holstad, Erin E.; Long, Stephanie D.; Veldkamp, Nicole L.; Hollman, John H. (2018-3). “Magnitudes of muscle activation of spine stabilizers in healthy adults during prone on elbow planking exercises with and without a fitness ball”. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice. 34 (3): 212–222. doi:10.1080/09593985.2017.1377792. ISSN 1532-5040. PMID 28922049.
2-Lehman, Gregory J; Buchan, Day Deans; Lundy, Angela; Myers, Nicole; Nalborczyk, Andrea (June 30, 2004). “Variations in muscle activation levels during traditional latissimus dorsi weight training exercises: An experimental study”. Dynamic medicine : DM. 3: 4. doi:10.1186/1476-5918-3-4. ISSN 1476-5918. PMID 15228624.
3-Huxel Bliven, Kellie C.; Anderson, Barton E. (2013-11). “Core Stability Training for Injury Prevention”. Sports Health. 5 (6): 514–522. doi:10.1177/1941738113481200. ISSN 1941-7381. PMC 3806175. PMID 24427426.
4-Schoenfeld, Brad J.; Contreras, Bret; Krieger, James; Grgic, Jozo; Delcastillo, Kenneth; Belliard, Ramon; Alto, Andrew (01 2019). “Resistance Training Volume Enhances Muscle Hypertrophy but Not Strength in Trained Men”. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 51 (1): 94–103. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000001764. ISSN 1530-0315. PMC 6303131. PMID 30153194.
