Tag: Women

Primobolan
Primobolan for Women – Comprehensive Guide to Primobolan (Methenolone) is an anabolic steroid that is well-tolerated by many women due to its low androgenic properties. It is often considered one of the safer choices for female athletes and bodybuilders. However, like any steroid, it should be used with caution and proper knowledge. This guide will…

Intermittent Fasting Blueprint For Women Over 50
As people age, it becomes tough for them to maintain a healthy weight and a slender body. This is especially true for women over 50 experiencing menopause. During menopause, they encounter a sudden dip in estrogen levels and other hormonal imbalances that lead to increased abdominal fat, mood swings, rapid muscle loss, osteoporosis, a slow metabolism, sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, and stress.[1]
Insulin resistance and loss of body and bone mass are the root causes of various health issues associated with aging in women over 50. Plus, a sedentary lifestyle is a major contributor to weight gain in women over 50.
In such a scenario, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes eating nutritious food, sleeping well, being active, and managing stress is essential to combating age-related issues. Time-restricted feeding or intermittent fasting has been shown to benefit seniors by improving insulin resistance and reducing body weight and inflammation.[2]
In this article, we will delve more deeply into what intermittent fasting is, its benefits, and how it works to retain muscle mass, improve metabolism, and keep weight in check in women over 50.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between voluntary fasting and non-fasting over a given period. However, it does not focus on restricting calories; rather, it emphasizes how much time you abstain from eating. It encourages eating only in a specific time window, and you consume no calories for the rest of the day.
However, keeping yourself hydrated during the fasting period is crucial. So you must drink water and zero-calorie beverages like black coffee or tea (of course, without sugar or cream) throughout the fasting period.
You can eat normally at the end of the fasting window. A balanced diet consisting of healthful foods is always encouraged. It is recommended for women over 50 to eat a balanced diet, as it helps boost your metabolism, reduces insulin resistance, and alleviates other hormonal issues.
However, you must keep yourself away from inflammatory foods such as sugary and carbonated drinks, refined sugar and grains, fried food, processed meat, etc., as these can exacerbate the adverse effects of menopause, such as hot flashes.
There are several types of intermittent fasting, of which some of the most popular are:
Time-restricted eating (TRE): It involves alternating between periods of restricting calories and eating normally.[3] An example of TRE is the 16/8 method, which includes calorie restriction for 16 consecutive hours and consuming food within the rest of the eight-hour window. It is a popular method as it is the most doable and least restrictive, which can suit the schedule of most people.
The 5:2 method: This method includes eating normally for five days and restricting your calorie intake to 500 calories for two non-consecutive days of the week.
Alternate day fasting: It involves fasting on every alternate day and eating. However, you can consume a maximum of 500 calories on fasting days. Research says this method is beneficial for shedding weight, improving heart conditions, and lowering oxidative stress and inflammation.[4]
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting For Women Over 50
According to research, intermittent fasting can benefit women over 50 in various ways, including:
Improved metabolic and heart health [5][6]
Better weight loss [7]
Type 2 diabetes management [8]
Increased insulin sensitivity [9]
Preventing metabolic syndrome, which generally leads to neurological disorders [10]
Enhanced circadian rhythm [11]
Improved conditions such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia [12]
Improved fitness levels and athletic performance [13]
Reduced inflammation and improved liver and gut health [14][15][16][17]
Enhanced cognitive function [18]
Does Intermittent Fasting Work for Women over 50?
Yes, it does. Intermittent fasting has shown promising results in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women. A 2020 study indicated that intermittent fasting reduces fat mass, insulin levels, insulin resistance, and blood pressure, regardless of sex or menopausal status. It also reduces LDL cholesterol levels, a potential risk factor for heart disease in post-menopausal women [19].
Another study revealed that time-restricted feeding, or TRF, is beneficial in reducing fasting insulin, insulin resistance, fat mass, and oxidative stress in both pre and postmenopausal women. It also helps improve their metabolism. [5]
Since estrogen levels in women over 50 decline naturally, pre and postmenopausal women are at a higher risk of gaining weight, developing cardiovascular disease, and having problems with blood sugar regulation. Intermittent fasting helps alleviate these issues. [20]
Intermittent Fasting and Diet Quality
Although intermittent fasting is beneficial for overall metabolic health, you should exercise caution while choosing your food. Additionally, you must carefully watch your activity schedule, sleep quality, and stress management.
Your diet must include whole foods such as grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits. Since women over 50 are at a greater risk of losing muscle mass and developing fat mass, your diet should also have enough protein (Paleo or Mediterranean diets are good options).
As people grow older, they naturally lose muscle mass. This problem increases if you don’t remain physically active or do not consume enough protein in your diet. Losing muscle mass causes metabolic dysfunction and fat gain.
Since intermittent fasting involves calorie restriction, it may lead to a lower protein intake. If women over 50 do not consume their goal protein within the eating window, they may lose muscle mass. Thus, you must carry out strength training and optimize your protein consumption to overcome this issue.
How Much Protein Do You Require?
Animal Protein Sources
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight to maximize muscle health. However, your body does not efficiently use dietary protein as you age. Hence, you need more protein to maintain muscle health. [21]
Experts recommend elderly adults consume 1.2 to 2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. [22]
For example, if you are over 50 and weigh 55 kilograms (121.25 pounds), you must consume at least 66 to 110 grams of protein daily, or possibly more.
Optimizing Protein Intake When Fasting
Women over 50 that are intermittent fasting are more likely to fall short of their protein intake goal than women eating a normal diet. In such a scenario, you may maintain your muscle mass by engaging in strength training and optimizing your dietary protein intake.
Here is a list of some protein-rich foods and the amount of protein per serving.[23]
Protein Source
Serving Size
Amount of Protein (gm)
Whey protein
3 scoops
50
Chicken gizzard
1.0 cup chopped or diced
44
Yellowtail fish
0.5 fillets
43
Black beans
1 cup
42
Chicken breast
3 ounces
28
Turkey breast
3 ounces
25
Pork
3 ounces
23
Salmon
3 ounces
22
Tuna
3 ounces
22
Shrimp
3 ounces
20
Greek yogurt
6 ounces
18
Cottage cheese
4 ounces
14
Soy nuts
1 ounce
12
Lentils
½ cup
9
Pumpkin seeds
1 ounce
9
Milk
1 cup
8
Soy milk
1 cup
8
Almonds
1 ounce
7
Egg
1 large
6
Quinoa
½ cup
4
Chia seeds
1 ounce
5
It is evident from the above list that animal-based foods are packed with protein. But that does not mean you should only consume animal proteins. You must incorporate various foods into your diet to reach your protein target.
Is Intermittent Fasting Right For You?
Intermittent fasting not only benefits overweight people or folks with metabolic disorders, but it also benefits people who are of normal weight and are healthy. When you consider intermittent fasting, you must know whether it is right for you.
Intermittent fasting is good for you if you:
Feel good when eating a restricted diet
Don’t have a negative relationship with food
You feel better when you do short-term liquid-only fast
Intermittent fasting is not for you if you:
Feel dizzy, exhausted, irritable, and hungry upon skipping a meal
Always are constantly hungry
Feel uncomfortable during a fast
Fasting Tips for Women Over 50
Women over 50 can follow the following fasting tips when considering intermittent fasting.
Start Small
If you are new to intermittent fasting, keeping the fasting windows short is always recommended. You can start with overnight fasting, which is fasting from dinner to breakfast. If you feel comfortable with it, then increase your fasting hours gradually.
Don’t Restrict Your Calories Too Much
Intermittent fasting allows you to consume the required calories within the eating window. But most people restrict themselves and end up in a calorie deficit. Cutting down too many calories can impair your metabolism, and you will begin to lose muscle mass instead of gaining it. Your blood pressure may rapidly decrease, and you may encounter an electrolyte imbalance. Instead, you can maintain a minor calorie deficit to avoid these issues and obtain better results.
Prioritize Your Protein Intake
Insufficient protein can lead to sarcopenia, which is age-induced muscle loss. Insufficient protein can also impair your immunity and make you fall ill very often. It may also decrease your overall strength.
Focus on Strength Training
Complement intermittent fasting with strength training. It can help you retain muscle mass and strength.[24]
Retaining muscle mass as we age is difficult, eventually resulting in muscle loss and weight gain. However, regular strength training exercises and consuming sufficient protein can help overcome this issue.
Keep a Check on Electrolyte Imbalances
Extended intermittent fasting can lead to electrolyte imbalances by drastically dropping your sodium and potassium levels. This can lead to muscle cramps, headaches, and fatigue. Drinking electrolyte water, coconut water, and eating electrolyte-rich foods such as spinach can boost your electrolyte levels.
Always Focus on a Nutrient-Dense Diet
Although intermittent fasting focuses on when to eat only, what to eat is equally crucial to sustain fasting in the long run and maintain good health. Your diet should comprise whole grains, complex carbs, lean proteins, healthy fats, and enough fiber. Additionally, your water intake should also be intact. Eating a healthy and balanced diet can help combat many chronic diseases and keep you healthy. Skipping refined, deep-fried, excessively salty, sugary, and packed foods is highly recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many hours should a woman over 50 do intermittent fasting?
If you are new to intermittent fasting, keeping the duration of fasting short is always recommended. You can start with an overnight fast of 12 hours. This refers to fasting from dinner to breakfast. If you feel comfortable with it, then increase your fasting hours gradually.
2. Is intermittent fasting safe for women over 50?
According to research, intermittent fasting is safe for women over 50 [25]. However, you must consult your healthcare provider if you encounter conditions like hypoglycemia, dizziness, weakness, fatigue, or muscle loss.
3. What is the best intermittent fasting method for menopausal women?
16:8 Intermittent fasting is believed to be the most convenient method for menopausal women, as it is much more flexible to follow.
Bottom Line
Women over 50 undergo several bodily changes, such as weight gain, increased blood glucose levels, insulin resistance, rapid muscle loss, a slow metabolism, mood swings, anxiety, etc., during menopause. These occur due to the decrease in estrogen levels and hormonal imbalances.
Although research is limited, some studies indicate that intermittent fasting can benefit women over 50 with weight loss, reduced insulin resistance, blood glucose, and LDL cholesterol. It may improve heart and metabolic health as well. Before starting any intermittent fasting plan, consult your healthcare provider, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions.
References
Peacock, K., & Ketvertis, K. M. (2022, August 11). Menopause – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. Menopause – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507826/
Lin, S., Oliveira, M. L., Gabel, K., Kalam, F., Cienfuegos, S., Ezpeleta, M., Bhutani, S., & Varady, K. A. (2020, October 31). Does the weight loss efficacy of alternate-day fasting differ according to sex and menopausal status? PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2020.10.018
Soliman, G. A. (2022, October 28). Intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating role in dietary interventions and precision nutrition. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1017254
Johnson, J. B., Summer, W., Cutler, R. G., Martin, B., Hyun, D. H., Dixit, V. D., Pearson, M., Nassar, M., Maudsley, S., Carlson, O., John, S., Laub, D. R., & Mattson, M. P. (2006, December 14). Alternate Day Calorie Restriction Improves Clinical Findings and Reduces Markers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Overweight Adults with Moderate Asthma. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.12.005
Changes in body weight and metabolic risk during time-restricted feeding in premenopausal versus postmenopausal women – PubMed. (2021, October 15). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2021.111545
Intermittent fasting for the prevention of cardiovascular disease – PubMed. (2021, January 29). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013496.pub2
Effects of Intermittent Fasting in Human Compared to a Non-intervention Diet and Caloric Restriction: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials – PubMed. (2022, May 2). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.871682
Effect of Intermittent Compared With Continuous Energy Restricted Diet on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Noninferiority Trial – PubMed. (2018, July 6). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.0756
Clinical Implications for Women of a Low-Carbohydrate or Ketogenic Diet With Intermittent Fasting – PubMed. (2021, April 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nwh.2021.01.009
Fasting as a Therapy in Neurological Disease – PubMed. (2019, October 17). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102501
Longo, V. D., & Panda, S. (n.d.). Fasting, circadian rhythms, and time-restricted feeding in a healthy lifespan. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.001
Berthelot, E., Etchecopar-Etchart, D., Thellier, D., Lancon, C., Boyer, L., & Fond, G. (2021, November 5). Fasting Interventions for Stress, Anxiety, and Depressive Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113947
Effects of fasted vs fed-state exercise on performance and post-exercise metabolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed. (2018, May 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13054
Effects of intermittent fasting diets on plasma concentrations of inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials – PubMed. (2020, December 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.110974
The effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on liver function in healthy adults: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression – PubMed. (2021, August 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108951
Repercussions of intermittent fasting on the intestinal microbiota community and body composition: a systematic review – PubMed. (2022, February 10). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuab108
Changes in human gut microbiota composition are linked to the energy metabolic switch during 10 d of Buchinger fasting – PubMed. (2019, November 12). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2019.33
Gudden, J., Vasquez, A. A., & Bloemendaal, M. (2021, September 10). The Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Brain and Cognitive Function. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093166
Does the weight loss efficacy of alternate day fasting differ according to sex and menopausal status? – PubMed. (2021, February 8). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2020.10.018
Menopause, but not age, is an independent risk factor for fasting plasma glucose levels in nondiabetic women – PubMed. (2007, June 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.gme.0000247014.56254.12
Protein Consumption and the Elderly: What Is the Optimal Level of Intake? – PubMed. (2016, June 8). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8060359
Baum, J. I., Kim, I. Y., & Wolfe, R. R. (2016, June 8). Protein Consumption and the Elderly: What Is the Optimal Level of Intake? PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8060359
Nutrient Lists from Standard Reference Legacy (2018) | National Agricultural Library. (n.d.). Nutrient Lists From Standard Reference Legacy (2018) | National Agricultural Library. https://www.nal.usda.gov/human-nutrition-and-food-safety/nutrient-lists-standard-reference-legacy-2018
Keenan, S., Cooke, M. B., & Belski, R. (2020, August 6). The Effects of Intermittent Fasting Combined with Resistance Training on Lean Body Mass: A Systematic Review of Human Studies. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082349
Domaszewski, P., Konieczny, M., Pakosz, P., Bączkowicz, D., & Sadowska-Krępa, E. (2020, June 10). Effect of a Six-Week Intermittent Fasting Intervention Program on the Composition of the Human Body in Women over 60 Years of Age. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17114138

Intermittent Fasting For Women Over 40: Revealing the Secrets
After the age of 40, women may encounter difficulties when it comes to losing weight due to factors such as hormonal fluctuations, alterations in physical composition, and various life stressors.
As women grow older, their nutritional requirements also change. After 40, your estrogen level starts to drop. This leads to slower metabolism, increased insulin level, and impaired thyroid levels. These factors make you eat more, and due to less physical activity, you burn fewer calories, leading to muscle mass loss and fat accumulation. This results in significant weight gain in women after 40.
Intermittent fasting, or IF, is an excellent strategy for women over 40 to shed and keep weight off. It boosts your metabolism without restricting your food choices.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting involves alternating between periods of eating and fasting. IF does not bother with tracking calories; instead, it focuses on your eating schedule.
An intermittent fasting plan allows you to consume all foods within a specified period of a day. For example, a 16:8 plan involves fasting for 16 consecutive hours and eating in an eight-hour window.
During fasting, your insulin levels drop gradually, and the body starts to deplete its glycogen reserve (stored glucose) as energy.
When you repeat this process for multiple days, your body utilizes all the stored glycogen, leading to weight and fat loss. A recent study has revealed that intermittent fasting can be an excellent weight loss tool for obese people. [1].
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting For Women Over 40
For women over 40, intermittent fasting brings several health benefits:
Helps Induce Autophagy
Autophagy naturally declines with age. However, intermittent fasting boosts autophagy which helps our body to rest and heal. Our body cells recycle during autophagy to better adapt to stress. [2][3]
Promotes Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting can help limit calorie intake. In a 2018 study, it was found that intermittent fasting resulted in an average weight loss of 15 pounds in overweight adults in a three to 12-month duration. [4]
Another research indicated that overweight adults experienced a 3-8% bodyweight loss within 3 to 24 weeks of following an IF plan. [5]
Reduces Risk of Heart Disease
High blood pressure and increased LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels are the major contributing factors to cardiovascular disease. A 2009 study of 16 obese males and females demonstrated that intermittent fasting helped them reduce their blood pressure by 8%, LDL cholesterol by 25%, and triglyceride levels by 32% in just eight weeks6], eventually reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Helps Manage Diabetes
Women usually get diabetes after the age of 40. As per studies, people with type 2 diabetes can control their blood sugar levels with intermittent fasting. [7][8]
Intermittent fasting helps lower insulin levels and reduce insulin resistance. However, if you have diabetes, you must consult a doctor before starting an intermittent fasting plan. [9]
Increases Longevity
A study on 2,000 adults was done over four years, of which 20% were intermittent fasting for at least five years. It was found that IF improved longevity, metabolic response, tissue resurgence, and various health markers and reduced age-induced diseases. [10]
Helps Improve Mental Health
According to research, intermittent fasting improves mental well-being. It also helps alleviate depression and boosts emotional health. [11][12]
Preserves Muscle Mass
Intermittent fasting can help with body recomposition. The eat-fast aspect of IF helps maintain muscle mass and burn more calories.[13] Also try our body recomposition calculator.
Best Intermittent Fasting Plans For Women Over 40
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to intermittent fasting, especially for women. Some best intermittent fasting plans for women over 40 are discussed below.
The Crescendo Method
This plan includes fasting for 12 to 16 hours for two to three non-consecutive days distributed evenly across the week. It is usually recommended for women who are new to intermittent fasting. The shorter fasting periods are usually kinder on women’s hormone levels.
The Eat-Stop-Eat Method
Eat-stop-eat method involves fasting for two non-consecutive days in a week. You must fast for the entire 24-hour period for those two days. For the remaining five days of the week, you can eat normally. However, you must eat mindfully to avoid unnecessary calorie consumption.
The 5:2 Diet Method
In 5:2 method, you can eat normally for five days and must fast for the remaining two days in a week. During your fasts, you can eat a limited amount of calories (around 500) per day. The two fasting days should be non-consecutive.
Research indicates that this intermittent fasting regimen helps improve cardiometabolic health by reducing insulin resistance, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and oxidative stress. [14]
The 16:8 Method
16:8 method involves fasting for 16 consecutive hours and meeting your daily calorie needs within eight hours. This is a popular plan because it is less restrictive and usually suits everyone’s regimen. A 2016 study suggests that this IF plan, along with strength training, could help build muscle mass while losing fat. [15]
Although no foods are off-limit in this plan, you shouldn’t binge on junk food during the eating window. Instead, you should eat nutrient-dense whole foods.
The Alternate-Day Fasting Method
As the name suggests, it involves fasting every alternate day and eating a healthy diet on non-fasting days. However, you can consume up to 500 calories on your fasting days.
According to research, alternate-day fasting helps reduce obesity, heart disease, oxidative stress, and inflammation. [16]
How Can Women Over 40 Safely Implement Intermittent Fasting?
Although intermittent fasting barely has any adverse effects, it is not as easy for ladies over 40 as women in their 20s or 30s. Women over 40 need to be extra cautious while following this pattern of fasting because of the following:
A sluggish metabolism
Hormonal imbalances
Higher stress level
Considering the above factors, women above 40 must calibrate their fasting pattern in the following ways.
Continue Fasting For a Longer Duration
Women over 40 need to fast longer to reap the benefits of IF. Fasting for extended hours will help you achieve your weight loss goals faster. It will keep a check on your daily calorie consumption as well.
Have More Protein
Protein plays a crucial role in any kind of fasting. When you have adequate protein, it helps increase your muscle mass and reduce fat. More protein in your diet makes you feel less hungry, leading to less calorie intake. Try our protein intake calculator.
Drink Plenty of Water
Water helps remove toxins from your body, and it turns out to be more effective during intermittent fasting. Water also keeps you satiated, leading to less calorie intake, and eventually helps shed those extra kilos. Find your optimal water intake.
Healthy Meal Plans
Just fasting may not be enough to reap all the intermittent fasting benefits. Combining intermittent fasting with healthy meal plans is a must. Consider adding a lot of veggies, fruits, low-fat milk, whole grains, lean meat, and healthy fats to your diet.
Focus on Portion Control
A portion is the amount of food you eat at a time, which can be more or less than the recommended serving size. Even if you can eat anything during the eating window, controlling the portion size is crucial for weight loss. Find calorie breakdown per meal.
Exclude the Unhealthy Eating Habits
To enhance the advantages of intermittent fasting, you must exclude these unhealthy habits from your fasting regimen:
Eating fast
Munching while watching TV
Snacking directly from the packets instead of in a bowl or plate
Binge eating during weekends
Late night snacking
Consuming alcohol
Related: 7 Ways To Stop Binge Eating – For Good!
Manage Sleep
A good night’s sleep is essential to maintain a healthy weight during intermittent fasting. Lack of sleep may cause an impaired metabolism in women over 40 doing intermittent fasting. Not having enough sleep can have a negative impact on appetite hormones and can cause weight gain.
Consult your Doctor
If you are a woman over 40, you must consult a registered healthcare practitioner to determine the suitability of intermittent fasting for you. Talk to your doctor before opting for intermittent fasting if you have any of the following conditions:
An autoimmune condition
Eating disorder
Hypoglycemia or low blood sugar tendency
You are trying to conceive
Pregnant or breastfeeding
Diabetes
You are underweight
History of amenorrhea or missed periods
Best Foods for Intermittent Fasting for Women Over 40
Eating nutritious food is crucial to avoid hunger during intermittent fasting and managing a healthy weight. Here are some choices of foods to consider.
Vegetables: Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, cucumber, broccoli, and green leafy vegetable such as bok choy, arugula, collard greens, kale, spinach, etc.
Fruits: Bananas, apples, oranges, berries, pears, peaches, grapes, tomatoes, etc.
Proteins: Poultry, meat, eggs, fish, legumes, nuts, seeds, etc.
Whole grains: Brown rice, oats, barley, quinoa, bulgur wheat, etc.
Healthy fats: Olive oil, avocados, low-fat dairy products like cheese, low-fat milk, and yogurt
Omega 3: Tuna, sardine, mackerel, cod, salmon, anchovies, herring, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is intermittent fasting safe for women over 40?
There are no known disadvantages or side effects of intermittent fasting. Women over 40 face slow metabolism and hormonal issues, and intermittent fasting can be beneficial in such conditions. Intermittent fasting is safe for women. In fact, it can help in weight loss, reduce the risk of heart disease, help manage diabetes and improve longevity and mental health.
How can a 40-year-old woman lose weight fast?
Here are some tips that will help you lose weight faster if you are a woman over 40:
Eat healthy food
Practice portion control
Plan your meals well in advance
Add more fiber to your diet
Control your carb intake
Stay away from processed food
Avoid sugary beverages, excess salt, and sugar
Keep yourself active and workout diligently
Hydrate yourself adequately
Focus on quality sleep
What is the best intermittent fasting plan for women over 40?
The most recommended and sustainable fasting plan for women over 40 is the 16:8 diet plan, where you fast for 16 hours and eat within an eight-hour window.
Wrapping Up
Intermittent fasting has many benefits to offer to women over 40. But when you plan to implement intermittent fasting into your regimen, it should gel with your lifestyle. It should not make you feel weak or drained.
It is normal to feel hungry during the initial phases of an intermittent fasting plan. You might also get exhausted if you combine your fasting regimen with exercise during the first few days. But, if you encounter fatigue, dizziness, soreness, or exhaustion, your body is not ready for the new diet plan. Listen to your body and act accordingly.
References
Welton, S., Minty, R., O’Driscoll, T., Willms, H., Poirier, D., Madden, S., & Kelly, L. (n.d.). Intermittent fasting and weight loss: Systematic review. PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7021351/
The effect of fasting or calorie restriction on autophagy induction: A review of the literature – PubMed. (2018, November 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.08.004
Chung, K. W., & Chung, H. Y. (2019, December 2). The Effects of Calorie Restriction on Autophagy: Role on Aging Intervention. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122923
Intermittent fasting interventions for the treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed. (2018, February 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003248
Patterson, R. E., Laughlin, G. A., Sears, D. D., LaCroix, A. Z., Marinac, C., Gallo, L. C., Hartman, S. J., Natarajan, L., Senger, C. M., Martínez, M. E., & Villaseñor, A. (2015, April 6). INTERMITTENT FASTING AND HUMAN METABOLIC HEALTH. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2015.02.018
Short-term modified alternate-day fasting: a novel dietary strategy for weight loss and cardioprotection in obese adults – PubMed. (2009, November 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28380
Arnason, T. G., Bowen, M. W., & Mansell, K. D. (2017, April 15). Effects of intermittent fasting on health markers in those with type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.154
Cho, Y., Hong, N., Kim, K. W., Cho, S. J., Lee, M., Lee, Y. H., Lee, Y. H., Kang, E. S., Cha, B. S., & Lee, B. W. (2019, October 9). The Effectiveness of Intermittent Fasting to Reduce Body Mass Index and Glucose Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101645
The effects of intermittent or continuous energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers: a randomized trial in young overweight women – PubMed. (2011, May 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.171
Abstract 11123: Intermittent Fasting Lifestyle and Human Longevity in Cardiac Catheterization Populations:https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.140.suppl_1.11123
Effect of intermittent vs. daily calorie restriction on changes in weight and patient-reported outcomes in people with multiple sclerosis – PubMed. (2018, July 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2018.05.002
Influence of short-term repeated fasting on the longevity of female (NZB x NZW)F1 mice – PubMed. (2000, May 18). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0047-6374(00)00109-3
Intermittent Fasting Promotes Fat Loss With Lean Mass Retention, Increased Hypothalamic Norepinephrine Content, and Increased Neuropeptide Y Gene Expression in Diet-Induced Obese Male Mice – PubMed. (2016, February 1). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2015-1622
Cardiometabolic Benefits of Intermittent Fasting – PubMed. (2021, October 11). PubMed. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-052020-041327
Moro, T., Tinsley, G., Bianco, A., Marcolin, G., Pacelli, Q. F., Battaglia, G., Palma, A., Gentil, P., Neri, M., & Paoli, A. (2016, October 13). Effects of eight weeks of time-restricted feeding (16/8) on basal metabolism, maximal strength, body composition, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors in resistance-trained males – Journal of Translational Medicine. BioMed Central. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-1044-0
Johnson, J. B., Summer, W., Cutler, R. G., Martin, B., Hyun, D. H., Dixit, V. D., Pearson, M., Nassar, M., Maudsley, S., Carlson, O., John, S., Laub, D. R., & Mattson, M. P. (2006, December 14). Alternate Day Calorie Restriction Improves Clinical Findings and Reduces Markers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Overweight Adults with Moderate Asthma. PubMed Central (PMC). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.12.005
Three Leg Day Workouts for Women
A lot of guys, especially younger lifters, tend to skip leg day. Instead, they focus all their energy on training their pecs, lats, delts, and arms. This creates a very unbalanced physique, which is why many men are happy to be seen shirtless but keep their legs covered with long pants.
In contrast, many women are overly focused on training their lower bodies, especially their glutes. Some even train their legs every day, combining their lower body workouts with hours of leg-centric cardio.
So, why are so many women unhappy with the shape and condition of their legs?
In many cases, the reason is quantity over quality. In other words, some women’s leg workouts are high in volume and frequency but low in effective exercises. So instead of using a targeted approach, it’s more of a kitchen sink affair, with workouts containing so many exercises that many of them are actually redundant.
While such enthusiasm and dedication are to be applauded, there are better ways to use your training time and energy. These are valuable commodities that should be invested wisely and not wasted on unproductive or unnecessarily long workouts.
Get better results from your training time with these three tried and tested leg day workouts!
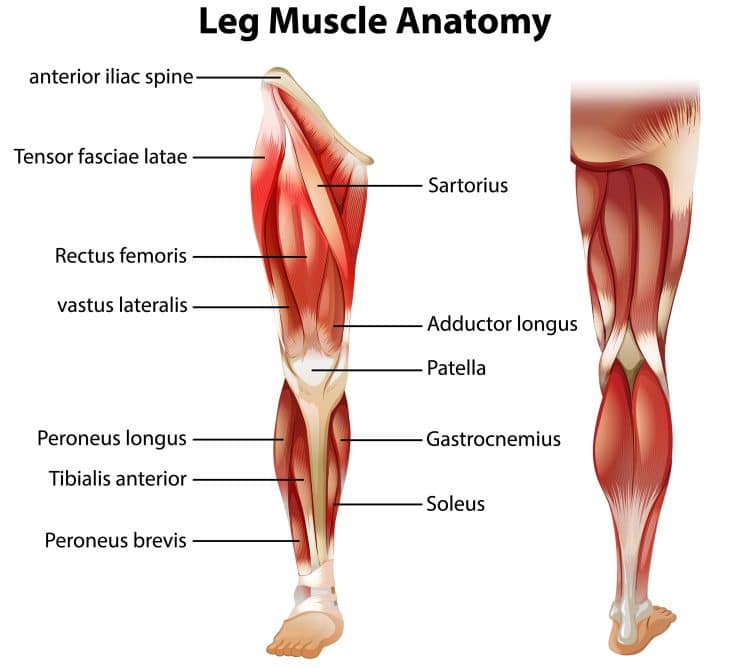
Leg Anatomy Basics
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of effective lower body training, let’s take a moment to look at the muscles you’ll be working. That way, you’ll be able to name the parts of your body you can feel during each workout.
The main muscles that make up your lower body are:
Gluteus maximus
Located on the back of your hips, the gluteus maximus (glutes for short) is the largest muscle in the human body and potentially the most powerful. The main role of the glutes is hip extension, but it’s also involved in external rotation and abduction of the hip.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings are a biaxial muscle that crosses the back of your knees and hips. As such, it has two main functions – knee flexion and hip extension. There are three hamstring muscles: biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus. You can develop the hamstrings by performing leg curls and hip hinging exercises.
Quadriceps
The quadriceps extend your knee and flex your hips. There are four quadriceps muscles: the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. Known as the quads for short, these muscles are located on the fronts of your thighs.
Hip abductors
The hip abductors are located on the sides of your hips and thighs. They are responsible for lifting your legs out and away from the midline of your body. The hip abductors are the gluteus maximus and medius and tensor fascia latae.
Hip adductors
Located on the inside of your thighs, the hip adductors are responsible for drawing your legs in toward the midline of your body. The three hip adductor muscles are longus, brevis, and magnus, meaning longest, shortest, and biggest.
Triceps surae
Triceps surae is the collective name for the muscles of your calves – the gastrocnemius and soleus. These muscles work together to point your foot in a movement called plantar flexion. In addition, gastrocnemius, the uppermost calf muscle, also works with the hamstrings to flex your knees.
Six Benefits of Leg Training for Women
Most women don’t have to be told to train their lower bodies. After all, sculpted, toned legs are a common training goal. That said, in case you are unsure about the benefits of leg training for women, here is a list of six reasons why you should work your lower body hard and often!
Increased functional strength
Almost all strenuous activities involve your legs. A stronger lower body will make these activities easier and less tiring. For example, walking upstairs, running, and lifting heavy items off the floor are less demanding when you’ve got strong legs.
More shapely legs
While lower body-centric cardio can help increase muscle tone and endurance, if you want your legs to look their best, you need to include direct leg training in your workouts. You can use strength training to target each muscle with laser-like precision, sculpting your legs to create the lower body of your dreams.
Stronger bones and healthier joints
Lower body strength training is not just good for your muscles but also for your bones and joints. Like your muscles, your bones get stronger with training. Load-bearing exercises trigger the release of bone-building cells called osteoblasts. Increasing bone strength and density can help ward off age-related bone loss (osteopenia) and may prevent osteoporosis.
Strength training is also good for your joints, namely the hips and knees. Lifting weights makes your joints more mobile and stable and can help prevent or reduce knee and hip pain.
Increased calorie and fat burning
Your lower body contains about 40% of your total body muscle – possibly more, depending on your build and genetics. Powering these muscles through a workout requires a lot of energy, which is measured in calories. Leg workouts use far more energy than most upper-body workouts. Training your legs can help increase your weekly caloric expenditure, leading to fat and weight loss.
Better balance and coordination
Balance is your ability to keep your center of mass over your base of support. In contrast, coordination is your ability to move your limbs in a controlled, harmonious way. Freeweight and bodyweight leg exercises enhance both of these fitness qualities. Better balance and coordination mean that you won’t just look more athletic but will feel it, too.
Improved posture
Long periods of sitting can cause havoc with your posture and leave you with weak legs. Poor glute muscle tone, for example, can affect your lower back, leading to pain and poor posture.
Leg training, especially when you do standing exercises, can improve your posture so you can sit and stand more upright. Good posture makes you look slimmer and younger and takes pressure off your muscles and joints.
Leg Day Workouts for Women
Here are your three leg day workouts for women. But, before doing any of them, you must prepare your joints and muscles for what you’re about to do by warming up. Start with 5-10 minutes of easy cardio, e.g., air bike, rower, jogging, or jumping rope, followed by dynamic mobility and flexibility exercises for your lower body.
A ten-minute warm-up can save you months of lost training caused by an otherwise avoidable injury, so don’t skip it.
Ready? Then let’s get to work!
Home Leg Day Workout for Women
No gym? No problem! You can get a GREAT leg workout almost anywhere. All you need is a little space and an exercise mat. Do this workout at home, in your hotel room, at the park – anywhere you want!
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Glute bridge
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
2
Plie squat
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Side leg raises
2-4
12-20 per leg
60-90 seconds
4
Alternating lunges
2-4
12-20 per leg
60-90 seconds
5
Standing calf raise
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
1. Glute bridge
Target muscles: Gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs bent and feet flat. Brace your core and press your lower back into the floor.
Drive your feet into the deck and lift your hips up so your body forms a straight line.
Pause for 1-2 seconds.
Lower your butt to the floor and repeat.
Make this exercise harder by using one leg at a time.
2. Plie squat
Target muscles: Adductors, quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about 1.5 shoulder-widths apart. Turn your toes outward. Brace your core and pull your shoulders down and back.
Bend your legs, push your knees outward, and descend until your thighs are roughly parallel to the floor.
Stand back up and repeat.
3. Side leg raises
Target muscles: Hip abductors.
Steps:
Lie on your side so your body is straight. Rest your head on your outstretched arm.
Lift your uppermost leg up to about 45 degrees. Turn your hip slightly inward to maximize glute and adductor engagement.
Lower your leg and repeat.
On completion, roll over and do the same number of reps on the other side.
Make this exercise more challenging by putting a booty band around your knees.
4. Alternating lunges
Target muscles: Quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together and your arms by your sides.
Take a large step forward, bend your legs, and lower your rearmost knee down to within an inch of the floor.
Push off your front leg and return to the starting position.
Do your next rep leading with the opposite leg.
Alternate legs for the duration of your set.
5. Standing calf raise
Target muscles: Calves
Steps:
Stand on the edge of a step, using your hands for balance.
Point your toes and rise up onto your tiptoes.
Lower your heels down and get a stretch in your calves.
Alternate between these two positions for the required number of reps.
Make this exercise harder by using one leg at a time.
Dumbbell Leg Workout for Women
Dumbbells are the perfect training tool for home exercisers, and gyms have them too. Use dumbbells to overload your muscles and build more strength. Choose weights that fatigue your muscles within the prescribed rep range.
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Dumbbell Romanian deadlift
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
2
Dumbbell goblet squat
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Dumbbell leg curl
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
4
Dumbbell lateral lunge
2-4
12-20 per leg
60-90 seconds
5
Dumbbell swing
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
6
Seated dumbbell calf raise
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
1. Dumbbell Romanian deadlift
Target muscles: Gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together and a dumbbell in each hand, arms by your sides. Bend your knees slightly, brace your core, and pull your shoulders down and back.
Hinging from your hips, lean forward and lower the weights down toward the floor. Do not round your lower back.
Stand back up and repeat.
2. Dumbbell goblet squat
Target muscles: Quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus.
Hold a dumbbell in front of your chest, just below your chin. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, core braced, and shoulders back and down.
Bend your knees and squat down until your thighs are roughly parallel to the floor. Take care not to round your lower back.
Stand back up and repeat.
3. Dumbbell leg curl
Target muscles: Hamstrings.
Steps:
Lie on an exercise bench so your knees are on the edge. Clamp and hold a dumbbell between your feet. Secure it using a yoga strap or resistance band if necessary.
Bend your legs and curl the weight up until your knees are bent to 90 degrees.
Extend your legs and repeat.
You can also do this exercise lying prone on the floor.
Dumbbell lateral lunge
Target muscles: Quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, abductors, adductors.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together and a dumbbell in each hand, arms by your sides. Brace your core and set your shoulders back and down.
Take a large step to your left, bend your left knee, and descend until your left thigh is close to parallel to the floor. Keep your right leg straight.
Push off your left leg and return to the starting position.
Repeat this movement to your right side.
Alternate sides for the specified number of reps.
5. Dumbbell swing
Target muscles: Gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Steps:
Hold a single dumbbell in both hands and stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Brace your core, pull your shoulders back and down, and bend your knees slightly.
Hinge forward from your hips and lower the weight down between your knees. Do not round your lower back.
Drive your hips forward and use this momentum to swing the weight forward and up to shoulder height.
Lower the weight and repeat.
6. Seated dumbbell calf raise
Target muscles: Calves
Steps:
Sit on an exercise bench or sturdy chair, so your knees are bent to 90 degrees and your shins are vertical. Rest the balls of your feet on a low step, e.g., a thick book, wooden block, or weight plates.
Rest and hold a dumbbell on each knee.
Extend your ankles and rise up onto your tiptoes.
Lower your heels down, get a stretch in your calves, and repeat.
Gym Leg Workout for Women
Access to a well-equipped gym means you’ve got everything you need to easily target your leg muscles. However, don’t get distracted and try to do every exercise you see. Instead, pick the best movements for each lower body muscle group. Remember – quality is always better than quantity!
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Smith machine donkey kick
2-4
12-20 per leg
60-90 seconds
2
Leg press
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Cable hip abduction
2-4
12-20 per leg
60-90 seconds
4
Cable hip adduction
2-4
12-20 per leg
60-90 seconds
5
Barbell hip thrust
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
6
Tiptoe farmer’s walk
2-4
40-60 seconds
60-90 seconds
1. Smith machine donkey kick
Target muscles: Gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Set the bar on a Smith machine to around waist height.
Kneel on the floor beneath the bar and place the sole of one foot against it.
Extend your hip and drive the bar upward, taking care not to hyperextend your lower back.
Lower the bar and repeat.
Do the same number of reps on both sides.
2. Leg press
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Sit on the leg press machine and place your feet on the footplate so they’re roughly shoulder-width apart. Release the weight catchers.
Bend your legs and lower the weight down until your knees are bent to at least 90 degrees. Do not round your lower back.
Extend your legs and repeat.
Reengage the weight catchers and then rest.
3. Cable hip abduction
Target muscles: Hip abductors.
Put an ankle strap around your lower leg and then attach it to a low pulley machine.
Stand sideways onto the machine, your working leg furthest from the weight stack. Hold the machine for balance.
Keeping your leg straight, raise your foot out and away from the midline of your body.
Lower your leg and repeat.
Do the same number of reps on both legs.
4. Cable hip adduction
Target muscles: Hip adductors.
Put an ankle cuff around your lower leg and then attach it to a low pulley machine.
Stand sideways onto the machine, your working leg closest to the weight stack. Hold the machine for balance.
Keeping your leg straight, cross your foot in front of you.
Return to the starting position and repeat.
Do the same number of reps on both legs.
5. Barbell hip thrust
Target muscles: Gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Sit on the floor with your upper back resting against a sturdy bench. Rest a barbell across your hips. Bend your legs and put your feet flat on the floor.
Drive your feet into the floor and lift your hips to form a straight line with your knees and shoulders.
Lower your butt back to the floor, and then repeat.
6. Tiptoe farmer’s walk
Target muscles: Calves.
Stand with a dumbbell in each hand and your feet together. Brace your core and pull your shoulders down and back.
Rise up onto your tiptoes and then start walking around your training area.
Continue for the designated distance or until you are unable to keep your heels off the floor.
Leg Day for Women – FAQs
Do you have a question about these workouts or leg training for women in general? No problem, because we’ve got the answers!
1. How often should I train my legs?
It’s generally accepted that it takes 48-72 hours for a muscle to recover from training. This means you can work your legs every 2-3 days or 2-3 times per week. More workouts could lead to overtraining, while just one workout per week may not produce the results you want.
So, hit your legs 2-3 times per week, e.g., Monday and Thursday or Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. This will create a good balance between work and rest.
2. Can I change the exercises in these workouts?
While you are free to make changes to these programs, avoid using exercises that are too different. For example, while doing machine leg curls instead of dumbbell leg curls is fine, doing leg extensions instead of leg curls is not, as the replacement movement uses an entirely different muscle group.
So, make changes if you wish, but make sure you switch “like for like” and don’t use completely different movements. However, avoid changing the exercise order, as doing so can unbalance your entire workout.
3. Do I have to stick to the 12-20 rep range?
Unless you are training for pure strength, it really doesn’t matter all that much how many reps you do per set. Studies suggest that you can perform 5 to 35 reps per set and still make progress (1). Almost any rep count will work if you take your set close to momentary muscular failure.
However, if you want to build strength, you need to use heavy weights and do lower reps, typically 1-5. However, this is a very specialist type of training and not something many women (or men) need to do.
So, if you want to do eight, ten, twenty, or thirty reps per set, you are free to do so.
4. How do I make my thighs thinner?
Reducing the circumference of your thighs is usually more about your diet than your workout program. Invariably, big thighs are the result of excess fat storage rather than muscle mass. So if your thighs are bigger than you want and you’re not a weightlifter or bodybuilder, you probably need to adjust your diet and shed the excess fat.
However, it’s worth noting that no amount of dieting guarantees you’ll develop a “thigh gap” or achieve any other Instagram body standard, as your shape is primarily determined by your genetics.
So, don’t compare how you look to anyone else; just be the best you can be.
5. What is the best diet to use with these workouts?
Healthy eating and regular exercise go hand in hand – or they should! Eating right will make your workouts more productive, while an unhealthy diet could undermine your progress. However, there is no single perfect diet that’s right for everyone, and what you eat will depend on your fitness goals, likes and dislikes, cooking skills, and grocery budget.
So, rather than follow a cookie-cutter diet, why not take a shot at creating your own healthy eating plan? It’s actually easier than you think!
Check out this guide to overhauling your diet in six weeks. It could be the last diet you ever need.
Closing Thoughts
Friends don’t let friends skip leg day, or so the popular meme goes. That’s true for men AND women. Leg workouts offer a lot of benefits, including increased functional strength, better endurance, greater bone density, and enhanced fat burning.
In fact, leg training is so good for you it’s hard to think of many reasons not to do it.
Sure, leg training is demanding and can leave you tired and sore. But you’ll soon learn to love it when you see and feel how good it is for you.
So, give one of these leg day workouts for women a try. You’ll soon be on the way to leaner, shapelier, stronger legs.
References:
1 – Lasevicius T, Ugrinowitsch C, Schoenfeld BJ, Roschel H, Tavares LD, De Souza EO, Laurentino G, Tricoli V. Effects of different intensities of resistance training with equated volume load on muscle strength and hypertrophy. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018 Jul;18(6):772-780. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1450898. Epub 2018 Mar 22. PMID: 29564973. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29564973/

Workout Split For Women: The Ultimate Guide To Get Fit and Fabulous
Over the last decade, women have been cozying up to weight training. However, this has led us into a unique situation; the ladies look like deers caught in headlights as soon as they enter the weight room.
Although girls no longer need to be convinced to start lifting weights, only a handful of these women follow a structured workout split. Performing a few dumbbell curls one day, a couple of sets of squats the next day, and a little of everything every other day isn’t going to do you any good.
Finding the right workout split can be daunting. Furthermore, stepping inside the free-weight section of a gym for a newbie can be overwhelming, especially if they have no idea what they are doing.
A balanced training program is key to achieving your dream figure. Furthermore, the ideal workout regimen for an individual can change depending on their preferences, schedules, goals, and experience levels. Following an incompatible training split increases your risk of injury.
In this article, we dive into the meaning of workout splits, the factors and tips to consider while choosing a workout split for women, its benefits, and the five best workout splits for women at different experience levels. We have a lot to cover. So, sit tight.
What are Workout Splits?
A workout split refers to how you divide your training into different muscle groups or body parts. Many exercisers avoid picking a workout split as they find it too restrictive. Although a workout split requires you to train a specific muscle group on a particular day of the week, you are free to choose the exercises you perform in each training session.
Notably, programming a workout is best left to advanced lifters or personal trainers. Each muscle consists of different heads that must be trained from multiple angles for optimal growth. Performing similar movements can lead you to a muscle and strength plateau. For example, the deltoid muscle has three heads — anterior, lateral, and posterior. If you only perform shoulder press and front raise exercises in your training regimen, you’ll have substandard lateral and posterior deltoid head development. Does this sound like too much work? Don’t worry; we have included a sample workout plan for overall muscle and strength development with each workout split.
Many people think the ‘bro split’ is the only workout program. A bro split includes training chest on Mondays, back on Tuesdays, shoulders on Wednesdays, and so on. While there is nothing wrong with this split, most exercisers can get better results by following a more focused workout split.
For example, ladies with lagging lower bodies would want to train their legs twice a week. However, the bro split has no provisions for accommodating a second leg workout. An upper and lower body workout split will be a better fit in this case.
Benefits of Following a Structured Workout Split For Women
Here are the advantages of selecting a structured workout split for women:
Makes Your Workouts More Efficient
Many lifters treat the gym as a restaurant, and their training split as an à la carte menu. They enter the iron paradise without a plan and tackle their workout on the fly; these lifters perform the exercises that feel the most comfortable and put the least strain on their muscles. As you could have guessed, these folks see little to no progress and are most likely to drop off.
A structured workout split leaves nothing to chance. Here, you plan your workouts weeks in advance. Everything from the exercises, sets, and reps is determined before entering the gym. Having an action plan ensures you make the most of your time in the gym.
Built-in Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is indispensable if you want to make strength or muscle gains. It includes placing ever-increasing stress on your muscles by increasing the intensity and volume of your workouts. You could achieve this by doing more sets, reps, and exercises, reducing rest between sets, or incorporating advanced training principles in your workouts, such as super sets, drop sets, intra-set stretching, etc. [1]
A balanced workout split will help progressively overload your muscles and reduce your risk of hitting a plateau by shocking your muscles with varying training intensity and volume. Furthermore, an efficient workout split also allows your muscles to rest and recuperate between workouts, reducing your risk of injury.
Fix Muscle and Strength Imbalances
An effective workout split can aid in fixing muscle and strength imbalances by allowing you to work on your weaknesses multiple times a week. At the same time, it will help you polish your strengths.
Monitor Progress
You must stick to a workout split for at least 12 weeks before arriving at conclusions about its effectiveness. Since you’ll perform the same exercises, number of sets, and reps in each workout for the entire duration, it’ll make it convenient for you to track your progress.
Additionally, following a workout split and tracking your progress will help you stay accountable. Sharing your progress with your friends and family can be a potent motivator.
Keeps You Interested
Choosing a workout program is like choosing a life partner — you want someone who compliments your strengths and weaknesses.
Although the workout splits below define the exercises you’ll perform in each training session, you are free to perform their variations instead. You must, however, ensure that the replacement exercises target the same muscle groups. For example, you could do the cable side lateral raise instead of the dumbbell side lateral raise. You must, however, not replace side lateral raises with shrugs.
Knowing the exercises you’ll perform in a workout in advance can allow you time to prepare for a workout, which can improve your performance. Plus, tracking your progress will keep you hooked to your workout split.
5 Best Workout Splits For Women
Depending on your current physique and experience level, you can choose a workout split that aligns with your goals. Each workout split has its unique benefits and allows you to focus on particular muscles to fix imbalances and take you to your objectives.
Below, you’ll find five workout splits for women that involve training up to three muscle groups per training session twice a week.
Full-Body Workout Split For Women
The basic full-body workout split for women is a two-day-a-week training regimen. It is perfect for beginners and ladies with busy schedules who can only make time for a couple of weekly training sessions.
In the full-body training split, you could work all your muscle groups in a single workout or divide them into two sessions.
Since this workout split involves training most of your muscle groups in a single workout, you must follow a HIIT (high-intensity interval training) method for these workouts to get a lot of work done in a short period. Women aiming to shed weight must engage in full-body cardio exercises.
Day 1
Full-Body Workout
Day 2
Rest
Day 3
Rest
Day 4
Full-Body Workout
Day 5
Rest
Day 6
Rest
Day 7
Rest
As you gain more experience, you could go from performing two weekly full-body training sessions to doing four weekly workouts. Perform variations of the exercises listed in the sample workout below on the two additional days to add variety to your training regimen.
Full-Body Workout 1:
Beginners must seek expert help to drill the movements. It will help you make the most of the exercises while limiting your risk of injury.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Barbell Bench Press
3
8-12
Barbell Bent-Over Row
3
8-12
Dumbbell Shoulder Press
3
8-12
Barbell Biceps Curl
3
8-12
Cable Triceps Extension
3
8-12
Barbell Squat
3
8-12
Crunch
3
8-12
Full-Body Workout 2:
Since these workouts are programmed to induce hypertrophy, avoid resting for more than 60 seconds between sets, as it can significantly hamper your training intensity.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Dumbbell Chest Fly
3
8-12
Dumbbell Deadlift
3
8-12
Barbell Skull Crusher
3
8-12
Dumbbell Side Lateral Raise
3
8-12
Dumbbell Hammer Curl
3
8-12
Barbell Sumo Squat
3
8-12
Hanging Leg Raise
3
8-12
Full-Body HIIT Cardio Workout
The HIIT cardio workout below includes nine exercises; perform two rounds of this circuit. You must perform each exercise for 45 seconds. Rest 15 seconds between exercises. Plus, you are allowed a two-minute rest after completing a round.
Exercise
Time (in seconds)
Rest (in seconds)
Lunge
45
15
Push-Up
45
15
Burpee
45
15
Star Jump
45
15
Leg Raise
45
15
Squat Jump
45
15
Bicep Curl
45
15
Lateral Shuffles
45
120
Use appropriate dumbbells for exercises like bicep curls and lunges. Feel free to use additional resistance in the squat jump. However, you must ensure you are not compromising your form to lift heavy weights.
Benefits of Full-Body Workout Splits
Here are the advantages of doing a full-body workout split for women:
The full-body workout split is excellent for beginners as it helps them acclimatize to weight training.
This workout regimen is great for ladies on a tight schedule, as the most basic version of the full-body split requires hitting the gym twice a week.
Since you’ll do only one exercise per muscle group, we’ll mostly stick to compound lifts for this workout program. Besides helping you build muscle and strength, multi-joint exercises improve your overall functionality.
Training twice weekly gives your body enough time to rest and recuperate between workouts.
Drawbacks of Full-Body Workout Splits
Here are the cons of doing a full-body workout split for women:
As you’ll be training all your muscles in a single workout, it can be incredibly exhausting, especially as you graduate to training four days a week.
Full-body strength training workouts can take longer to complete. Expect to spend 60-120 minutes in the gym.
The full-body workout split is not the best for fixing strength and muscle imbalances unless you want to boost your training volume significantly.
Upper Lower Body Workout Split For Women
The upper lower body is the perfect next step for ladies wanting to move up from a two-day training regimen. It is a four-day workout split that involves training half of your body on a single day.
Notably, you should ideally start the training week by training your weaker half. Lifters with lagging lower bodies should start the week with a leg workout instead of hitting an upper body training session.
Many lifters go all-out on their stronger muscle group training day, leaving them tired and sore for their weaker muscle group workouts. Since this is a four days a week workout split, you can also rest after each workout to allow your muscles enough time to rest and recuperate between training sessions.
Day 1
Upper Body
Day 2
Lower Body
Day 3
Rest
Day 4
Upper Body
Day 5
Lower Body
Day 6
Rest
Day 7
Rest
As this workout regimen involves training all your muscles twice a week, you shouldn’t add more training days to this training split. Instead, you could increase your training volume and intensity to get the best bang for your buck.
A study found that an upper and lower body workout split is more effective at helping you build muscle strength and size over 10 weeks than a full body workout regimen done thrice a week. [2]
Upper Body Workout:
The upper and lower body workouts primarily consist of functional (multi-joint) exercises to maximize your muscle and strength-building potential. Focus on contracting your muscles with each rep to induce hypertrophy.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Barbell Bench Press
3
8-12
Dumbbell Bent-Over Row
3
8-12
Arnold Press
3
8-12
Barbell Biceps Curl
3
8-12
Close-Grip Bench Press
3
8-12
Russian Twist
3
8-12
Lower Body Workout:
You could change the order of the exercises depending on your preferences. If you have lagging calves, we recommend starting your leg workout with the standing calf raise. Use a weight that helps you achieve muscle failure between the eighth and 12th rep.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Barbell Squat
3
8-12
Walking Lunge
3
8-12
Romanian Deadlift
3
8-12
Goblet Squat
3
8-12
Leg Curl
3
8-12
Standing Calf Raise
3
8-12
Benefits of Upper Lower Body Workout Splits
The pros of the upper-lower body workout split include the following:
It allows you to train all your muscle groups twice a week.
Training your upper and lower body muscles separately can help you fix muscle and strength imbalances, improving your overall physique proportions and symmetry.
The upper-lower body workout split will help you build a solid foundation. You could easily pivot to a powerlifting or bodybuilding-focused workout program after following this workout split for 12 weeks.
This workout split for women allows sufficient recovery time between workouts, which can fast-track results and reduce your risk of injury.
Training four days a week allows you the flexibility to program your workouts according to your schedule. You could take an off day after each workout or reshuffle the training days.
Drawbacks of Upper Lower Body Workout Splits
The cons of the upper-lower body workout split include the following:
The upper-lower body workout split is volume heavy since you’ll be training all your muscles twice weekly, which is not the best for newbie lifters.
On the other hand, although you’ll be training all your muscles twice a week, the training volume for each muscle group can be limiting.
Since you’ll be training half of your body in a single workout, these workouts can take a lot of time to complete. Expect to spend 60-120 minutes in the gym during your upper-lower body workouts.
Push-Pull Workout Split For Women
The push-pull workout split for women is the perfect middle ground between full-body workouts and upper-lower body workouts. Gym exercises can be broken into two main categories — push and pull.
As the name suggests, the pushing exercises involve pressing weights away from your body, for example, the bench press, overhead triceps extension, and leg extension. On the flip side, the pulling exercises include pulling the weights toward your body, such as the deadlift, biceps curl, and seated cable row.
Push-pull workouts are popular among bodybuilders and powerlifters as they help focus on a single movement pattern. This workout split can help you achieve muscle-ripping pumps and ensure you’ve got nothing left in the tank by the end of a workout.
Day 1
Push
Day 2
Pull
Day 3
Rest
Day 4
Push
Day 5
Pull
Day 6
Rest
Day 7
Rest
Although the push-pull workout split is a four-day training program, you could increase your training volume by adding a couple of workout sessions to the split — one for each movement pattern. Also, you could increase your training volume gradually by alternating between an additional push and pull workout for the initial 4-6 weeks.
Push Workout
In the push-pull workouts, the first two exercises of the training schedule are the big lifts. The remaining four to six exercises are considered accessory lifts, which help improve your performance in the main lifts.
The ladies training for hypertrophy should stay in the 8-12 rep range and perform three sets with a moderate weight. On the other hand, lifters trying to maximize strength should do 3-5 sets of 1-5 reps with 80-90% of their one-rep max. [3]
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Squat
3
8-12
Bench Press
3
8-12
Cable Triceps Extension
3
8-12
Dumbbell Chest Fly
3
8-12
Machine Shoulder Press
3
8-12
Seated Calf Raise
3
8-12
Keep the main lifts, such as the squat, bench press, and deadlift, constant throughout the 12 weeks. However, you could change the accessory lifts each week to keep your workouts interesting.
Pull Workout
The deadlift is the main lift in the pull workout. All the other movements in this workout are accessory lifts. We recommend using weightlifting accessories, such as a weightlifting belt, lifting straps, wrist wraps, and knee sleeves, in these workout splits, as they help maximize your performance and reduce your risk of injury.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Deadlift
3
8-12
Wide-Grip Lat Pulldown
3
8-12
Barbell Biceps Curl
3
8-12
Lying Leg Curl
3
8-12
Dumbbell Romanian Deadlift
3
8-12
Dumbbell Side Lateral Raise
3
8-12
Benefits of Push-Pull Workout Splits
Using the push-pull workout split entails the following benefits:
The push-pull workout split for women is great for building strength and muscle mass. Change the number of reps on the three big lifts (squat, bench press, and deadlift) to 1-5 and the number of sets to five to focus on building strength.
Training a specific movement pattern can help you achieve a better mind-muscle connection, improving hypertrophy.
Since this workout split involves training the same muscle group at least twice, the high volume will speed up your results.
This training split is great for powerlifters that want to improve their performance on the big three lifts.
It allows you to further boost your training volume by doing up to two more weekly workouts.
The push-pull workouts involve a healthy balance of compound and isolation exercises, which can help develop a balanced, proportionate, and conditioned physique.
The four-day push-pull training split allows you ample time to recover between workouts.
Drawbacks of Push-Pull Workout Splits
Using the push-pull workout split entails the following disadvantages:
Since this workout split involves compound and isolation exercises and requires training multiple muscle groups, the push-pull workouts can take longer to complete than the conventional workouts.
The push-pull split is not ideal for beginners.
This training split can be exhausting, as the push workouts include high-demanding exercises, such as the bench press, squat, and overhead shoulder press in the same workout.
Push, Pull, Legs Workout Split For Women
This training split takes the push-pull workout program up a notch. Although the push-pull routine was originally designed for powerlifters, many lifters didn’t appreciate training for the bench press and squat on the same day; hence, the push, pull, and leg workout split was born.
The push, pull, and leg split is a six-day workout program. It increases the training volume of the basic push-pull regimen by a massive 50%. This training split is best suited for advanced female lifters, as the trainers will only get one day to recover from their workouts.
Although you could do the push, pull, and leg split three days a week, you would have to increase the volume and intensity significantly, which will not only make the workouts more exhausting but would also considerably increase your risk of injury.
Day 1
Push
Day 2
Pull
Day 3
Legs
Day 4
Push
Day 5
Pull
Day 6
Legs
Day 7
Rest
Since you have two training sessions in this workout split for each muscle group, you don’t have to do the three big lifts in each workout. Do them at the beginning of the training week and resort to accessory movements for the remaining three workout sessions.
Pay close attention to the number of sets and reps in the workouts below.
Push Workout 1
The first exercises of the first three training days of the week will be strength-focused, meaning you’ll be doing one to five reps of the exercises for three to five sets using 80-90% of your one-rep max. You must only perform these big lifts with a spotter.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Bench Press
3-5
1-5
Incline Dumbbell Press
3
8-12
Cable Crossover
3
8-12
Behind-the-Neck Shoulder Press
3
8-12
Weighted Dips
3
8-12
Lying Leg Raise
3
8-12
Rest for three to five minutes for the strength-focused exercises. You must, however, limit the rest between sets to 60 seconds for the remaining lifts to ensure optimal training intensity for inducing hypertrophy.
Pull Workout 1
You are allowed a five-minute rest after the strength-focused exercise to reset and prepare for the high-rep workout. Track your workouts (sets, reps, and weights) in a journal to ensure you’re hitting your goals and are progressively overloading your muscles in each training session.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Deadlift
3-5
1-5
Dumbbell Curl
3
8-12
Lat Pulldown
3
8-12
Bent-Over Barbell Row
3
8-12
Dumbbell Side Lateral Raise
3
8-12
Upright Row
3
8-12
Leg Workout 1
You could rejig the exercises in this workout if you prefer doing quad-focused accessory lifts before the hamstring-focused movements.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Squat
3-5
1-5
Leg Extension
3
8-12
Leg Curl
3
8-12
Romanian Deadlift
3
8-12
Leg Press
3
8-12
Leg Press Calf Raise
3
8-12
Push Workout 2
Use advanced training principles, such as super sets, drop sets, and intra-set stretching in the second half of the push, pull, and leg training split to push up your training intensity. You must use a weight that allows you to perform each exercise with a picture-perfect form.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Dumbbell Bench Press
3
8-12
Decline Barbell Press
3
8-12
Pec Deck Fly
3
8-12
Arnold Press
3
8-12
Barbell Skull Crusher
3
8-12
Cable Crunch
3
8-12
Pull Workout 2
We encourage using different hand grips on these exercises each week (supinated, pronated, and neutral) to train your muscles from different angles. It will help induce hypertrophy and keep your workouts interesting.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Dumbbell Deficit Deadlift
3
8-12
Cable Biceps Curl
3
8-12
Seated Cable Row
3
8-12
Inverted Row
3
8-12
Dumbbell Front Raise
3
8-12
Barbell Shrug
3
8-12
Leg Workout 2
Feel free to swap the accessory exercises in the second workouts for the week to address any lagging muscle groups.
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Box Squat
3
8-12
Walking Lunge
3
8-12
Leg Curl
3
8-12
Stiff-Legged Deadlift
3
8-12
Hip Thrust
3
8-12
Standing Calf Raise
3
8-12
Benefits of Push-Pull-Legs Workout Splits
Performing the push-pull-legs training split has the following pros:
It is one of the best workout splits for powerlifting enthusiasts. Furthermore, bodybuilders can use this 12-week program to improve their overall strength without compromising on their muscle mass.
This six-day training split allows you to focus on each muscle group twice a week.
A high-volume and intensity training regimen that is incredibly effective for breaking through plateaus.
The push-pull-legs training split can accommodate many modifications to suit the lifter.
Drawbacks of Push-Pull-Legs Workout Splits
Performing the push-pull-legs training split has the following cons:
A six-day training regimen that is best left to advanced lifters.
Not enough recovery time, especially for lifters pushing their limits on this training regimen.
The push-pull-legs workout split can take longer to complete than all the other training splits listed in this article.
Bro-Split Workout Split For Women
We know what you are thinking. Yes, we were kind of dissing the bro-split at the beginning of this article. However, if your goal is to build muscle mass, you cannot go wrong with this training split.
The standard bro-split is a six-day training program that includes training each muscle group once weekly. It allows you to train each muscle with ample volume and intensity to induce hypertrophy.
You could modify the workout split depending on your personal goals and preferences. For example, ladies with weaker lower bodies should begin their training week with a leg workout instead of a chest session. Restructure your workouts according to your needs.
Day 1
Chest
Day 2
Back
Day 3
Shoulders
Day 4
Biceps
Day 5
Triceps
Day 6
Legs
Day 7
Rest
Avoid training two large muscle groups on consecutive days, such as legs and back. Have at least 48 hours between large muscle group workouts to ensure optimal rest and recovery. It also reduces your risk of injury.
Chest Workout
Many lifters leave gains on the table by following a restricted range of motion. It limits your muscle fiber engagement and leads to suboptimal gains. Use a weight that allows you to follow a full ROM.
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Barbell Bench Press
3
8-12
Incline Dumbbell Press
3
8-12
Decline Dumbbell Fly
3
8-12
Dips
3
8-12
Cable Crossover
3
8-12
Decline Crunch
3
8-12
Back Workout
During your back workouts, focus on driving through your elbows. Pulling the weight using your biceps can remove tension from your back and put it on your guns. Use a false (thumbless) grip where possible to limit biceps engagement. You could also experiment with using lifting straps to limit forearm stimulation.
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Deadlift
3
8-12
Bent-Over Barbell Row
3
8-12
Lat Pulldown
3
8-12
Seated Cable Row
3
8-12
Hyperextension
3
8-12
Seated Calf Raise
5
8-12
Shoulders Workout
You must include exercises for all three shoulder heads (anterior, lateral, and posterior) and the trapezius muscle to ensure overall growth.
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Military Press
3
8-12
Dumbbell Side Lateral Raise
3
8-12
Barbell Front Raise
3
8-12
Bent-Over Rear Delt Fly
3
8-12
Barbell Shrug
3
8-12
Cable Crunch
3
8-12
Biceps Workout
You’ll use pronated, supinated, and neutral grips in the biceps workout to ensure optimal biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis development. The forearm exercises at the end of the workout ensure you don’t leave any stone unturned.
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Barbell Biceps Curl
3
8-12
Alternating Hammer Curl
3
8-12
Cable Reverse Curl
3
8-12
Machine Preacher Curl
3
8-12
Concentration Curl
3
8-12
Wrist Curl
3
8-12
Reverse Wrist Curl
3
8-12
Triceps Workout
The triceps workout in the bro-split targets all three triceps heads (long, lateral, and medial) for building horseshoe triceps.
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Cable Triceps Pushdown
3
8-12
Dumbbell Overhead Extension
3
8-12
Dumbbell Kickback
3
8-12
EZ Bar Skull Crusher
3
8-12
Reverse-Grip Triceps Pushdown
3
8-12
Cable Wood Chopper
3
8-12
Legs Workout
Since this training session involves performing the squat and deadlift, you’ll have to go extra hard on this one. Ensure your pre-training nutrition is on point to make the most of these workouts.
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Barbell Squat
3
8-12
Leg Extension
3
8-12
Leg Curl
3
8-12
Barbell Walking Lunge
3
8-12
Romanian Deadlift
3
8-12
Standing Calf Raise
5
8-12
Benefits of a Bro-Split Workout Regimen
Sticking to the bro-split allows you to:
This workout split for women allows you to focus on a single muscle group in a training session, which can help boost your strength and muscle mass gains.
The bro-split is highly customizable and allows you to modify it according to your needs.
Since this workout focuses on a single muscle, it requires lesser time to complete than the multiple muscle group training sessions.
This is a versatile training split that can be used by beginners and advanced athletes alike.
Drawbacks of a Bro-Split Workout Regimen
The bro-split regimen has the following cons:
Since you’ll be training six days a week, it gives your muscles limited time to recover.
Folks with a busy schedule might have difficulty sticking to the six days a week training split.
Factors To Consider While Choosing a Workout Split For Women
You must consider the following factors before choosing a workout split:
Experience Levels
You must always choose a training split that is fitting for your experience level. For example, beginners should stay away from the push, pull, and leg training split and instead favor the full-body training regimen.
Further; you must adjust your training intensity and volume based on your experience. Choosing a training split based on your experience level helps streamline your progress and reduces your risk of injury in the gym.
Goals
Setting a goal before starting a training program gives you a road map. Lifters that want to build strength should opt for the push, pull, and legs training split, ladies that want to build a chiseled figure should go for the bro-split, and the women that want to hit the gym for overall fitness should stick to the full-body workouts.
Time
You should choose a training program that will fit into your lifestyle. Choosing a workout split that necessitates you to go to the gym six times a week, but you can only fit in four workouts per week is a recipe for failure. You will likely lose motivation and drop out before achieving your fitness goals.
Focus Muscle Groups
Many exercisers join a gym to improve a particular muscle group. Some ladies want a bigger booty, whereas others might want shapely arms. If you want bigger muscles, you’ll be better off choosing a training split that allows you to focus on a particular muscle group, like the bro split.
Other training splits that involve training a muscle group twice weekly, such as the push-pull regimen, can also come in handy for fixing muscle and strength imbalances.
Tips For Workout Split For Women
The following tips will help you maximize your results:
Be Open to Trial and Error
Even after you spend days reviewing the pros and cons of a workout split, the program you choose might not work for you — which is perfectly fine. Choosing the right workout split requires trial and error. Give your training split 12 weeks to work its magic. If you’re unhappy with your results, move on to something different. Ensure that you implement the learning from the previous workout split into the new one.
Nutrition and Recovery
Whether you want to build strength or carve a Greek goddess-like figure, you must back up your workout regimen with a balanced and proven nutrition and recovery program. Follow a macronutrient-focused diet to ensure you are meeting your daily protein, carbs, and fat goals. Ladies trying to gain muscle should stay in a calorie surplus, whereas those trying to shed the spare tire should be in a calorie deficit.
Plus, you must ensure you are giving your muscles enough time to rest and recuperate from your workouts. Sleep seven to eight hours each night to ensure you are properly rested for your upcoming workouts. We recommend using sports nutrition supplements to speed up your recovery process between workouts. Alternatively, you could lower your training frequency if you experience chronic muscular fatigue or soreness.
Seek Guidance
Starting a workout split can be intimidating, especially for beginners. Plus, performing the exercises with an incorrect form can increase your risk of injury. Hiring a personal trainer can help shorten your learning curve and fast-track your progress.
Stay Consistent
Consistency is key in any training program. You must stick to a suitable workout split for at least 12 weeks to achieve your desired results. Avoid skipping training sessions unless absolutely necessary.
Warm Up and Cool Down
Spend 5-10 minutes performing a mix of dynamic and static stretching exercises before each training session. It helps improves your flexibility and mobility and reduces your risk of injury. Furthermore, spend 5-10 minutes cooling down after a workout to kickstart your recovery process.
More Workout Splits:
FAQs
What is the ideal workout split for women?The ideal workout split will depend on your training goal, experience, time availability, and if you have any muscle groups that you want to focus on. With that said, beginner trainers will be better off starting with a full-body workout regimen; intermediate lifters can try the push-pull workout split, and advanced lifters should go for the push, pull, and legs regimen.
Can you alter a workout split?You could switch the exercises in the workout splits mentioned above to better suit your training needs. However, we advise against tinkering with the foundations of a workout split. For example, you should not combine the push and pulls workouts in the push, pull, and leg routine.
Which workout split for women is best for weight loss?Ladies trying to shed excess body fat should opt for the full-body HIIT workout listed in this article. HIIT workouts force your body to use energy from fat instead of carbs, making losing fat more efficient.
Wrapping Up
Congratulations, ladies! You are now equipped with everything you need to know to pick the most effective workout split for yourself and begin your journey to get fit and fabulous. We have also included a sample workout with each workout split, making starting your workout regimen as frictionless as possible.
Nonetheless, fine-tuning a training split to fit your needs might require some trial and error. Stay patient and consistent; work hard, and the results will follow. Best of luck!
References
Yue FL, Karsten B, Larumbe-Zabala E, Seijo M, Naclerio F. Comparison of 2 weekly-equalized volume resistance-training routines using different frequencies on body composition and performance in trained males. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018 May;43(5):475-481. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2017-0575. Epub 2017 Dec 7. PMID: 29216446.
Lasevicius T, Schoenfeld BJ, Grgic J, Laurentino G, Tavares LD, Tricoli V. Similar Muscular Adaptations in Resistance Training Performed Two Versus Three Days Per Week. J Hum Kinet. 2019 Aug 21;68:135-143. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2019-0062. PMID: 31531139; PMCID: PMC6724585.
Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.
5 Back Workouts for Women: Bring the SexyBack!
Most women want an hourglass figure. However, some girls mistake an hourglass figure for a tennis racket figure. These ladies spend considerable time working on their booties but almost always overlook a vital aspect of achieving their dream figure — a shapely back. Ladies that want to rock a strapless dress or tank top must prioritize training their backs. Plus, a shapely back can add to your physique aesthetics by making your waist look smaller.
To build a curvy figure, you must incorporate back workouts into your training regimen. Your back workouts should have a balance of rowing exercises, such as barbell rows, dumbbell rows, seated cable rows, and horizontal pulling movements, such as lat pulldowns, pull-ups, etc.
After your legs, your back is the second-biggest muscle group, meaning your back workouts will be as brutal as your lower body training sessions. Plus, since it is a large muscle group, it will help burn more calories than the small muscle group workouts. If you feel fresh and energetic after a back workout, know that you didn’t go all-out in that training session.
Unlike smaller muscle groups like the biceps, which have only two muscle heads, your back consists of several muscles, such as the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, teres major and minor, trapezius, posterior delts, and erector spinae. Furthermore, your back is divided into two portions — upper and lower. You must train your back from different angles, using different grips for overall posterior chain development.
In this article, we go over the back anatomy, the five best back workouts for women, the importance and benefits of building a strong back for women, and tips to make the most of your workouts.
Back Anatomy
Understanding your back anatomy can help you program an effective back workout and ensure there are no weak areas in your back. Here are the back muscles you should know about for building an eye-catching backline:
Back Anatomy Muscles
Latissimus Dorsi
Latissimus dorsi, or lats, are the biggest back muscle. A pair of developed lats can accentuate your V-taper. They are located on both sides of the middle and lower back and are responsible for moving your arms down and toward the body.
Teres Major and Minor
These are present at the back of the shoulder and are responsible for rotating the arm and stabilizing the shoulder joint.
Rhomboids
They are located on your upper back underneath the trapezius muscle and between the shoulder blades. They help maintain a good posture and stabilize your shoulder blades.
Erector Spinae
These are a group of muscles present on both sides of the spinal column. As their name suggests, they help maintain an erect spine and allow for bending and twisting movements. The erector spinae is also referred to as the lower back.
Posterior Deltoids
Although the posterior or rear delts are located on your back, they are mostly trained in a shoulder workout. They help move your arm backward.
Trapezius
The trapezius muscle is located over the back of the neck and shoulders and extends down to the middle of the back. It helps moves the head and shoulder blades. Many people train their traps in a shoulder workout.
Best Back Workouts For Women
Our goal with these workouts is to build a toned back that looks amazing and improves your overall health and fitness. We have included five workouts in this article for ladies at different experience levels. The resistance band back workout is perfect for when you don’t have access to a gym.
Beginner Back Workout For Women
Women that are just starting their fitness journey should perform foundational exercises that will help them build a solid base and improve their mind-muscle connection. Your focus with this workout will be to drill each movement until you know them, like the back of your hand.
Seek expert advice to learn the correct technique for performing these exercises. Hiring a personal trainer can expedite your learning process, lower your risk of injury, and fast-track your progress.
Advanced Back Workout For Women
Ladies with at least a few months of lifting experience should graduate to the advanced back workout. Use an assisted pull-up machine or a spotter if you cannot perform bodyweight pull-ups.
You’ll also be doing rear delt flyes for the rear delts and barbell shrugs for the trapezius muscle in this workout. Expect this workout to take between 45-60 minutes. However, keep your rest durations between sets limited to 30-60 seconds to maintain a high training intensity.
Machine-Only Back Workout For Women
Machines follow a fixed movement trajectory, which can help you focus on establishing a mind-muscle connection and achieve muscle-ripping pumps. Plus, machine workouts take less time than free-weight workouts, which is a boon for lifters on a tight schedule.
You can swap the GHD back extension with a conventional back extension if you lack the posterior chain strength to perform the exercise. Focus on contracting your muscles with each rep to get the most out of this workout.
Resistance Band Back Workout For Women
The resistance band back workout is an excellent place to start for beginners and when you are traveling. Contrary to what most people think, you don’t always need free weights or machines to build a chiseled physique. Resistance bands help maintain constant tension on your muscles throughout the motion, helping induce hypertrophy.
We recommend using loop bands for this workout; grab the heaviest bands you can find. Furthermore, you’ll be performing a higher number of reps in this workout than in the other workouts to ensure you’re not leaving anything in the tank.
HIIT Back Workout For Women
HIIT, or high-intensity interval training, workouts consist of short periods of high-intensity exercises followed by periods of rest or lower-intensity exercises. A HIIT workout aims to push your body to its maximum capacity in a short period. It is a great training protocol for breaking through strength and muscle plateaus. Furthermore, it is perfect for folks that can only dedicate 30 minutes to a training regimen.
You’ll perform five rounds of this HIIT workout. Do each exercise for 30 seconds and rest for 10 seconds after completing a movement. You are allowed a 60-second rest after completing each round.
Read more: HIIT Workouts for Women: 6 Best Workout Plans, Benefits, and Pro Tips
Back Workout Tips For Women
Follow these tips for carving a head-turning back:
Focus on Form
Beginners must prioritize lifting with the correct form instead of chasing heavy weights. Using a picture-perfect form maximizes an exercise’s muscle and strength-building potential and reduces the risk of injury.
Plus, focus on contracting your target muscles with each rep. Going through the motions for the sake of it won’t cut it. Slow down your rep tempo if you have trouble establishing a mind-muscle connection.
Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the name of the game when it comes to building muscle mass. You could make your workouts harder and increase your training volume and intensity by lifting heavier, doing more sets and reps, shortening your rest duration between sets, or incorporating advanced training techniques like super sets, drop sets, intraset stretching, rest-pause sets, etc.
You must gradually increase the demands placed on your muscles. It will challenge your muscles to adapt and improve, leading to gains in strength, muscle size, and overall fitness.
You Don’t Have To Reinvent The Wheel
Many exercisers tend to do too much too soon. These people think that doing out-of-the-box exercises will speed up their progress. However, this is not the case. You don’t have to join a cult or follow a charlatan to build a chiseled back. The exercises mentioned in this article are all you need to develop a shapely back.
Nutrition and Sleep
You cannot out-train a bad diet and recovery program. You must back your workouts with a balanced diet to optimize muscle growth. Further, a seven to eight-hour sleep is a must as it allows your body enough time to rest and recuperate between workouts.
Since the back is a large muscle group, perform one of the workouts mentioned in this article weekly. As you gain more experience, you could perform two weekly back workouts to expedite your back growth. However, avoid doing more than two back workouts a week as it increases your risk of overtraining.
Change Grips
Performing the same exercise with a different hand grip can target your muscles differently. For example, you could do a barbell bent-over row with an underhand or overhand grip. You could also perform the seated cable row with a supinated, pronated, or neutral grip to train your back from different angles.
Why Building a Strong Back is Important For Women?
Incorporating back workouts into your training regimen entails the following advantages:
Improves Aesthetics
Building a bigger back can add to your physique aesthetics. It can create an illusion of a smaller waist and broader shoulders, which are essential features of an hourglass figure. A diced back will also make you look stunning in backless dresses and tank tops.
Promotes a Better Posture
Most of us spend the majority of our days hunched over a computer or phone screen. Training our backs can help improve our posture by strengthening the muscles responsible for maintaining a proper upright position. Plus, back exercises can increase back flexibility and mobility, which can help pull the shoulders back, open up the chest, and align the spine in its natural S-shape curvature.
Helps Burns Calories
Your back is the second-biggest muscle group. Performing an intense back workout that involves compound (multi-joint) exercises can spike your heart rate, helping you burn a decent amount of calories. Plus, back workouts help increase overall muscle mass and boost metabolism, both of which lead to a higher calorie expenditure even when you are physically inactive. However, if your goal is to burn more calories, you should follow the HIIT back workout listed in this article.
Boosts Functionality
Most back exercises are functional movements that improve overall strength, mobility, and stability. Your back plays a crucial role in many everyday activities, such as lifting, carrying, and bending, as well as in sports and other physical activities. Balanced back workouts improve your performance in all these activities while reducing your risk of injury.
Help Alleviate Lower Back Pain
Training your spine-supporting muscles (erector spinae) in your back workout can help alleviate and reduce the risk of lower back pain, especially in women with large breasts or those that remain seated for most of the day.
FAQs
How can women build a toned back?
Building a chiseled back requires following a balanced back workout focusing on building muscle mass and strength. Perform one of the workouts given in this article weekly for 12 weeks to see noticeable back development. You could also switch between the workouts to add variety to your training regimen.
Should men and women follow different back workouts?
No exercise is gender specific. The workouts in this article can be used by men and women alike. With that said, girls don’t need to worry about building a cobra back like their male counterparts. The ladies don’t produce enough testosterone to build the same amount of muscle mass as men.
How to program a back workout for hypertrophy and strength gains?
The number of sets, reps, and exercises you perform and your workout intensity will depend on your training goals. Perform 3 sets of 8-12 reps of an exercise and rest 60-90 minutes between sets if you want to build muscle mass. On the other hand, do 3-5 sets of 1-5 reps of an exercise with 2-5 minutes of rest between sets if you want to maximize strength. [1]
Wrapping Up
To carry the heavy burden of the world, you must have a strong back. The five back workouts for women listed in this article will help improve your posture, boost your functional fitness and calorie expenditure, and enhance your physique aesthetics.
These workouts are apt for women of any experience level. Furthermore, the HIIT back training session is great for ladies on a tight schedule. Pair these workouts with a balanced recovery program for optimal results. Best of luck!
References
Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.
Average Ankle Size For Men and Women
If you asked someone to make the list of the most glamorous body parts, ankles would indeed feature at the bottom; it is if that person doesn’t forget about the ankles altogether. Although usually forgotten, ankles are one of the most crucial body parts.
Ankles play a crucial role in standing, walking, or running by allowing up-and-down foot movement. Ankles also play a crucial role in fashion; they can make or break an outfit. Whether you’re in the market for ankle-length pants or ankle boots, knowing the average ankle size for men and women and how you stack up against it can help you make the right buying decision. Knowing your ankle circumference is also a must for buying accessories like anklets.
Ask your friend about their most unaesthetic body part, and they’ll probably point down to their ankles. Most of us are reminded of our weak ankles every time we bend down to put on our socks and shoes.
However, have you ever stopped to wonder if you really have weak ankles or if everyone has small ankles like you? Probably not.
For this article, we analyzed several anthropometric studies to learn about the average ankle size in men and women. Furthermore, we go over how to measure your ankles correctly, the factors that affect your ankle size, and the effects of your ankle size on your frame and overall health.
We have a lot to cover. So sit back, kick up your feet (but not too far — we need to measure those ankles), and get ready to learn all there is to know about your ankle size.
Why You Should Know The Average Ankle Size
Your ankles are much more than the bony things that connect your feet to your legs. They can help you pick the right style and size of shoes and socks and give you valuable insight into your overall health.
Folks with a bigger-than-average ankle size generally have wider feet, which requires you to buy shoes with a wider toe box. Knowing your ankle size will help you choose shoes and accessories that fit well, preventing discomfort or injury.
Furthermore, understanding the average ankle size can give you critical insights into your health. For example, swelling or edema in the ankles can be a sign of circulatory problems, heart failure, or kidney disease.
Lymphedema, a condition in which fluid builds up in the lymphatic system, can also cause ankle swelling. On the flip side, thin or bony ankles may be a sign of osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions. Doctors often measure ankle size during a physical exam to check for underlying health issues.
Average Ankle Size in Men
According to US anthropometric data from a 1988 report that measured the ankles of 1,774 men, the average male ankle size is 8.73 inches or 22.17 cm. This data is based on the body measurements of US military personnel. [1]
The average ankle size depends on multiple factors, including gender, age, height, weight, genetics, and lifestyle choices. Below is the average ankle size in men:
Percentile
Ankle Size (inches)
1
7.61
2
7.70
3
7.77
5
7.88
10
8.06
15
8.18
20
8.29
25
8.38
30
8.46
35
8.53
40
8.60
45
8.67
50
8.73
55
8.80
60
8.87
65
8.93
70
9.00
75
9.08
80
9.16
85
9.26
90
9.38
95
9.56
97
9.67
98
9.76
99
9.90
In these tables, the one percentile represents the men with the smallest ankle sizes. Conversely, the 99 percentile represents men with the biggest ankle circumference. In this study, the men with the smallest ankle size had 7.61-inch ankles, whereas 9.90 inches was the largest recorded ankle size. The 50th percentile represents men with the average ankle size — 8.73 inches.
Notably, there is a significant difference in the ankle size in the sample group. The man with the biggest ankle circumference had 2.29 inches on the man with the smallest ankles. The height, age, weight, genetics, and body composition were probably responsible for this discrepancy.
You can expect the person with 9.90-inch ankles to have a substantially bigger frame than the individual with 7.61-inch ankles.
Average Ankle Size in Women
The 1988 report also measured the ankles of 2,208 women and concluded that the average female ankle size was 8.08 inches or 20.53 cm.
Interestingly, there is only a 0.65-inch gap between the average ankle size of women and men. However, the biggest and smallest women’s ankle size were separated by a 2.23-inch gap — almost the same as the men. Nonetheless, women generally have smaller ankles than their male counterparts.
Percentile
Ankle Size (inches)
1
7.08
2
7.17
3
7.23
5
7.32
10
7.48
15
7.59
20
7.68
25
7.76
30
7.83
35
7.89
40
7.95
45
8.01
50
8.07
55
8.13
60
8.19
65
8.25
70
8.32
75
8.39
80
8.47
85
8.57
90
8.69
95
8.88
97
9.02
98
9.12
99
9.31
Like in the case of men, the average ankle size in women can change depending on their body structure and composition. Ladies in the one percentile have 7.08-inch ankles, meaning these were the smallest ankles of the bunch. On the other hand, 9.31 inches was the biggest ankle circumference recorded in the group.
The slight difference between the average male and female ankle size is mainly because the ladies have a higher amount of body fat, especially in their lower bodies. Furthermore, body parts like the ankles and wrists store the least amount of muscle, leading to a minimal difference in measurement between the sexes.
Average Ankle Width For Males and Females
While the ankle size is measured by wrapping a tape measure around the circumference of your ankle, the ankle width (or breath) is measured by placing the arms of a breadth caliper on each of your ankle bones where they are the thickest.
Average Ankle Width in Men
According to the above-referenced data, the average ankle breadth for adult males is 2.87 inches or 7.28 cm.
Many healthcare professionals prefer the ankle width (or bimalleolar breadth) measurement over the ankle circumference because it is less prone to deviation, as there are no fat stores on the ankle bones. The lower leg fat is stored just above the ankle joint and below the calf, which can skew ankle size measurements.
Percentile
Ankle Breadth (inches)
1
2.52
2
2.56
3
2.58
5
2.62
10
2.67
15
2.71
20
2.73
25
2.76
30
2.78
35
2.80
40
2.82
45
2.84
50
2.86
55
2.88
60
2.90
65
2.92
70
2.95
75
2.97
80
3.00
85
3.03
90
3.07
95
3.31
97
3.16
98
3.19
99
3.23
You will notice that the individual with the biggest ankle breadth (3.23 inches) only had 0.98 inches on the person with the smallest ankle width (2.52 inches). This is a significant deviation from the 2.29 inches difference in the biggest and smallest ankle size in males.
Average Ankle Width in Women
As per the US anthropometric data, the average ankle width for a woman is 2.54 inches or 6.44 cm.
The difference between the biggest ankle width (2.83 inches) and the smallest (2.25 inches) is a minuscule 0.58 inches. It is almost half the difference between the biggest and smallest ankle width in males.
Percentile
Ankle Width (inches)
1
2.25
2
2.29
3
2.31
5
2.34
10
2.38
15
2.41
20
2.43
25
2.45
30
2.47
35
2.49
40
2.50
45
2.52
50
2.53
55
2.55
60
2.56
65
2.58
70
2.60
75
2.62
80
2.64
85
2.66
90
2.70
95
2.74
97
2.78
98
2.80
99
2.83
How To Measure Your Ankle Size
Unlike measuring your wrists or forearms, measuring your ankles is relatively easy and more convenient as you can use both your hands.
To take your ankle circumference, place your foot on an elevated surface, such as a bed or chair. Doing so makes taking the reading easier. You must, however, ensure your lower leg is perpendicular to the floor. Measuring your ankles with your lower leg at an angle can skew the results.
Alternatively, you could ask for someone’s help to measure your ankles while you stand upright with both feet placed on the floor in a shoulder-width stance.
This is how to measure your ankle size accurately with a tape measure:
Place your dominant foot on an elevated surface, such as a chair, while the other foot is on the floor. The lower leg of the dominant side should be perpendicular to the floor, and your knee should be over your ankle.
Wrap a tape measure around the narrowest part of your ankle. It is usually an inch or so above your ankle bone.
The tape should be wrapped snugly around your ankle.
Note down the number where the tape overlaps. This will be your ankle size.
Repeat the process on the other leg.
How To Measure Your Ankle Width
Taking your ankle width measurement is a little more complicated than measuring your ankle circumference. Don’t get us wrong. It is not complex because it requires you to do some insanely difficult mathematical calculations. We say complicated just because you need a breadth caliper for this measurement, and most households don’t own a breadth caliper, whereas a measuring tape is quite common.
Measuring your ankle breadth involves measuring between your ankle’s medial and lateral malleoli. In layperson’s terms, you must measure between the thickest parts of your ankle bones.
Here is how to measure your ankle width using a breadth caliper:
Stand erect with a shoulder-wide stance with both feet placed on the floor.
Have someone place the arms of the breadth caliper on each of your ankle bones where they are the thickest.
Record the measurements.
Repeat 2-3 times to verify the results.
Measure your other ankle.
How To Measure Your Ankles Without a Tape
Folks that don’t have a measuring tape don’t need to hang their heads low. You can measure your ankle circumference using a piece of thread. You could also use a piece of paper if you don’t have a measuring tape.
Here is a step-by-step process to measure your ankles using a piece of string:
Place your dominant foot on an elevated platform.
Wrap the thread around the thinnest part of your ankle, above your ankle bones.
The thread should neither be too loose nor too tight around your ankle.
Record the number where the thread overlaps.
Place the thread on a flat surface and measure between the two points using a scale.
Repeat 2-3 times to ensure accurate sizing.
Measure your other ankle.
Notes
The tape should wrap snuggly around your ankle. However, it shouldn’t be so tight that it digs into your skin.
The tape should be parallel to the floor during the measurement. Wrapping the tape at an angle can skew the results.
Your foot should be placed flat on the floor during the measurements, and your toes should be in line with your knees. Lifting your toes or heels off the floor will give you an incorrect reading.
Take your ankle measurements barefoot. Wearing a shoe with a significant heel-to-toe drop can skew your results.
Factors Affecting Ankle Size
Your ankle size can depend on multiple factors, including:
Height: Taller folks generally have bigger ankles than their shorter counterparts. It is mainly because your ankle size is proportional to your overall body frame.
Weight: Overweight people tend to have larger ankles because of fat and fluid accumulation in the lower legs. If left unchecked, it can contribute to swelling and edema.
Age: Your ankle size can change with age. Most people experience muscle atrophy as they grow older, leading to smaller ankles. Furthermore, hormonal changes can also cause changes in ankle size, especially in women. Medical conditions, such as arthritis or osteoporosis, can also change your ankle size.
Genetics: Genetics can also influence your ankle size. Men with a family history of bigger joints are more likely to have larger ankles than the average.
Lifestyle: Lifestyle can play a crucial role in your ankle size. Active people generally have thicker ankles than their sedentary counterparts.
Ankle Size and Frame Size
According to a Journal of Sports Sciences study, there is a strong correlation between ankle and frame size. Folks with a bigger ankle circumference than their peers are more likely to have a larger frame. [2]
Furthermore, there is a correlation between the ankle bones and the wrist and elbow bones. People with bigger ankle bones are more likely to have bigger elbows and wrists, allowing them to hold more muscle mass than individuals with smaller joints.
Notably, people with a higher body fat percentage will have a bigger ankle circumference than their counterparts with a normal BMI. In this case, it is better to evaluate your ankle width against the average.
Ankle Size and Health
Medical professionals often analyze your ankle size to screen for certain health conditions as part of a physical exam.
Edema, lymphedema, and arthritis are a few conditions that can be diagnosed by measuring your ankle circumference. Doctors measure ankle size using a tape measure or other specialized equipment to diagnose and monitor these health issues. Furthermore, you can monitor your ankle size to track your progress in these conditions over time.
Note: You must consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment if you have concerns about your ankle size or are experiencing swelling or pain in your ankles.
Large ankle size can indicate a higher chance of contracting certain conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes. Notably, frame size is just one factor that can contribute to these health risks. While assessing your health risks, you must also consider other factors such as diet, exercise, and family history.
FAQs
Where should you measure your ankles?
You should measure your ankles just above your ankle bones at the thinnest point. However, doctors generally measure around your ankle bones, as it is a more effective way to diagnose certain health conditions that can cause swelling in the ankles.
Are both my ankles supposed to measure the same?
Generally, both ankles should measure roughly the same. However, you shouldn’t panic if your dominant ankle is slightly bigger than the other.
Also Check Out:
Wrapping Up
This article covered the average ankle size and width for males and females, the factors that affect ankle size, and the implications of ankle size on your health and frame size. In short, it has everything you never knew you wanted to know about ankle size.
To sum it up, whether you’re trying to find the perfect pair of shoes, dealing with a health issue, or just curious about your body, understanding your ankle size can help you understand your physique better.
References
Gordon, Churchill, Clauser, Bradtmiller, McConville, Tebbetts, & Walker, (1989, September). 1988 Anthropometric survey of U.S. Army personnel: Methods and Summary Statistics. United States Army Natick Research, Development and Engineering Center Natick, Massachusetts.http://tools.openlab.psu.edu/publicData/ANSUR-TR89-044.pdf
Peters DM, Eston R. Prediction and measurement of the frame size in young adult males. J Sports Sci. 1993 Feb;11(1):9-15. doi: 10.1080/02640419308729957. PMID: 8450591.
Average Shoulder Width For Men and Women
What do Superman, Batman, Wonder Woman, and Captain Marvel have in common? They have broad and chiseled shoulders. Big and round shoulders are associated with power and dominance.
Wide shoulders can improve your physique aesthetics by making your waist look smaller and accentuating your V-taper. It is no surprise bodybuilding enthusiasts spend a considerable amount of time working on their shoulders.
The shoulder muscle, also known as the deltoids, consists of three heads — anterior, lateral, and posterior. You must work on all three heads from multiple angles to ensure overall development.
In this article, we cover why you should know about your shoulder width, the average male and female shoulder size, how to measure your shoulder width, factors that affect your shoulder size, and how to increase or reduce your shoulder width. There is a lot to cover, so sit tight.
Why is Shoulder Width Important?
Any fitness freak can tell you that building big shoulders is important. Only a few, however, can tell you why that is so.
If you are a sportsperson, knowing the average shoulder width of the top athletes in your sport can help you compare your biomechanics with theirs and design a diet and training program to maximize your potential. Shoulder width and strength can play a crucial role in sports such as bodybuilding, CrossFit, strongman, swimming, boxing, and weightlifting.
On the other hand, knowing your shoulder width can help you purchase clothes that look and fit better. Folks looking to create a new wardrobe after a physique transformation should measure their shoulders to avoid buying ill-fitting clothes. You don’t want to wear baggy clothes after spending months slimming down.
What is the Average Shoulder Width For Men?
According to the CDC data based on 7,476 American men, the average male shoulder width is 16.2 inches or 41.1 cm. Notably, these measurements refer to the biacromial breadth, which is measured between the outermost bony points on the top of each shoulder. [1]
The average shoulder width for men stays almost the same in the 20-59 age group and tapers off gradually as they enter their 60s.
Men, on average, have a 16.3-inch biacromial breadth in the 20-29 age group. It remains the same until they turn 50. Men see a 0.2-inch drop in their shoulder width as they enter the 50-59 age group.
Furthermore, men between 60-69 have a 15.9-inch shoulder width, which further shrinks to 15.6 inches in their 70s. According to American anthropometric data, an average American male in his 80s has a 15.4-inch shoulder span.
Age
Average Shoulder Width (inches)
Average Shoulder Width (cms)
20-29
16.3
41.5
30-39
16.3
41.5
40-49
16.3
41.3
50-59
16.1
41
60-69
15.9
40.5
70-79
15.6
39.7
80+
15.4
39
Notably, the average shoulder width can vary according to ethnicity, genetics, weight, body type, diet, exercise, and family history. People of the same origin tend to have a similar physical structure.
What is the Average Shoulder Width For Women?
According to the same CDC report, the average shoulder width for American females is 14.4 inches or 36.7 cm. This data is based on 8,411 women aged 20 and above.
The average shoulder width for women in the 20-29 age group is 14.5 inches; it increases slightly to 14.6 inches for women in the 30-39 age group. However, women see a slight decrease in their shoulder width in the 40-59 age group as their shoulder size reverses to 14.5 inches.
Ladies, on average, see another fall in their shoulder size as their shoulder width falls to 14.3 inches in the 60-69 age bracket. The downward trajectory continues as the average shoulder width slips to 14.1 inches for women in their 70s. Finally, the biggest drop comes after women turn 80, as their shoulder size drops by 0.4 inches to 13.7 inches.
Age
Average Shoulder Width (inches)
Average Shoulder Width (cms)
20-29
14.5
36.9
30-39
14.6
37
40-49
14.5
36.9
50-59
14.5
36.9
60-69
14.3
36.4
70-79
14.1
35.7
80+
13.7
34.8
What is the Average Shoulder Circumference For Men?
Are you confused already? You are not alone. Many people confuse shoulder width with shoulder circumference.
Here’s an easy way to remember the difference. A tailor takes your shoulder length measurement for making custom suits by placing a measuring tape across your shoulders.
On the other hand, shoulder circumference is measured by wrapping a tape around your shoulders. It is like taking a chest measurement, but a few inches above your pectoral muscles. Wrapping the tape around the middle of the deltoids gives you your shoulder circumference.
According to the anthropometric data published by the US Army Natick Soldier Research, Development and Engineering Center, the average male shoulder circumference is 46.25 inches or 117.5 cm. [2]
Notably, this data is based on US Army soldiers, who tend to be fitter than ordinary folks. Furthermore, the average shoulder circumference tends to change with height. Taller folks generally have a bigger shoulder circumference.
What is the Average Shoulder Circumference For Women?
As per a 2016 study, the average shoulder circumference for adult females is 39.4 inches or 100 cm. The subjects of this study were, on average, around 21 years old, 5’7″ tall, and had a 20-21 BMI. [3]
Shorter women, on average, will have a smaller shoulder circumference than 39.4 inches. Similarly, some shorter ladies might have a bigger shoulder circumference because of their genetics and broader shoulder structure.
Differences in skeletal structure and hormones lead to different shoulder widths in men and women. This difference can result in discrepancies in physical performance, especially in athletics. Since men have broader shoulders, male athletes have more upper body strength than their female counterparts in the same weight category. On the flip side, smaller clavicle bones give women an edge in sports that require flexibility and range of motion, such as gymnastics and dance.
4 Ways To Measure Your Shoulders
If measuring your shoulders was so easy, there would be no ill-fitting clothes in this world. The fact that this article shows four methods of measuring your shoulders should tell you that it is much more complex than what most people assume.
However, we have broken down these three methods into easy-to-follow step-by-step instructions to help you determine your exact shoulder width.
How To Measure Your Shoulder Length
This method is most commonly used by tailors. You need a tape measure and another person’s help for this method; it helps you determine your clavicle width and upper back size.
Steps:
Stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance and your arms at your sides.
Ask your friend to run a tape measure across your upper back (shoulder to shoulder).
Instead of running the tape straight across your shoulders, curve the tape slightly upward to factor in the size of your upper back.
Place each end of the tape on the edges of your shoulders, where they begin to curve down.
Note down your shoulder measurement.
How To Measure Your Shoulder Circumference
To measure your shoulder circumference, you must wrap the tape measure around your shoulders. You’ll need a friend’s help to determine your shoulder size in this method.
Steps:
Stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance.
Have your friend wrap the tape around your shoulders. The tape should be parallel to the floor and wrap around the meatiest part of your deltoids. A tilted tape will give you an incorrect reading.
Avoid pushing out your chest or rounding your shoulders during shoulder measurement.
Record the number where the tape overlaps.
How To Measure Your Biacromial Breadth
This is the most accurate method of measuring your shoulder breadth. This method is used in the military and in scientific research, where they depend on accurate data.
This method involves using a large bone caliper to record the distance between your acromia, which is the bony part on the ends of your shoulders; hence this method measures your bone structure breadth and disregards your muscle mass.
Steps:
Take the biacromial breadth measurement shirtless for the most accurate results.
Use a bone caliper and adjust the edges above your shoulder joints, where the shoulder caps begin.
Note down the reading.
How To Measure Your Shoulders Yourself
The three methods listed above require a friend’s help, which might not be possible for everyone. To this effect, we are including a technique you can use to measure your shoulder width on your own. Notably, this method is not as effective and accurate as the three mentioned above as it includes shoulder and arm muscle mass and overlooks the back.
This method is also known as the triceps-to-triceps shoulder measurement. You will need a pencil for this measurement, and since it involves marking the surface, you want to do it on a wall that you don’t mind spoiling or stick a piece of paper on the wall before doing this.
Steps:
Stand upright with your back against a wall.
Your head, shoulders, upper back, hips, and feet should be in contact with the wall.
Grab a pencil in your right hand.
Turn to your left side and mark the wall just outside the meatiest part of your left deltoid.
Repeat on the right side.
Use a tape measure or a scale to measure the distance between the two points on the wall.
How To Measure Your Shoulder Width For Bodybuilding
The sport of bodybuilding is all about aesthetics. You must have the perfect size, structure, balance, proportions, and conditioning to win a bodybuilding show. In short, it requires a holistic approach to developing your physique.
In this regard, you must measure your shoulder circumference to ensure you are on the right track. Measuring your shoulder circumference instead of your shoulder width helps you track your body fat, muscle mass, and shoulder development. On the other hand, measuring your shoulder width will only give you your clavicle width.
Using your shoulder circumference measurements will give you more data points, which can help you work toward your goal physique. Nonetheless, you can also use the shoulder width and biacromial breadth measurements for a holistic approach. However, if you want to limit yourself to only one measurement, it should be the shoulder circumference.
Factors that Affect Shoulder Width
Shoulder width depends on a mix of factors. Some, such as diet, exercise, and body weight, are under our control, whereas others, like gender at birth, ethnicity, genetics, and hormones, are beyond us. Let’s take a closer look at these factors:
Gender
Men tend to have wider shoulders than their female counterparts. Wider shoulders are one of the reasons why males have greater upper-body strength than women, which translates to better performance in activities that require upper-body muscle power.
Ethnicity
Shoulder sizes among people of different ethnicities in the same age and weight group can vary because of a difference in skeletal structure and body composition. Notably, the shoulder size difference between different ethnicities is relatively small.
Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role in determining your shoulder width. Our genes determine the skeletal structure of our shoulders, including the size and shape of the clavicle, scapula, and humerus bones.
Hormones
Your shoulder width greatly depends on your hormones. With that said, testosterone is the main hormone responsible for muscle and strength gains. Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. It is also the primary reason men have broader and stronger shoulders than women.
Lifestyle Factors
This is one of the often overlooked aspects that affect shoulder width. Your lifestyle can majorly impact your shoulder width. Your diet, exercise, and sleeping schedule dictate your strength and muscle gains and can affect the shape and size of your shoulders.
Following a balanced diet and training program is one of the most effective ways of building bigger and stronger shoulders. Furthermore, you must sleep for at least 7-8 hours each night to give your body enough time to recover from your workouts.
Conversely, following a sedentary lifestyle can result in muscle atrophy, leading to smaller and slanting shoulders over time.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like scoliosis, which causes the spine to curve sideways, can cause uneven shoulder height and affect shoulder width. Other medical conditions that lead to overall health deterioration can also reduce your shoulder width. Plus, injuries can also affect shoulder width by causing muscle atrophy.
Check also: Find Your Body Type Endomorph, Ectomorph, or Mesomorph?
The Ideal Shoulder Width
Bodybuilding enthusiasts and folks chasing aesthetics chase muscular symmetry and balance. Knowing the ideal shoulder width can help them design a workout program to achieve the magic number.
The ideal shoulder width will be subjective. It is based on the factors listed above. Furthermore, the two ratios mentioned below will help you arrive at a number that will aid you in carving a more balanced and aesthetically appealing physique.
Shoulder-To-Waist Ratio
Broad shoulders and a narrow waist can accentuate your V-taper and add to the illusion of a bigger physique. It can make your waist look smaller and give you a commanding and authoritative presence.
The shoulder-to-waist ratio compares your shoulder and waist circumference. It is a great tool for assessing your body composition and gives an overall view of your health and fitness levels. Furthermore, it can help you arrive at the ideal shoulder width to improve your physique aesthetics.
Dividing your shoulder’s widest part’s circumference by the circumference of the narrowest part of the waist will give you your shoulder-to-waist ratio. For example, if you have a 32-inch waist and your shoulder circumference is 46 inches, your shoulder-to-waist ratio would be 1.4375 (46 divided by 32).
Routinely measuring your shoulder-to-waist ratio can be an incredibly effective way of tracking your transformation progress.
Generally, a higher shoulder-to-waist ratio is considered desirable for men as it is associated with a more athletic and powerful physique. A shoulder-to-waist ratio of 1.6 or greater is typically considered ideal for men. Conversely, a shoulder-to-waist ratio of 0.7 or lower is desirable for women.
Remember, these are just ideal numbers. Don’t beat yourself up if you cannot get close to these numbers. In his prime, the legendary bodybuilder Steve Reeves had a shoulder-to-waist ratio of 1.47, and he was considered to have the best structure in the business.
Use our Shoulder-to-Waist Ratio Calculator to learn more about achieving your dream physique.
Grecian Ideal Ratio
The Grecian ideal ratio is great for bodybuilding enthusiasts. It is easy to use and gives you all the data you need to build a Greek god-like physique. This calculator uses your wrist circumference to calculate your ideal muscle group proportions.
The Grecian ideal measurements include:
Shoulders: 1.618x larger than waist
Flexed arm: 2.5x larger than non-dominant wrist
Flexed calves: Same size as flexed arms
Chest: 6.5x larger than non-dominant wrist
Upper leg: 1.75x larger than knee
Frank Zane / Instagram
Eugen Sandow, also known as the “Father of Modern Bodybuilding,” is credited with creating the Grecian ideal ratio. He visited museums and measured the proportions of the statues to create the Grecian ideal ratio. Bodybuilders like Steve Reeves, Reg Park, Arnold Schwarzenegger, Frank Zane, and Lee Labrada followed the Grecian ideal to build their iconic physiques.
You shouldn’t, however, look at the shoulder-to-waist ratio or the Grecian ideal ratio in isolation to assess your fitness levels. Combine them with your body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and body fat percentage to get a holistic view of your overall health.
Check out our Grecian Ideal Calculator to determine your ideal body measurements.
How To Increase Shoulder Width?
Now that you’ve learned about the average shoulder width, the ideal shoulder width and the shoulder-to-waist ratio, and the Grecian ideal ratio, it’s time to put all this knowledge to work.
Let’s say you now know you are an inch away from your ideal shoulder width but have no idea how to get there. This section is for you!
Below is how to add meat to your shoulders:
Improve Your Posture
Poor posture is one of the biggest reasons behind smaller shoulders. Most people spend a good part of their day hunched over their phone or laptop. This leads to a rounded back and shoulders, which can make your delts look smaller.
Improving your posture will enhance your physique aesthetics and instantly make your shoulders look wider. Pull your shoulder back and push out your chest. You must monitor your sitting and standing posture throughout the day.
Doing resistance training exercises and actively correcting your posture throughout the day will be your first step toward broader shoulders.
Resistance Training
Non-trainers must start lifting weights to build wider and stronger shoulders. On the other hand, exercisers must perform a dedicated shoulder training session in their weekly training regimen to build a more aesthetically appealing physique.
Your shoulder workouts should have a mix of compound (multi-joint) and isolation (single-joint) exercises and should target all three deltoid heads (anterior, lateral, and posterior) from multiple angles to ensure overall development.
Furthermore, you must include advanced training principles like dropsets, supersets, intraset stretching, and rest-pause sets to progressively overload your muscles and induce hypertrophy. Switch up your training intensity, volume, and frequency to keep your muscles guessing and avoid hitting a plateau.
Alternating between strength-focused and hypertrophy-focused workouts can help build thick and dense muscles. Perform 1-5 reps per set to build strength. On the other hand, stay in the 8-12 rep range to induce hypertrophy. [4]
Also, you must work on your supporting muscles, such as the triceps and core, to improve your pressing performance. Perform all exercises with the perfect form to get the best bang for your buck and reduce your risk of injury.
Proper Nutrition
It doesn’t matter how hard you train; you cannot out-train a bad diet. You must back your workout regimen with a balanced diet with the right proportions of macro and micronutrients. Eat a protein-rich diet to build muscle mass and strength and improve your recovery. Plus, eat a good balance of fruits, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates to support your energy levels during workouts.
When you eat a balanced diet, you are in a better position to lose weight, which can help you lose the spare tire and improve your physique aesthetics. Ir will make your shoulders look wider and stronger.
Rest
You must give your muscles enough time between workouts to ensure optimal recovery. Sleeping for 7-8 hours each night puts you in the sweet spot. It fastens your muscle recovery and boosts growth hormone production, which can aid in boosting muscle and strength gains. [5]
Dress To Impress
Dressing according to your body shape can make all the difference in boosting your aesthetics. If you have small shoulders, wearing clothing with shoulder pads like blazers and coats can make your shoulders look wider.
On the flip side, donning fitting clothing can make your shoulders pop during the summer. Folks with narrow shoulders should avoid baggy clothing, as they can make their delts look small, slanting, and weak — a trio you want to avoid.
Wearing horizontal stripes can make your shoulders look wider. Overweight folks, however, should avoid horizontal stripes as they can make them appear larger.
How To Reduce Shoulder Width?
Reducing your shoulder size can be harder than gaining shoulder width. Your genetics, gender, hormones, and ethnicity generally determine your shoulder width. It can be challenging to lose shoulder width if you have a normal BMI and have never engaged in strength training.
On the other hand, overweight folks might find some success in losing shoulder width by adjusting their diet and training program. Furthermore, you could influence your physique aesthetics and make your shoulders look smaller by working on your lower body.
Here are some ways to reduce shoulder width:
Do More Cardio
This tip is primarily for overweight people. Losing weight is one of the most effective ways to shed shoulder width. Do two cardio sessions daily to prioritize weight loss. The first should be a 15-20 minute high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workout done on an empty stomach first thing in the morning.
You should then do a 30-40 minute low-intensity steady state (LISS) cardio session later in the evening. Doing two cardio workouts in a day will help you enter a calorie deficit and spike your metabolic rate, which will ensure you are burning calories throughout the day, even when you are physically inactive.
Modify Your Workout Routine
If you are a regular lifter, you must make significant changes to your workout training regimen to lose shoulder width. You must begin by cutting out shoulder workouts from your training routine. That’s right, no more shoulder presses, lateral raises, upright rows, or shrugs.
Cutting out shoulder workouts will ensure that you are not building new muscle tissue in your shoulders, making them bigger and denser. Plus, you must recomp your training program and add another leg workout into your schedule instead of the shoulder workout.
Building bigger legs can take away the attention from your shoulders and contribute to developing a more balanced physique.
Change Your Diet
Folks trying to lose weight should enter a calorie deficit, meaning they should burn more calories daily than they consume. Additionally, you must rejig your diet by lowering your calorie intake or adjusting your macronutrient ratios.
You must, however, ensure that you are eating enough protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to support muscle maintenance and recovery. Hiring a professional with a proven track record can save you time, effort, and money in your goal of reducing your shoulder width. Don’t hesitate to ask for help, especially if you are a beginner and aren’t equipped to complete a physique recomp.
Avoid Lifting Heavy
Some lifters develop physique imbalances by overemphasizing a certain muscle group. If you are one of them, you must take your foot off the pedal and lower your training intensity and volume.
Besides cutting out shoulder workouts from your training regimen, you must lower the weight you lift on other compound movements, such as the incline chest press. After achieving your body structure goals, you can ramp up your training intensity, volume, and weight.
Must read: Quick Guide to Reducing Broad Shoulders
FAQs
How many inches is a broad shoulder?
This is a subjective question, the answer to which depends on your height, weight, and gender. Generally speaking, you can consider folks with wider-than-average shoulders (according to the tables above) to have broad shoulders.
Are shoulder width and shoulder length the same thing?
Yes, you can use shoulder width and shoulder length interchangeably to refer to the clavicle width. Measuring your shoulder width using a tape measure (the first method in this article) and the bone caliper (the third method) will give you your shoulder length.
Can I measure shoulder width without a tape measure?
Yes, you could use the fourth method mentioned in this article to measure your shoulder width without a tape. Plus, you don’t need a friend’s help with this method. You will, however, need a scale and a pencil for this method. The bone caliper method also doesn’t require a tape measure, but you will need someone’s help for it.
Wrapping Up
This article gives you the average shoulder width for men and women across age groups. You can use this data to determine how you stack up against your peers. However, you must remember that there is nothing like the perfect or ideal shoulder width. Your shoulder width will vary based on your ethnicity, genetics, weight, body type, diet, exercise, and family history.
Use the tips in this article to build muscle mass or reduce your overall body fat. Your shoulder size will depend on your clavicle width, and it might take some time before you begin to see the needle budge in the right direction. Be patient, and the results will follow. Best of luck!
References
McDowell MA, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Anthropometric reference data for children and adults: United States, 1988–1994. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat 11(249). 2009
Mitchell, K. B., Choi, H. J., & Garlie, T. N. (2017). Anthropometry And Range Of Motion Of The Encumbered Soldier. U.S. Army Natick Soldier Research, Development and Engineering Center. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/AD1028746.pdf
Keizer A, van Elburg A, Helms R, Dijkerman HC (2016) A Virtual Reality Full Body Illusion Improves Body Image Disturbance in Anorexia Nervosa. PLoS ONE 11(10): e0163921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163921
Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.
Dattilo M, Antunes HK, Medeiros A, Mônico Neto M, Souza HS, Tufik S, de Mello MT. Sleep and muscle recovery: endocrinological and molecular basis for a new and promising hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. 2011 Aug;77(2):220-2. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.04.017. Epub 2011 May 7. PMID: 21550729.

Average Forearm Size For Men and Women
Forearms are one of the most overlooked muscles, even though they are right under the most loved muscle group — the biceps. Developed forearms can add to your physique aesthetics and make you stand out by improving your symmetry, proportions, and balance. Your forearms are constantly on display. Whether you wear a t-shirt to work…
- 1
- 2

