Tag: exercise
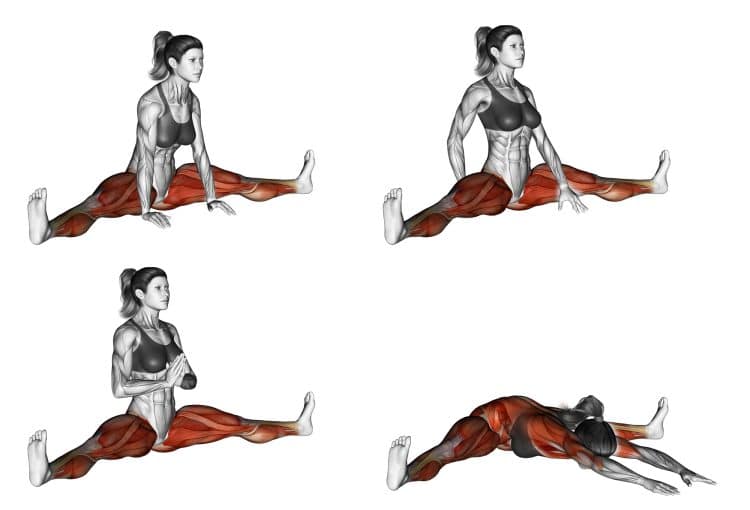
Spread Leg Forward Fold Upavistha Konasana — Benefits, Common Mistakes, and Variations
This one’s a throwback to gym class days when you were instructed to sit, spread your legs wide, and reach as far forward as you could for ten to twenty seconds. And you probably got pretty good at it with enough repetition, but once free from that school requirement, most of us said goodbye and good riddance! (no more torture). But wisdom is power, and those body aches and tight muscles aren’t going to relieve themselves…
Spread leg forward fold or Upavistha Konasana, is a fundamental pose that will benefit your entire body, and there’s an easy technique to progress into the full forward fold that we’ll show you in this guide. Plus learn key form tips and progress with some handpicked advanced variations.
Muscles Involved During Spread Leg Forward Fold Upavistha Konasana
“Spread”, “leg”, “fold”… sounds like a whole lot of stretching going on, for various muscles. In fact, you can easily modify Upavistha Konasana to give yourself a major stretch in the posterior chain from the heels all the way through the trunk, and releasing tension in the neck.
Here’s a short anatomical lesson on the muscles stretched and strengthened in this pose.
Thighs
During spread leg forward fold, proper technique will activate the thighs, hips, and groin, giving them a nice stretch along the way. You’ll also get the adductors that draw the thigh inward. Keeping these muscles loose is a good way to maintain mobility in the lower body, and prevent hard injuries and muscle pulls.
Erector spinae
Elongating the torso, and stretching out the lower back is a big part of the seated forward fold. In fact, to exaggerate this benefit, you can grab the toes, giving you more room to move your upper body.
How to do Spread Leg Forward Fold Upavistha Konasana
For such a simple looking exercise, there are a lot of important steps that you can’t miss when setting up and executing this yoga technique. This is to ensure your body is in a comfortable, supportive, and ergonomic position.
Below are written steps as well as a very detailed, and appropriate video demonstration of the spread leg forward fold upavistha konasana.
Steps
Gently sit on your mat, with your knees bent, feet flat on the floor, and arms relaxed over your legs.
Then straighten your legs out in front of you, and spread them out wide.
Use your hands and gently adjust your glutes by pulling them out to ensure you’re able to maintain an upright posture and lengthened torso without limitation.
Flex your feet by pulling the toes back toward your ankle, and press the heels into the ground.
Now place your fingertips behind your butt on the floor, and pull the shoulder blades slightly toward each other, and down. Then lift your chest up.
Hold this position and feel a nice stretch throughout your body.
If you’re ready for a bigger stretch, place your hands in front of you on the floor, then slowly walk your hands forward as much as you comfortably can.
Now allow your upper body to sink down toward the floor to accentuate the stretch. But remember to maintain a lengthened back, not simply hunching over.
From here, if you do not have the flexibility to descend further, you can use a yoga bolster and/or stacked blankets for support.
Gently, lie your head down, looking to either side, and rest your elbows on the floor with your palms facing up.
Let your entire body relax and sink into the cushions, allowing your arms to also become heavy.
Bring awareness to your groin, feeling the wide position of your legs, while allowing your lower body to sink down into the floor.
Slowly breathe in and out.
Stay here for about 5 minutes.
To come out of the pose, turn your hands over onto your palms, then slowly sit up, walking your hands back toward you for support.
Before you finish the pose, and if you’re comfortable, from the sitting position, place the bolster/blankets on one leg, and lie your head down to that one side for 3-5 minutes. Repeat on the other side.
You’ve now performed the spread leg forward fold!
Check out the soothing demonstration of this yoga technique via the video tutorial provided below.
Tips
You can use a bolster, blankets, and yoga blocks for support as you gradually increase flexibility.
Holding straps around your feet is another great training tool that helps reinforce proper form, and train for improved flexibility.
Never push your body to the point of pain or discomfort. Many yoga poses require great flexibility, and joint mobility but the body needs time, progress, and persistence to achieve deep stretches.
Benefits of Spread Leg Forward Fold Upavistha Konasana
A phenomenal activity that we should all fit in our routines, spread leg forward fold has benefits that go well beyond an amazing body stretch. Here are other reasons why this pose can improve your mind and body.
Stretch your groin, hips, and back
From the spread leg forward fold you can emphasize the point of stretch. Reaching straight forward you’ll focus on stretching the torso and lower back. But you could change direction, leaning into either side, and increase the stretch in your hamstrings.
Stretching your lower back is helpful in preventing injuries by enhancing mobility, while the hamstrings are highly injury prone, and stretching is non-negotiable if you’re highly active. Plus, most people sit a lot, which affects the hips and legs.
Reduce and improve body stress, anxiety, and pain
For the same reason as above, stretching gives us relief from muscles that are overused, not used enough, or that have been injured. Nowadays, our butts are glued to our seats for hours on end, which can lock everything up, and that’s when you start to have issues with hips, knees, etc.
Well, stretching can do a lot to counteract that. In fact, one study on Spanish logistics workers found that implementing a stretching routine in the workplace effectively helped with bodily pain, exhaustion, while reducing anxiety, and improving mental and general health (1). It was seen as a potential low cost way to improve well-being in the workplace.
Additionally, as the above video example pointed out, this pose could potentially improve health situations common in women such as regulating menstruation. Although, we cannot make this claim definitely.
Fight smartphone posture
We’re wreaking havocs on our necks with our phones, laptops and tablets, maintaining terrible forward head posture. It’s said the average human heads weigh on average 5 kilograms or 11 pounds. That’s pretty heavy, and not fair to our necks and spine.
Performing daily stretching and yoga techniques is one of the best ways to hold ourselves accountable for bad posture. Because if we’re making the effort to maintain healthy bodies, then good posture should go along with that.
Additionally, there’s research that could support the positive effects of stretching and core exercises on posture and alignment (2).
Common Mistakes When Performing Spread Leg Forward Fold Upavistha Konasana
These common mistakes are counterproductive to achieving a proper spread leg forward fold pose.
Rounding your back
There are few instances where it’s good to round your back, like the cat pose, for example. However, the goal of upavistha konasana is lengthening the spine by reaching forward, and keeping the back straight. If you notice your back rounding, use assistance such as a bolster, block, or blankets, and slowly lower yourself, focusing on good form.
Rolling your feet forward
Throughout this pose, your feet and knees should be pointed up toward the ceiling. Rolling them forward could place too much pressure on your knees.
Forcing it too quickly
The spread leg forward fold appeals to beginners because it seems so simple and straightforward (pun intended). And as mentioned, most of us have done it at some point. However, if you don’t stretch these muscles regularly, you will be surprised at how bad your flexibility is. So don’t try to rush it just because you used to do it in grade school. Your muscles and body still need time to open up and adjust.
Variations of Spread Leg Forward Fold Upavistha Konasana
The sitting wide leg fold over is a nice pre-requisite for twist and standing fold over poses. Here are some alternatives we’d choose that are similar in nature.
Strap assisted spread leg forward fold
There are a few different ways that you can ease into a full forward leg spread. Many people may not have the flexibility to do it as shown in the primary example provided in this guide. So, you can actually wrap some short straps, belts, or similar under the bottoms of your feet while in a wide leg seated position, grab onto the ends, and gradually pull yourself closer.
This is actually a great form training technique, that reinforces keeping the legs grounded, shoulders down, and chest up. Remember, ground down with the legs, and lift up with the chest. Go as far down as you comfortably can, as your hamstring and back flexibility allows. Make sure to keep the legs pressed firmly into the floor, and use a blanket under your butt to modify the range of motion.
Spread leg forward fold holding toes
The advantage of grabbing your toes instead of reaching your arms forward is that you can get more range of motion. If you have the flexibility, you can lower your chest and chin to touch the floor, enhancing the stretch and activating more core.
Steps
With the legs spread wide, reach your arms toward your feet and grab the toes.
Hinge forward at the hips, slowly lower your chest toward the floor, and gently rest the front of your torso and chin to the ground if your flexibility enables you to do so. Your toes and kneecaps should be pointing toward the ceiling.
Hold here to get a good stretch, then you can reset, and repeat a few more times.
Spread leg parivrtta (revolving)
Getting some rotation in the pose is going to help open up the chest, and work the rotational oblique muscles of the core. This technique is also commonly performed standing on both feet, but it’s beneficial both ways.
Steps
From a spread leg seated position, inhale, and raise your arms overhead.
Exhale, bend sideways down to either leg and use the same side hand to grab the lower foot. Use the top hand to grab the top part of the foot.
Rotate your upper body toward the ceiling as far as you can, fixing your gaze up. Focus on breathing in and out.
Inhale, free your hands, and slowly come up to an upright position. Exhale and bring your arms down.
Repeat the prior steps on the other side, performing everything in reverse.
Seated forward bend
A basic pose in hatha yoga, the primary difference between seated forward bend and spread leg forward fold is the former is performed with the feet together in front of you. Also referred to as Paschimottanasana, this pose provides a stretch from neck to heels, and it’s just as mentally relaxing.
Steps
Sit on a yoga mat with your legs straight out in front of you and feet close together. Flex your toes back toward your shins.
Inhale, raise both arms overhead and stretch them toward the sky.
Exhale, bend forward from the hips, and reach as far forward as you can without straining or pain. If you’re flexibility allows, grip one wrist with the opposite hand past the bottom of your feet. Or, grab where you’re able to on your lower legs.
Stretch your spine forward, and rest your face and torso on the top of your legs. Make sure to breath in and out in this position.
From here, extend the arms forward, slowly sit up and inhale. Then, exhale and drop your arms down.
Urdhva upavistha konasana upward facing wide angle pose (Variation B)
Now you’ll get to focus on balance, total body stability, core strength, and flexibility. Keep in mind, there are more detailed examples of this upright seated wide legged pose, but for simplicity, we included the basic form steps with a video explanation and demonstration.
Variation B will teach you contrasting styles in muscle activation and relaxation, improving functional skills, and making you a more capable human!
Steps
Start in a sitting position with your knees propped up and feet flat on the floor.
Then come into a baddha konasana by opening your hips, and pressing the bottoms of your feet together close to your body.
Now hook your pointer, and middle fingers underneath your big toes, and grab the tops with your thumbs.
Inhale, pull the shoulders back and lift your feet up. From here, find balance on your sitting bones. Keep a straight spine.
Slowly straighten your legs up toward the sky, and out wide. If you must, keep the legs bent until you gain more flexibility in the future. In this position, make sure your tailbone is straight and not tucked under.
Hold this position for as long as you comfortably can.
Bend your legs, and bring your feet back together like in the starting position.
Now slowly straighten your legs our in front of you one side at a time. You’ve finished this version of a spread leg pose!
Wide legged forward bend prasarita padottanasana
The sitting fold over has a special place in a yoga stretching routine, but if you want more functional benefits, you should try it standing. We have an entire guide on this pose, that explains the benefits, and shows some cool variations.
Choose a surface where your feet will not slide.
From a standing position, spread your feet apart into a wide stance, creating roughly 4-5 feet of space in between. You want a wide stance but not so wide that you lose stability and balance.
Point your toes forward or slightly inward to activate the inner thighs and glutes, keep your legs straight and engaged, and focus your weight on your outer feet. Place your hands on your hips.
Now hinge forward at the hips, and lower your torso until your upper body is roughly parallel to the floor. Make sure to keep your back straight. Then, slowly stand up straight.
Repeat step 4, but now stretch your arms down to the floor and touch it with your fingertips.
Walk your hands back until your fingers and toes are in line, and press your palms flat on the floor.
Lift your head up and gently stretch toward the sky.
Then drop your head and body down toward the floor, while bending your elbows. Try to relax your upper body.
Gently rest the crown of your head on the floor. Hold this position for a few seconds, trying not to exceed 10 seconds at first.
Now come up onto your fingers, walk your hands forward, and bring your hands on your hips, one at time, then slowly stand up in the starting position.
Related: How to do fish pose Matsyasana
Wrapping Up
Back then you probably thought it was a useless technique, but little did you know such a simple technique could do so much good for your body. Granted, we probably accumulate the most bodily tension as we mature and face adult life, which is more reason for us to get deeper into these types of intense stretches, and yoga exercises.
Spread leg forward fold upavistha konasana is a nice entry level, all-around pose for the posterior chain, anterior body, hips, core, spine, and neck muscles. And it’s very safe to do, so long as you be patient, don’t force what won’t go, and use proper progressions as included in this guide under the variations section.
References
Montero-Marín J, Asún S, Estrada-Marcén N, Romero R, Asún R. Efectividad de un programa de estiramientos sobre los niveles de ansiedad de los trabajadores de una plataforma logística: un estudio controlado aleatorizado [Effectiveness of a stretching program on anxiety levels of workers in a logistic platform: a randomized controlled study]. Aten Primaria. 2013 Aug-Sep;45(7):376-83. Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.aprim.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Jun 12. PMID: 23764394; PMCID: PMC6985483.
Kim D, Cho M, Park Y, Yang Y. Effect of an exercise program for posture correction on musculoskeletal pain. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015 Jun;27(6):1791-4. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.1791. Epub 2015 Jun 30. PMID: 26180322; PMCID: PMC4499985.
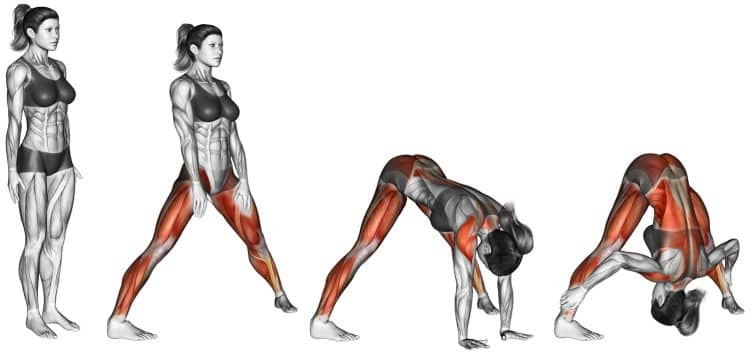
Wide Legged Forward Bend Prasarita Padottanasana – Muscles Worked, Benefits, Common Mistakes, and Variations
One of yoga’s many fold poses, the sangskrit name prasarita padottanasana describes five elements of the wide legged forward bend:
“Prasarita” – Spread
“Pada” – Foot/leg
“Ut” – Intense
“Tan” – To stretch
“Asana” – Pose
Putting the sequence into action, the yogi takes a wide, straddle stance which requires foot and thigh strength, hip flexibility, and core strength. Moving up the chain, the hips hinge the upper body forward, until the torso is inverted or folded over, and the head is upside down.
Wide legged forward fold is a common yoga pose, and it benefits everything from the feet (strengthening), to the head (increased blood flow to the brain which may yield some benefits).
In this guide, we detail how to perform this pose, with a short video demonstration, tips, common mistakes to avoid, and some arm variations.
Muscles Worked During Wide Legged Forward Bend
While wide legged forward bend isn’t working muscles to increase their strength and size (primarily although you may get a little of that), you can expect a phenomenal stretch, and to recruit muscles in a way they’re not usually.
Hamstrings
The most obvious muscles stretched during a forward bend are the hamstrings. On the back part of your upper leg strung between the hips and thighs, most ham stretches involve hinging the hips forward, to really lengthen the three sections of fibers that make up this muscle group.
Your hamstrings are athletic muscles, that can help us to perform explosive movements, acting as a rubber band being stretched, and released. They’re also key to the gait or walking cycle.
Glutes
Butt muscles that form a large portion of the hips, you have a large maximus, smaller medius, and smallest minimus muscle in your backside. Maximus is the largest, strongest, and most notable, creating most of what is your hips size and shape. Consequently, the role of maximus is controlling movements at the hip such as extension, and external rotation of the thigh.
Abdominal core muscles
You may not realize it, but when you hinge forward at the hips, and stand back up after the wide legged forward bend, your core muscles have to step into decelerate the descent, and extend the spine, respectively. It’s your deeper core muscles, transverse abdominis that stabilize the spine, while the erector spinae muscles by the spine, stand you up from a bent over position.
How To Do Wide Legged Forward Bend
Considered a beginner yoga pose, for many who attempt it for the first time, there’s nothing beginner about it. But the key is having the right setup, being patient, listening to your body, and keeping at it.
Before you thrust yourself into the wide legged forward bend, we recommend checking out the short video demonstration below, and using the written instructions below for reference and tips.
Steps
Note: The first four steps are to prepare your body for the full movement.
Choose a surface where your feet will not slide.
From a standing position, spread your feet apart into a wide stance, creating roughly 4-5 feet of space in between. You want a wide stance but not so wide that you lose stability and balance.
Point your toes forward or slightly inward to activate the inner thighs and glutes, keep your legs straight and engaged, and focus your weight on your outer feet. Place your hands on your hips.
Now hinge forward at the hips, and lower your torso until your upper body is roughly parallel to the floor. Make sure to keep your back straight. Then, slowly stand up straight.
Repeat step 4, but now stretch your arms down to the floor and touch it with your fingertips.
Walk your hands back until your fingers and toes are in line, and press your palms flat on the floor.
Lift your head up and gently stretch toward the sky.
Then drop your head and body down toward the floor, while bending your elbows. Try to relax your upper body.
Gently rest the crown of your head on the floor. Hold this position for a few seconds, trying not to exceed 10 seconds at first.
Now come up onto your fingers, walk your hands forward, and bring your hands on your hips, one at time, then slowly stand up in the starting position.
Tips
Make sure to perform this pose on an appropriate, non-slip surface, such as a yoga mat. Do not try it using socks on a slick floor, as it’s very difficult, and is not good for the groin, and knees.
If you’re not ready to rest your head on the floor in the full wide legged forward bend pose, then simply use your arms to keep your head up, and practice being in this position.
If your head touches the floor too easily, narrow your stance a little.
You can bend your knees slightly if you have tight hamstrings.
Do not try to rush the process. The body usually takes time to open up so that you can move into deeper positions.
You can also use yoga blocks under your hands to help decrease the range of motion, if you can’t reach the floor just yet, or if its uncomfortable.
This Exercise
Target Muscle Group: Hamstrings, glutes, core
Type: Yoga
Mechanics: Isolation
Equipment: Yoga mat
Difficulty: Intermediate
Benefits of Wide Legged Forward Bend
There are the most obvious and then there are some of the not so obvious benefits of folding yoga poses. Let’s see what they are…
Target your thigh and adductor muscles
One of the poses that involves a forward hip hinge, wide legged forward bend favors a hamstrings and adductors stretch. If you play sports or are regularly involved in resistance training or other activities, it’ll benefit you to keep these muscles loose and active. You’ll also help prevent injuries, and the hamstrings are so important for mobility.
Stretch the neck, back and shoulders too!
We hold lots of tension in our necks, shoulders, and backs, especially being slumped over in front of our devices for most hours of the day. Stretching is helping to reduce the long term negative effects of muscle tightness from prolonged inactivity.
Potential benefits of inverted position
It’s important to note that evidence for the potential benefits of inversion training are not conclusive.
However, hanging upside down does create changes in blood flow which may enhance circulation to the brain. Many believe this can enhance cognitive performance. Inversion type training does decompress the spine though, which is said to create more space between the vertebra, allowing better disk hydration and hence greater spine mobility and reduced risk of injury.
The advantages may extend further though, reaching as deep as the lymphatic system, possibly helping to drain the body of toxins. This process is said to only be able to occur via the movement of muscles, and breathing.
Build patience and mental fortitude
One of the most valuable tools in life is patience. The rewarding things require patience, and mental grit. Wide legged forward bend isn’t just picking up a dumbbell and doing a barbell curl, or sitting down in a squat or performing a push-up.
It requires a bit of many things to be able to maintain a wide stance, bend forward, and set your head on the floor. And for many, it won’t be possible the first few attempts.
Common Mistakes During Wide Legged Forward Bend
Here are some common mistakes that may make for a frustrating or painful experience attempting the wide legged forward bend.
Not spreading your feet wide enough
While it is called the forward fold, most people are not contortionists and will need to spread their feet wide enough to reach their head to the ground. Two to three and even four foot of distance between your feet won’t cut it for most. It’s perfectly normal to have a very wide stance, that way you can decrease the distance your head needs to travel.
But… if you’re just starting out, you could assume a narrower stance, and it’s fine if the head cannot yet touch the floor. Give your hips time to open up and then you can get lower and lower.
Forcing yourself into the pose
Forcing the body to do something is hardly ever recommended. In this case, you can pull tight muscles, or increase risk of injuries in the future.
A common and wise piece of yoga advice is to take it slow, and allow your body to open up when it’s ready. That’s why you’ll typically see professionals perform warmup steps before attempting the full pose. With that said, this pose requires decent flexibility.
Variations of Wide Legged Forward Bend
While the basic wide legged forward bend is a phenomenal practice to get into, here are some fun variations to try and challenge yourself while getting additional benefits.
Wide legged forward bend with hands behind your back
It’ll require more balance, and core control, but it’s just one progression that’ll prove you’re ready for something more challenging. Most people should be able to easily reach behind their body and interlock their fingers. It’ll give you a sweet stretch in the delts too!
Steps
Get into a wide stance as explained in the original instructions.
Bring your arms behind your body and interlock your fingers with the palms facing each other.
Slowly drop your torso under control, and then gently rest your head on the floor. If you cannot yet, place an object such as a yoga block between your feet to rest your head on and reduce the range of motion.
Grabbing your toes
For this variation, you’ll grab your big toes with your pointer fingers on each side as you’re dropping into the folded position resting on your head.
Steps
In your straddle stance, hinge forward at the hips, and hook your pointer fingers over and around your big toes.
Keep your elbows bent, pointed up, and try to squeeze your shoulders blades together. Hold this position for the desired time.
With rotation
Like wringing out a wet rag, including a twist in the forward bend will stretch out your oblique muscles that help us to rotate, and bend laterally. It’s also a good technique to help maintain coordination and mobility in the upper body.
Steps
From a bent over position, extend one arm toward the floor and place your palm flat directly in the center between your feet.
Now rotate your torso in the opposite direction of your arm, and reach the free arm straight up toward the sky with the fingers straight.
Now bring the top arm down and switch positions with the other arm, placing your arm in the exact same spot. Then reach up in the opposite direction with the free arm. Repeat for 3-5 repetitions.
Holding the opposite leg
Challenge flexible endurance and stretch your torso by gripping the opposite leg and holding for a static count.
Steps
From the forward fold position, grab your right ankle with your left hand, and bend the right arm behind your lower back. Breathe in, and then breath out as you release and change sides.
Now grab the left ankle with the right hand, and place your left arm behind your back. Hold, and repeat by alternating sides.
Seated forward bend pose
Otherwise called Paschimottanasana, the seated forward fold pose trains a similar technique but with the inversion.
Steps
Sit on the floor with your legs stretched out in front of you. Sit up tall, and pull your toes in toward you.
Inhale, and reach both arms overhead, then exhale and bend forward at the hips.
Reach toward your toes. Stop where you’re able too. If you’re flexible enough, grab one wrist with the other hand and your arms in front of the bottom of your feet.
If you’re flexibility allows, lie face down on your your shins.
Unlock your grip, and with both arms extended past your feet, inhale and sit up to the original position.
Exhale and lower the arms.
That’s the seated forward bend yoga pose.
Here’s a progression technique that you can do if you cannot perform the full pose yet. Use a strap of some type to wrap around the balls of your feet, and slowly try to stretch forward, grabbing the straps closer to your feet as you reach forward.
Wrapping Up
While yoga should incorporate various elements of mental and physical fitness, the wide legged forward bend is a swift and much needed change up from your usual exercises. Combining inversion, stretch, and strength, it’s a pose you should hang-up for the next day and bring it out because of the range of benefits it offers.

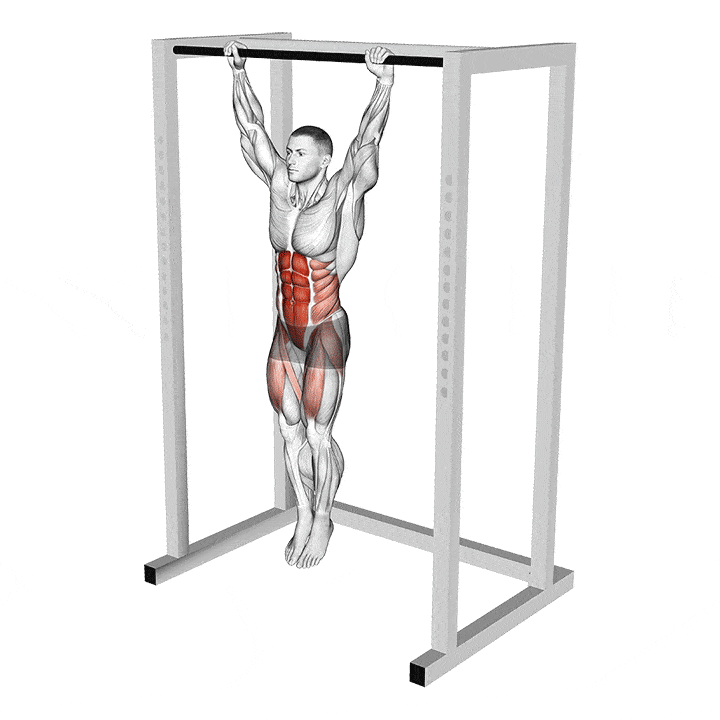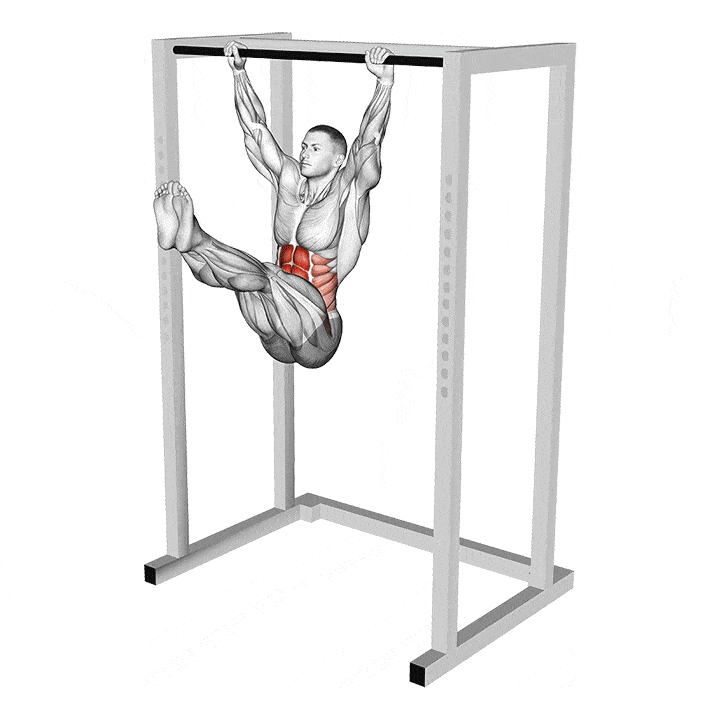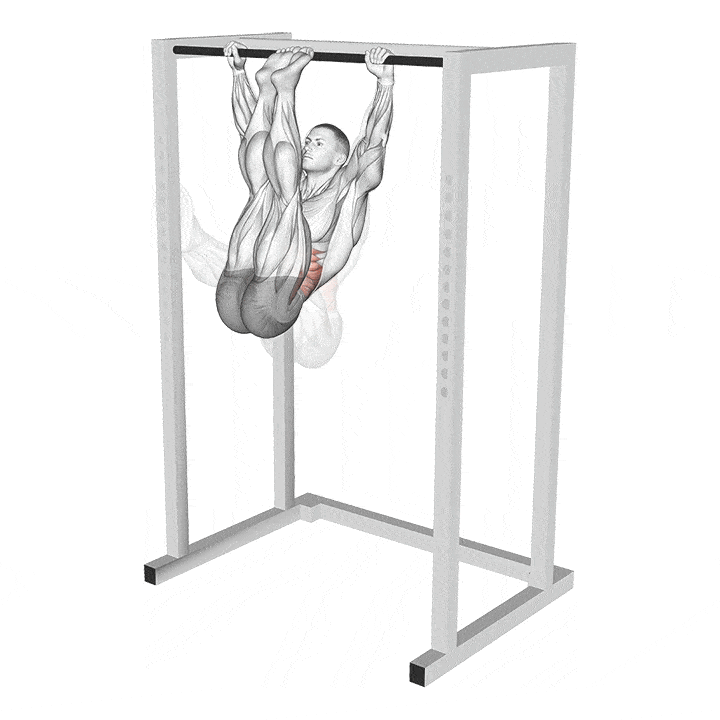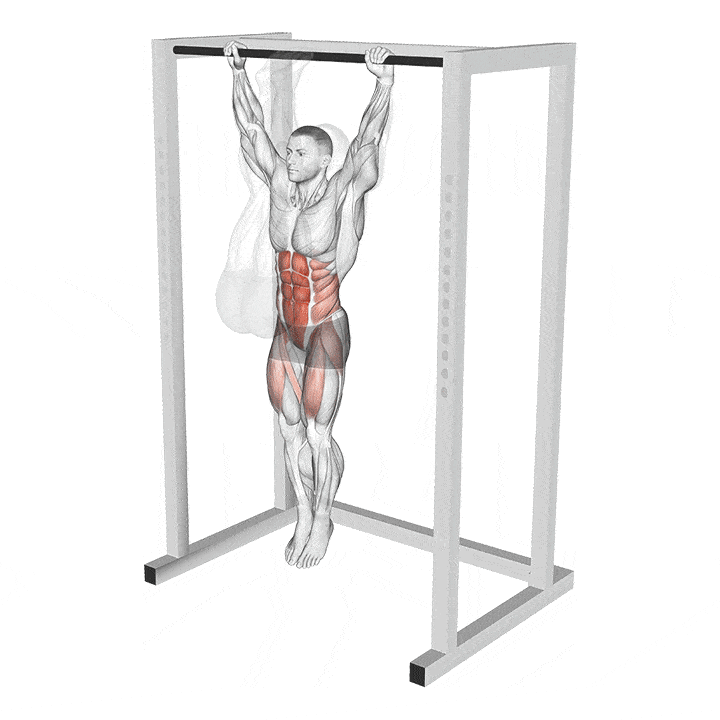
L-Sit Exercise Guide: How To, Benefits, Muscles Worked, and Variations
Some exercises look super easy, but when you try them, you fail to get even in the correct position; the L-sit is one of them.
The L-sit is a classic gymnastic movement that will set your core on fire. On the outside, the L-sit looks very easy. You sit on the floor, plant your hands next to your hips, and lift your hips and legs off the ground. However, this is easier said than done.
Beginners that do not have a gymnastics background will most likely find themselves grinding their teeth while they fail to lift themselves off the floor. I have had newbie exercisers tell me they are anatomically unfit to do the L-sit because they have a long torso and short arms. You might experience the same thing.
However, most people falter at doing the L-sit not because of their body mechanics but because of an incorrect form or a lack of core strength.
Since the L-sit is a bodyweight exercise, most people think that they should be able to do it from the get-go. This, however, is not the case. Like most gymnastic exercises, you will be better off starting with an L-sit progression plan.
In this article, we dive deep into the L-sit and cover its fundamentals, an effective progression plan; the muscles worked during an L-sit, its benefits, proper form, the most common mistakes, and the best variations and alternatives.
What is a L-Sit?
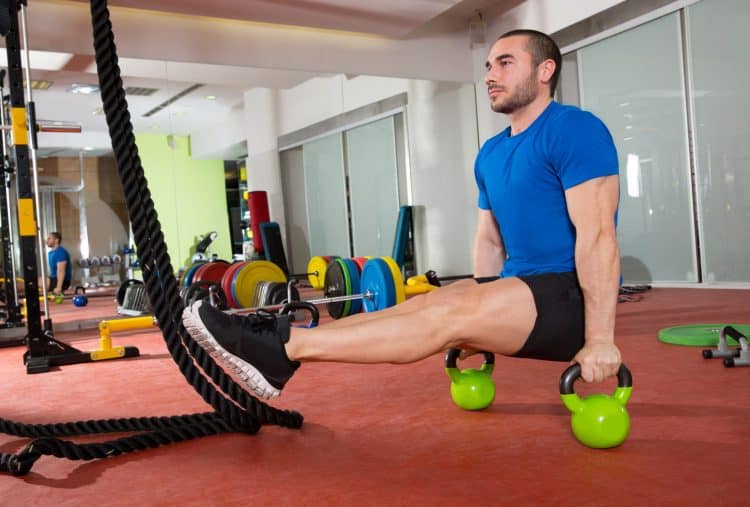
L Sit With Kettlebells
The L-sit is an isometric exercise that improves your core strength and balance. Isometric exercises involve static muscle contraction without visible movement in the joint’s angle. The L-sit is a fundamental gymnastic exercise that grew popular thanks to CrossFit. This exercise is also very popular in the calisthenics circuit.
Besides the conventional L-sit, CrossFit WODs (workout of the day) include several variations of this exercise, including L-sit bar pull-ups and L-sit ring pull-ups. The conventional L-sit demands decent core and hip flexor strength. On the other hand, the pull-up variations also engage most of your upper body, including the biceps, lats, traps, rhomboids, and teres major and minor.
Beginners should start practicing this exercise by placing their hands on an elevated object, such as yoga blocks, or perform this exercise on parallettes or parallel bars. If you still cannot perform this exercise, use the progression exercises listed in this article to build the required core strength.
Muscles Worked During L-Sit
The L-sit works the following muscles:
Abs: The core is the primary target muscle of the L-sit. This exercise requires you to keep your core contracted, resulting in a rectus and transverse abdominal recruitment.
Hip Flexors: These muscles run along the front of your upper thigh. You must engage your hip flexors to keep your legs parallel to the floor throughout the exercise.
Glutes and Quads: This exercise involves keeping your glutes and quads contracted to maintain a stable position.
Triceps: You’ll experience triceps stimulation as soon as you lock out your elbows and lift yourself off the floor. Furthermore, pointing your fingers behind you will engage your biceps.
Shoulders: The L-sit involves actively pushing into the floor, which will result in a sick deltoid pump. You will also experience trapezius muscle stimulation as this exercise requires pushing your shoulders back and down.
Benefits of L-Sit
Adding the L-sit to your training regimen entails the following benefits:
Build a Solid Core and Six-Pack
L-sits can help you build abs of steel. Holding your legs parallel to the floor while extended in the air will work muscles in your core that you didn’t know existed. A strong core can also improve your performance in compound exercise and daily functioning.
Enhance Stability and Balance
A strong core translates to robust stabilizer muscles, which can significantly improve your stability. The L-sit also improves your balance and performance in handstands, push-ups, toes-to-bar, deadlifts, and barbell squats.
Improve Posture
The L-sit strengthens the muscles responsible for maintaining an upright and stable spine, which can help improve your posture. This is an excellent exercise for people that spend most of their day sitting.
Boost Hip Flexor Strength
The hip flexors help bring the knee closer to the chest, meaning they are used in activities such as walking, running, jumping, and kicking. Since the L-sit involves holding your legs parallel to the floor, it engages and strengthens your hip flexors.
How To Do L-Sit
This is how to perform the L-sit with the correct form:
Steps:
Sit upright on the floor with your legs extended in front of you.
Place your hands on the floor next to your hips. Spread your hands and curl your fingers slightly so that your fingertips are pushing into the floor.
Straighten your arms and lock out your elbows. Simultaneously engage your lats and push your shoulders back and down.
Push your palms into the floor, engage your core, and lift your hips and legs off the floor. Your legs should be parallel to the floor throughout the exercise.
Your body should resemble an “L” at the top of the exercise.
Hold the position for as long as possible or a specific time.
Return to the starting position.
Repeat for the desired number of sets.
L-Sit Tips:
Keep your quads and glutes contracted and your toes pointed throughout the exercise.
Place your hands on yoga blocks if you have trouble pushing yourself off the floor.
Spreading your hands and pushing your fingertips and palms into the floor will help you maintain your balance.
Maintain an upright torso while pushing yourself off the floor. Bending forward will make lifting your legs off the floor more difficult.
Advanced exercises can wear a weighted vest to make this exercise harder.
In This Exercise:
Target Muscle Group: Abs
Type: Strength
Mechanics: Isometric
Equipment: Bodyweight
Difficulty: Intermediate
Best Rep Range: 30-60 seconds
L-Sit Progression Exercises
Use the following L-Sit progression exercises if you lack the strength to perform the conventional variation of the exercise:
Step 1: Boat Hold
The boat hold is an excellent core exercise that is suitable for trainers of all experience levels. It will help you build the foundational strength for L-sits.
Steps:
Sit upright on the floor and extend your legs in front of you.
Cross your arms in front of your chest.
Engage your core and tilt your torso backward. Anything between 1 to 2 o’clock will work.
Lift your legs off the floor while keeping your knees locked out.
Hold this position for as long as possible.
Pro Tip: If you have trouble maintaining your torso in position, place your hands next to your hips on the floor.
Step 2: Elevation
This L-sit progression exercise involves using an elevated platform, such as yoga blocks or parallettes. Furthermore, you will focus on lifting your hips off the floor while keeping your heels grounded.
Steps:
Sit on the floor with your legs extended and place parallettes on each side of your hips.
Grab the bars with an overhand grip. Your elbows will be bent at this position.
Extend your elbows while pushing your shoulders back and down. You must lock out your elbows at the top, and your hips should be off the floor.
Your heels should be the only point of contact with the floor.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Repeat for 15-20 reps.
Pro Tip: Avoid using your legs to push yourself into a lockout position. Conversely, beginners can bend their knees slightly and push their heels into the floor to generate force.
Step 3: Alternating Leg Lift
In this L-sit progression exercise, you’ll focus on the lockout and lifting one leg at a time.
Steps:
Sit upright on the floor and extend your legs in front of you.
Place your hands on your hip side.
Push your shoulders down and back, and extend your elbows. Your hips should be off the floor at this point. Your heels should be the only point of contact with the floor.
Contract your abs and lift your left leg off the floor until it is parallel to the floor.
Return your left leg to the floor and repeat with the right leg.
Alternate between sides for the recommended reps.
Pro Tip: As you get better at this exercise, lift your legs as high as possible without bending your knees. Hold for a five-second count before lowering your legs to the floor.
Step 4: Tuck Sits (on an elevated platform)
Tuck sits can be incredibly effective in building the required core strength and confidence to perform the L-sit. This is also the first exercise where we bring together most of what we’ve learned up to this point.
Steps:
Sit upright on the floor and extend your legs in front of you.
Bend your knees and plant your heels on the floor as close to your hips as possible.
Place your hands on the sides of your hips.
Push your shoulders back and down and extend your elbows to lift your hips off the floor.
Pull your quads to your chest as you lift your hips off the floor.
Hold for as long as possible.
Pro Tip: Holding your legs close to your chest is easier than maintaining straight legs. You can also use an elevated platform for this exercise if you have difficulty doing it on the ground.
Step 5: Tuck-Sit to L-Sit (on an elevated platform)
We push into the next gear with this L-sit progression exercise. This exercise begins in the tuck sit position and requires you to work into a full L-sit.
Steps:
Follow the steps mentioned above to get into a tuck-sit position.
While keeping your back straight, extend your legs until they are parallel to the floor.
You might lose balance as you extend your legs. In this case, pull your legs back to your chest.
Hold the L-sit position for as long as possible.
Pro Tip: Use elevated platforms for this exercise if you cannot do it on the floor. Performing this exercise on an elevated platform will ensure you have enough space to pull your legs into your chest without having your feet touch the floor.
Step 6: L-Sit
After you have spent enough time practicing the tuck-sit (step four) and tuck-sit to L-sit (step five), the conventional L-sit will be the natural next step. Use the steps mentioned in the “How To Do L-Sit” section to perform the L-sit.
Common Mistakes While Performing L-Sit
Avoid making the following mistakes while performing the L-sit to get the best bang for your buck:
Rounding Back
This is one of the most common mistakes exercisers commit while performing the L-sit. You must avoid hunching your back as you extend your elbows to lift your hips off the floor. Rounding your back makes it harder to lift your legs off the floor.
Skipping Warm-Up
Since the L-sit is a bodyweight exercise, many people skip warming up their bodies, which can hamper their performance. Before doing this exercise, you must spend 5-10 minutes warming up your wrists, arms, shoulders, abs, glutes, hamstrings, and legs to ensure you’re primed to hold this position for as long as possible.
Not Locking Out Your Elbows and Pushing Your Shoulder Back and Down
Maintaining soft elbows while performing the L-sit is a rookie mistake. You must lock out your elbows to ensure optimal stability and balance. Soft elbows usually lead to the rounding of the back. Also, you must push your shoulders back and down to gain an optimal height to lift your legs off the floor comfortably.
Variations and Alternatives of L-Sit
Add the following L-sit variations and alternatives to your training regimen to build a shredded midsection:
L-Sit Pull-Up
After mastering the L-sit, you can progress to the L-sit pull-up for an additional challenge. Most people tend to use their legs to perform a pull-up; however, since you’ll be holding your legs in front of you in this variation, this exercise is much more difficult than the conventional pull-up.
Steps:
Stand under a pull-up bar.
Grab the pull-up bar with a shoulder-wide grip.
Lift your legs until they are parallel to the floor.
Perform a pull-up while holding this position until your chin is over the bar.
Return to the starting position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Beginners can perform hanging L-sit until they develop the core strength to perform a pull-up.
L-Sit Pull-Up on Rings
Since you can pull your head between the rings, this exercise is a little easier than the L-sit pull-up on a pull-up bar, where you must pull your body at an angle. However, performing it on the rings requires more core stability.
Steps:
Jump and grab the gymnastic rings with a neutral (palms facing each other) grip.
Lift your legs until they are parallel to the floor.
While keeping your core contracted, perform a pull-up.
Return to the start position.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: Keep your shoulders pulled back and down while performing pull-ups.
Plank
You need a strong core to perform the L-sit. Planks are an incredibly effective beginner-friendly exercise to build the requisite core strength.
Steps:
Get on all fours on the floor.
Place your elbows under your shoulders and plant your forearms on the floor. Your forearms should be parallel to each other.
Extend your legs behind you.
Your body should be in a straight line from head to toe.
Hold this position for as long as possible.
Pro Tip: As you get more experienced, make this exercise more difficult by wearing a weighted vest or placing a weight plate on your back.
Check out our complete plank guide!
Hollow Body Hold
Hollow body hold is an excellent exercise to build core strength. It is used widely in CrossFit gyms to improve your kipping pull-up mechanics.
Steps:
Lie supine on the floor. Extend your arms over your head.
Contract your abs and lift your legs off the floor. Simultaneously lift your shoulders and arms toward the ceiling.
Your hips and lower body should be the only point of contact with the floor.
Hold the position for as long as possible.
Pro Tip: Focus on actively pushing your arms and legs toward the ceiling throughout the exercise.
Check out our complete hollow hold guide!
Toes-To-Bar
Performing toes-to-bar requires significant core strength. You must keep your core engaged throughout the exercise to avoid swinging between reps.
Steps:
Grab a pull-up bar with an overhand shoulder-wide grip.
Lock out your elbows.
Press on the bar using your lats; this will pull your torso behind the bar.
Simultaneously lean back slightly and raise your legs toward the pull-up bar.
Touch your toes to the bar.
Lower your legs to the starting position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Perform a kip to stabilize your body and generate momentum to raise your toes to the bar.
Wrapping Up
The L-sit is an isometric exercise that will help you build a strong core, strengthen your stabilizers, improve your balance and posture, and boost hip flexor strength. Mastering this exercise is a must if you are into gymnastics or CrossFit.
The five beginner-friendly progression exercises listed in this article are excellent movements to work toward an L-sit. Perform the variations thrice weekly, and you should be able to perform a picture-perfect L-sit by the end of six weeks. Best of luck!
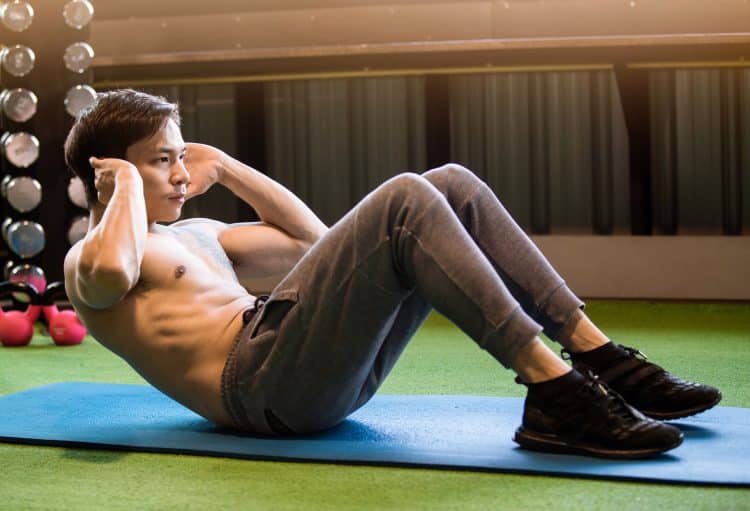

Sit-Up Exercise Guide: How To, Benefits, Muscles Worked, and Variations
The sit-up is one of the most popular exercises. It is taught in school PT classes, done at home, and is a part of the most complex metabolic conditioning workouts. This versatile exercise works your midsection and can help build a shredded six-pack. Sit-ups can also improve your posture, core strength, and balance.
Most people have a love-hate relationship with sit-ups. They love the results but hate doing the exercise. Although sit-ups look easy, they will have you begging for mercy halfway through a set. They are especially difficult for beginners that lack abdominal strength and endurance. Furthermore, many exercisers find sit-ups boring.
That said, thanks to their effectiveness and results, sit-ups are a part of most training regimens, and this doesn’t appear to be changing any time soon.
Notably, sit-ups are often confused with their cousin — crunches. Both these exercises look similar to an untrained eye, and ‘sit-ups’ and ‘crunches’ are often used interchangeably. However, these exercises have significant differences.
The biggest difference between the two exercises is their range of motion. The crunch is roughly a quarter of the sit-up’s range of motion (ROM). While performing the crunch, your lower back is always in contact with the floor; in fact, your upper back, too, barely leaves the floor. However, as the name implies, the sit-up involves sitting upright at the top of the range of motion.
The sizeable difference in the ROM leads to the isolation of your abdominal muscles while performing the crunch. On the other hand, sit-ups stimulate multiple muscle groups, including the abs, hip flexors, hips, and lower back.
In this article, I take you over the fundamentals of the sit-up, the muscles worked during this exercise, its benefits, proper form, the most common mistakes, and the best variations and alternatives.
What is a Sit-Up?
A shredded midriff and a six-pack are considered the epitome of fitness, and the sit-ups help you achieve just this. This exercise involves contracting your abs with every rep, which helps you develop a chiseled midsection. The sit-up is an isolation exercise that trains your abdominal muscles.
To perform a sit-up, lie supine and place your feet flat on the floor. While holding your hands at the side of your head, lift your torso off the floor by contracting your abs. Your upper body should be almost parallel to the floor at the top of the motion — anything between 12 and 1 ‘o clock is acceptable.
Since performing the sit-up requires no equipment, you can do it anywhere. As you gain more experience, you can make the exercise more challenging by incorporating additional resistance using a weighted vest or holding a dumbbell, weight plate, or kettlebell in front of your chest.
The sit-up primarily works the upper and middle abs. However, you can achieve better lower ab stimulation by performing this exercise on a decline bench. Conversely, beginners can perform this exercise on a stability ball, as it provides a little assistance at the bottom of the movement.
Muscles Worked During a Sit-Up
The sit-up works the following muscles:
Abs
Sit-ups work the rectus and transverse abdominis. The rectus abdominis is the long vertical muscle that runs down the front of your abdomen. It is also known as the six-pack. On the other hand, the transverse abdominis muscle wraps around the abdomen and provides stability and support to the spine and internal organs. The transverse abdominis plays a crucial role in core stability while performing sit-ups and other exercises.
Obliques
Sit-ups work the internal and external obliques. The external obliques are the fish-gill-like muscles at the side of the rectus abdominis and help with trunk rotation and bending movements. The internal obliques lie under the external obliques and also assist with trunk rotation and bending.
Hip Flexors
Hip flexors run along the front of your upper thigh. They are responsible for flexing the hip joint. Hip flexors engage during the sit-up’s concentric (upward) motion to lift the torso toward your thighs.
Hips
Your hips provide stability during the sit-ups. The hip joint flexion also allows you to move from a lying to a seated position. Strong hips will also help prevent lower back strain while performing the exercise.
Lower Back
Your lower back, especially the erector spinae, plays a crucial role by providing stability and maintaining proper spinal alignment while performing sit-ups. It helps you avoid rounding your lower back during the concentric motion.
Benefits of Sit-Ups
Here are the advantages of adding sit-ups to your training regimen:
Improved Core Strength
Performing sit-ups helps you build a stronger core, the benefits of which carry over to compound exercises. Furthermore, it improves your performance in daily activities, which helps you get done more quickly and effectively.
Boost in Athletic Performance
A strong core can help improve your athletic performance. Irrespective of your sport, sit-ups can improve your posture, stability, and form, which can boost your overall performance and results. It will also significantly delay the onset of fatigue.
Increase in Muscle Mass
Sit-ups can help build muscle mass and strength in the abdominal and hip muscles. This exercise can also be a valuable indicator of muscle loss. A 2016 study found that older women who could perform sit-ups were less likely to lose muscle mass with age. [1]
Improved Balance and Stability
Sit-ups help build a strong core, which improves your balance and stability. It can improve your performance in daily activities and other exercises. A stronger core can also help prevent falls in older adults.
Better Posture
Building a strong core helps keep your hips, spine, and shoulders in alignment, which helps promotes a better posture. Folks that have a desk job or spend the majority of their days sitting should make sit-ups a constant in their training regimen.
No Equipment
Sit-ups are a bodyweight exercise that you can do anywhere at your convenience. Plus, you can program this versatile exercise into most training regimens and use additional resistance for better results.
How To Do Sit-Up
This is how to perform the sit-up with the correct form:
Steps:
Lie supine on the floor. Bend your knees and plant your feet on the ground.
Hold your hands next to your ear.
Raise your torso off the floor by contracting your abs. Exhale sharply during the concentric movement.
Your torso should be perpendicular to the floor at the top of the movement.
Contract your abs as hard as possible.
Inhale as you slowly lower your torso to the floor.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Sit-Up Tips:
Your head should remain neutral throughout the range of motion. Bending your head during the concentric movement puts unnecessary strain on your neck.
Avoid interlacing your fingers behind your head as it increases your odds of bending your neck during the upward motion. Crossing your arms in front of your chest is a better alternative if you don’t prefer holding your hands next to your ears.
Exhale and contract your abs during the upward motion.
Keep your back straight throughout the range of motion. Rounding your back can strain your lower back.
Use an elevated surface to anchor your feet. This will help keep your feet planted on the floor and allow you to establish a better mind-muscle connection.
It is common for beginners to experience ab cramps while doing sit-ups. Stop the exercise if you experience cramps and stretch out your abs.
In This Exercise:
Target Muscle Group: Abs
Type: Strength
Mechanics: Isolation
Equipment: Bodyweight
Difficulty: Beginner
Best Rep Range: 8-12
Common Mistakes While Performing Sit-Up
These are some of the most common sit-up mistakes that you must avoid to maximize results and lower the risk of injury:
Using a Limited Range of Motion
Many people leave gains on the table by following an incorrect form and a restricted range of motion. Your back should be on the floor at the bottom, and it should be perpendicular to the floor at the top.
Using Momentum
Exercisers try to make this exercise easier by using momentum. Avoid throwing your arms toward your legs to lift your torso off the floor. Driving through your neck during the concentric motion can cause neck sprains.
Neck Strain
Sit-ups are a demanding exercise. You must keep your head, neck, and torso in a straight line throughout the exercise for optimal ab stimulation. Folks that interlace their fingers behind their necks or throw their heads forward during the concentric motion increase their odds of injury during the exercise.
Rounding Your Back at the Top
Think of your torso as a hardboard while doing sit-ups; it should move in a straight line. Rounding your back at the top of the motion causes unnecessary lower back strain. It will also hamper your form during the eccentric (lowering) motion.
Improper Breathing
Many people make the mistake of holding their breath while performing crunches. Breathing correctly while performing crunches can help amplify your results. Exhale sharply during the concentric motion and inhale during the eccentric motion.
Not Adding Variety To Your Training Regimen
Although crunches are a great exercise to build a shredded midriff, your training program must include exercises that train your torso from different angles for overall development. It will ensure you build a bulletproof midsection. This point is a perfect segue into…
Variations and Alternatives of Sit-Ups
Add the following sit-up variations and alternatives to your training regimen to build a shredded midsection:
Weighted Sit-Up
Weighted sit-ups are for advanced athletes. It involves holding additional resistance, such as a dumbbell, kettlebell, or weight plate, in front of your chest. The exercise form for this variation will remain the same as the conventional sit-up.
Pro Tip: Use an appropriate weight that allows you to keep your head and torso in a straight line throughout the range of motion. Using a weight that is too heavy can cause you to bend your head forward.
Stability Ball Sit-Up
Stability ball sit-ups are an excellent exercise for beginners as the exercise ball acts as a support at the bottom of the movement and delivers a pop that pushes you into the next rep.
Steps:
Sit upright on an exercise ball and plant your feet flat on the floor.
Hold your hands at your ear level and slide forward so your lower and middle back are on the exercise ball. Your shoulders should be hanging off the ball.
Exhale and contract your abs to lift your torso toward the ceiling.
Your torso should be perpendicular to the floor at the top.
Slowly return to the start position.
Rinse and repeat.
Pro Tip: Some trainers go down too fast during the eccentric motion to use the bounce from the ball to complete the next rep. However, this reduces the effectiveness of the exercise and increases your risk of lower back injury.
Reverse Crunch
Sit-ups and crunches work the upper and middle abs. On the other hand, reverse crunches focus on your lower abs. During a sit-up, your lower body remains steady while your upper body moves. The reverse is true for the reverse crunch.
Steps:
Lie with your back on the floor. Your body should be in a straight line at the starting position.
Place your hands under your hips for leverage.
Lift your feet off the floor so your heels are a few inches off the ground.
Pull your quads to your chest while bending your knees.
Your hips should be off the floor at the top.
Slowly return to the start position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Make this exercise more challenging by performing this exercise on an elevated platform, such as a flat bench. Let your feet touch the floor at the bottom of the movement for better abdominal stimulation.
Check out our complete reverse crunch guide!
V-Up
The V-up is a great exercise to build core strength, balance, stability, and coordination. This exercise targets your entire midsection, including your upper, middle, and lower abs.
Steps:
Lie flat on your back on the floor.
Extend your arms toward the ceiling so they are perpendicular to the floor. Simultaneously, raise your legs off the floor.
In a single motion, lift your legs toward the ceiling and bring your hands toward your feet.
Your body should resemble a “V” at the static contraction point at the top.
Slowly lower to the starting position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Experienced lifters can make this exercise more challenging by wearing ankle weights and holding a pair of dumbbells.
Check out our complete V-up guide!
Crunch
The crunch is the easier version of the sit-up and roughly involves a quarter of the sit-up’s range of motion. This exercise is a better option for people trying to maintain constant tension in their upper abs or undergoing rehabilitation.
Steps:
Lie supine on the floor. Bend your knees and plant your feet flat on the ground.
Hold your hands next to your ears.
Contract your core, and exhale as you lift only your head and shoulder blades off the ground.
Slowly lower to the starting position.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: Like with sit-ups, you can perform crunches while holding onto weights or on a decline for greater abdominal stimulation.
Check out our complete crunch guide!
Bicycle Crunch
The bicycle crunch is one of the few ab exercises that simultaneously work your lower and upper body. This ab exercise is incredibly effective at working your lower and upper abs and obliques.
Steps:
Lie flat on the floor while facing the ceiling.
Hold your hands next to your ears and lift your legs off the floor.
Exhale as you bring your right knee to your chest while driving your left elbow to the knee.
Return to the starting position.
Repeat on the other side.
Alternate between sides for the recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Focus on your breathing to make the most of this exercise. Breathe out during the concentric motion and breathe in during the eccentric motion.
Check out our complete bicycle crunch guide!
Wrapping Up
The sit-up is a versatile beginner-friendly exercise that will help improve your core strength, balance, stability, and posture, boost your athletic performance and muscle mass, and can be done anywhere at your convenience.
Although sit-ups are a great exercise to work your midsection, your ab training routine should include a variety of movements to ensure overall development. Remember, building a six-pack requires patience, dedication, commitment, and a low body fat percentage. Nail each aspect of your training, diet, and recovery regimen, and your abs will rival those of Greek statues. Best of luck!
Related: Crunch and Sit-Up Alternatives
References
Abe T, Yaginuma Y, Fujita E, Thiebaud RS, Kawanishi M, Akamine T. Associations of sit-up ability with sarcopenia classification measures in Japanese older women. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016 Dec;8(4):152-157. doi: 10.1556/1646.8.2016.4.7. PMID: 28180004; PMCID: PMC5283773.
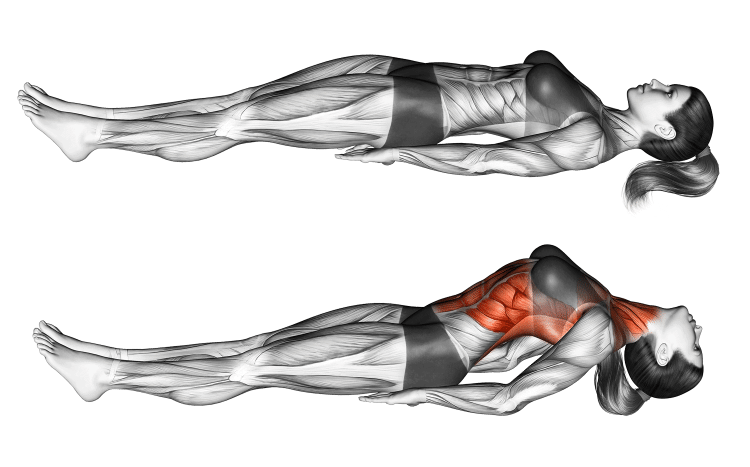
How to Do Fish Pose (Matsyasana): Muscles Worked, How-To, Benefits, and Variations
One of the fun parts about learning yoga poses is that you can imagine how the name correlates to what the movement looks like. Fish pose is a rear bending, counterasana (to the shoulder stand) technique, where you prop up on the elbows, lift the heart toward the sky, draw the head back, and gently settle the crown of the head on the floor.
The term matsyasana, its sangskrit name, is also used to identify this pose, matsya or “fish”, and asana, “posture”.
The benefits of this pose extend (pun intended) from the head down to the hips, relieving tension in the neck and throat, lengthening the back and spine, strengthening the arms and delts, and refreshing the abdomen and midsection.
Fish pose is a good counter to keyboard neck, while targeting the throat energy center, chest, and abdomen where we hold lots of anxious tension from stressful habits.
In this guide, you’ll find the best fish pose techniques, while learning about the benefits, beginner variations, and how to make Matsyasana more challenging and advanced.
Muscles Worked During Fish Pose Matsyasana
The fish pose is an opportunity to stretch and strengthen your upper body muscles. The following section is for those who’d like to better understand how these muscles work, their location, and benefits.
Back
The fish pose is a type of backbend pose where the elbows help support the upper body. It’s similar to a bodyweight variation that works the back muscles. However, in a yoga pose, you’ll strengthen the back via an isometric hold, rather than performing actual repetitions with a positive and negative component.
Having several muscles in the back, each has a special role, moving the shoulder blades and arms.
Arms
The arms have an important role in supporting your bodyweight as you tilt your head back onto the floor. Without them it’s not happening. Try the pose and notice that it requires strong arms and shoulders. The tree heads on the ear upper arm, aka triceps are great for stabilizing the arm while the back delts keep the arms behind you.
Deltoids
Fish pose also creates resistance for the shoulders to support, stabilize and decelerate the body when dropping the head back. The anterior delt stretches out when reclining on the elbows, while the back delts decelerate the drop, and keep you up.
Core muscles
No one every thinks about stretching the core muscles and midsection. Yoga techniques like fish pose give us an excuse to do so. Made of the abdominal muscles both deep and superificial, obliques, and spinal column muscles, the torso has many muscles that stabilize our trunk and help us bend in various directions.
How To Do Fish Pose Matsyasana
Not too difficult, most reasonable fit people have the ability to get into a fish pose. Use the following step by step instructions and video demonstration to guide your technique. Then, once you’ve mastered it, or if you need a regression, scroll down for some awesome variations.
Steps
Come onto your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. You also want to keep your lower back flat on the ground so there’s no space underneath.
Slide your hands under your butt, tucking your elbows under your back as close to together as possible, then straighten your legs.
Inhale deeply, then sit up halfway, look down at your feet, and place your elbows and forearms under your back in a reverse plank to hold yourself up.
Now lift your chest, roll your shoulders back, and slowly drop the top of your head onto the floor. Balance gently on your elbows and head. Hold this position for 10-15 seconds.
Slowly undo the pose by lying flat on your back, bending your knees, and moving your arms out from underneath your back.
Spread your legs a few feet apart, and move your arms slightly out away from your body in what’s called a corpse or Shavasana pose. Stretch your neck by moving it to the left and right. Remember to breathe in and out.
Now bring your feet together, reach your arms back overhead, and inhale. Then bring your arms back to a resting position next to your body and exhale.
Then slowly sit up.
Here’s a beautifully done tutorial on the fish pose Matsvasana.
Tips
Ideally, you should not be an absolute beginner before performing this exercise. Fish pose places the neck in extension and loads the spine, therefore, you should be somewhat fit, and aware of your body before attempting this technique.
We highly recommend using a yoga mat or soft surface for this pose for comfort, support, and to avoid hitting your head hard on the floor.
If you’re an absolute beginner, we recommend having something to support your back like a junior bolster, or some yoga blankets to prop you up roughly five to six inches high.
It’s important to not place too much weight on the head, the hips and shoulders be supporting most of your weight.
It’s crucial that your head is aligned with an even spine, not allowing your head to just fall back at a sharp angle.
This Exercise
Target Muscle Group: Back, abdomen, neck
Type: Yoga
Mechanics: Isolation
Equipment: Cushioned surface, exercise mat, junior bolster (Optional), yoga blankets (Optional), yoga blocks (Optional)
Difficulty: Intermediate
Benefits of Fish Pose Matsyasana
Fish pose incorporated a backbend which has many benefits in itself. Here are the highlights of this yoga technique.
Stretch your neck, chest, shoulders, back and throat muscles
Stretching is a healthy habit for healthy, flexible, mobile, and strong muscles. Functional joints that bend and move can only do so when a muscle contracts and expands. If they’re tight, you’ll have limited range of motion, and open yourself up for injuries.
The fish pose is a type of backbend technique that places the body in a position to lengthen the abdominal muscles in the core, the spine, back, neck, and even the front deltoids. It’s so useful that you could do it everyday.
Interrupts negative affects of declining posture
Let’s face it, our postural muscles take lots of abuse especially nowadays, due to being so immersed in the dopamine that comes out of our electronic devices. Forward head posture is a pose itself, although not a good one.
Fish pose does the opposite, helping to improve and reverse this common modern problem. Your chest, spine, shoulders, and neck are all affected from bad stance, and doing the opposite is part of the solution.
Counter stretch tech neck
Forward head posture, turtle neck, or whatever you’d like to call it… a common modern body posture where the neck is far in front of the head. This can cause pressure, sore muscles, a weak neck, more stress, and it’s bad news. The fish pose counters this posture by pulling the head back and stretching the muscles in the neck.
Target the stress centers
Fish pose is a triple whammy for relaxing and shedding off some stress. It targets the throat chakras (associated with expression, and confidence), the stomach muscles, and opens up the chest which are key areas we feel noticeable discomfort when anxious and stressed.
Opening up the chest is also good because we lean forward so much looking at our phones. This can cause thoracic outlet syndrome where the nerves, veins, and arteries become compressed in the neck and chest, causing numbness and the tingles in the arms, shoulders, and neck.
Common Mistakes While Performing Fish Pose
In a pose like this one, you want to be sure to avoid mistakes that could place you in a dangerous position.
Too much weight on the head
What you don’t want to do is focus on leaning your weight back on your head. Although it’s tempting! Instead, use your legs, core, back, arms and shoulders to control the movement, then gently tip the crown of your head on the floor into the fish pose.
A helpful trick is to try and distribute 80 percent of your weight through the legs, core and back, while only allowing 20 percent of your weight to shift onto the head.
Steep drop off at the head
If you’re in the correct position from toe to head, then you should be in the proper alignment to safely tilt your head back and rest it on the floor. The mistake is letting your head snap back, steeply bending at the neck. Think of arcing your torso in a semi rainbow shape, actively engaging your back muscles and shoulders to help you get in an accurate and safe pose.
Too much uneven (Lower) back arch
There does need to be some lower back arch to effectively complete the fish pose. But you don’t want to overdo it. You see, the lower back is more mobile compared to the upper back. And if you don’t have a proper hold on your positional abilities it’s easy to overcompensate and overarch your lower back. While that’s not reciprocated for the upper back.
This can cause issues in the disc fluids in your spine and hence, result in pain while making you more susceptible injuries.
The solution: Focus on lengthening your spine, lifting the chest toward the sky, and pulling the shoulders back to create more arch in the upper back, and torso as a whole.
Variations of Fish Pose Matsyasana
These variations can make the fish pose easier, more challenging, or touch an area that the basic fish pose doesn’t. See some common variations below.
Fish block with yoga block under the back
If the basic fish pose is too hard, yoga blocks are much appreciated. It’ll support your back so that you can rest in the arched position, and focus on your breathing with less muscular effort.
Steps
Place the block on the mat standing on its long end.
Lie back on the block so it’s across both shoulder blades, then straight your legs, and relax your arms by your sides after you’ve found a comfortable position.
Drop your head back until its resting on the floor. You may need to adjust the block under your back, then continue the technique. Bring our feet together and relax your body.
When you’re ready, lift up on your elbows, remove the block, and then lie flat on your back in the corpse pose. Rest here, then slowly get up.
For more support, use a block or junior bolster under your head and neck too.
Fish pose in lotus or with legs crossed
You can do a more basic or advanced version of fish pose with legs crossed. You can cross your legs under your bottom, or if you have good flexibility, you can cross them over your your upper thighs. The former is good for beginners, while the former will take more time.
Both will stretch the hips and groin, supporting healthy movement in the hip flexors and lower body.
Steps
While lying on your back with your arms under your body, cross your legs under your butt.
Proceed to lift up onto your forearms, and pull your head back to the floor.
Camel pose
More of a preparatory technique, the camel pose is a modified exercise that includes a backbend while sitting upright. It still carries all the same benefits, but is just performed a little differently to the fish pose.
Steps
The following instructions and video tutorial demonstrate two phases of the camel pose. One to prepare you for the backbend, and then the actual technique.
Begin in a vajrasana position sitting on the floor with your knees bent and calves under your bottom.
Stand on your knees, so that your shins and the top of your feet are in contact with the mat, and your torso is tall and upright. Widen your legs into a comfortably balanced position.
Now place your hands on your lower back, with the fingers pointed down.
Inhale, then slowly push your hips forward, while slowly arcing your upper body, leaning back, exhaling, and shifting your gaze up.
Repeat this a few more times.
Inhale, slowly push your hips forward while exhaling, slowly lean back and bring your arms down to your ankles. Arch your torso and drop your head back toward the floor, so the crown of the head is pointing straight down.
Inhale, then transition to the child’s pose where you lean forward into the floor while outstretching your arms forward.
Flying fish pose
You’ll engage more core, hips, and anterior deltoids, while the flying fish pose includes muscle strengthening components involving the legs and arms. Consequently, it’s more advanced but also more risky because now there’s more weight on the head and neck. So you need to be proficient in the regular fish pose, and you need to understand how to safely focus your weight through your body.
Steps
Note: For the flying fish variation, start with your arms by your sides, not underneath your back and butt.
From the fish pose position with your head back and resting on the floor, lift your legs until they’re roughly 45 degrees to the floor.
Now extend your arms in the same direction as your legs, so they’re roughly parallel.
Hold for about 10 seconds.
To undo the pose, bring your elbows to the supporting position, then slowly drop your legs down to the floor.
Reverse plank
While it’s not technically a type of fish pose, you’re already in a similar position. The reverse plank is arguably more challenging than basic plank where you’re facing the floor, and it will help to strengthen the muscles that we use in a fish pose.
FAQs
Who should not do the fish pose?The people who should avoid fish pose are those suffer from blood pressure issues, migraines, vertigo or injuries in the neck, back, and spine.
How long should I hold the fish pose position? Try to maintain the fish pose for 10-15 seconds which is approximately 3-5 breaths.
We recommend using props like yoga blocks or blankets if you want to hold the pose for longer and up to a minute or more.
Wrapping Up
Fish pose is a technique that’ll get you excited to get down on the mat, because it tackles elements that we’re not typically used too. Stimulating the throat chakras, expanding the pecs, stretching the abdominals, and unraveling bottled up tension and stress is an easy sell.
This guide has everything you need to simulate matsyasana, and if you’re not ready or a novice, there are beginner techniques, as well as a bigger challenge in more advanced versions. We strongly recommend checking out the fish pose tips section and don’t skimp over the common mistakes as this meditation includes neck and spine extension. But it can be performed perfectly safe with attention to proper technique!
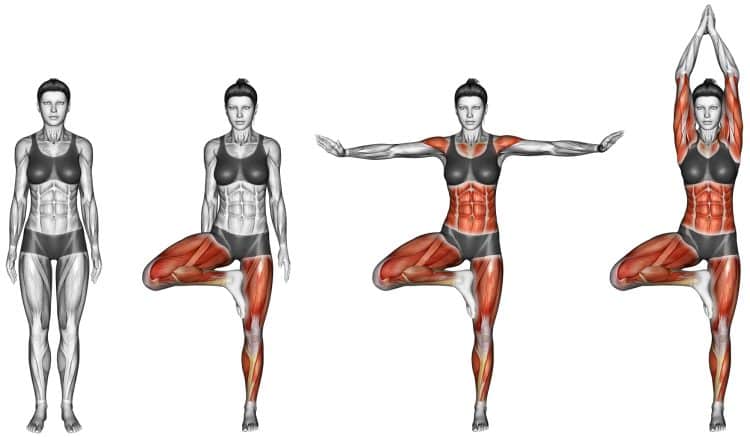
How to Do a Tree Pose (Vrksasana): Muscles Worked, Benefits, and Variations
Tree pose, also known as Vrksasana is a body posture reminiscent of a healthy, tall, and resilient tree. Rooted down by the feet, and supported by the pelvis and core muscles, this yoga technique combines balance, coordination, flexibility, pelvic stability, core strength, and upper body mobility. But you’re also reaping the rewards of increased focus, and concentration while opening the hips, lengthening the spine, and strengthening the legs and feet.
For such a simple pose, Vrksasana sure carries along lots of advantages, and there are lots of reasons to do it daily. In this guide, we want to walk you through a proper tree pose while discussing the advantages, drawbacks, commonly performed mistakes and more.
Muscles Worked
While the tree pose is NOT a “muscle-building exercise”, it is a body and mind-building pose that will help keep your muscles loose, flexible, and functional as they move the joints. Learn about the muscles targeted with this technique.
Legs
Powerful and resilient, the legs represent the trunk while the feet are the roots that ground you in the tree pose. The weight bearing leg takes on more of the load than normal, while the glutes, hips and pelvis help to stabilize the trunk and act as support for the remaining steps.
Core
Strong core muscles support an upright posture and open diaphragm, which translates to healthier breathing, and hence better focus, and energy.
Shoulders
Lifted shoulders also help open the chest and back area to release tension, and promote posing stamina.
How To Do The Tree Pose (Vrksasana)
If you have the flexibility, and experience, the tree pose may be easy for you. But for everyone else, it will take some practice. While this technique appears to be simple and easy, well, try it and see if that’s true. You may be very surprised at how difficult it can be.
That’s why we created this step by step guide with video demonstrations, tips, and how to fix common mistakes. The key is to be patient, don’t rush, and make sure your body is aligned, tall, and balanced, while engaging the necessary muscles.
Steps
Stand tall with your feet together.
Slowly lift one knee up to roughly belly button height, then grab the front of the knee with both hands to keep the leg up.
From here, root down through all four corners of your standing foot, and align your pelvis and core to find your balance. Keep your pelvis straight and in line with your body, and low back lengthened.
Then grab the ankle of your lifted leg with the same-side hand, and rotate your thigh outward to open the hips.
Now flex your foot by lifting the toes up, then bring the sole of your foot as high as you can on the standing-leg inner thigh with your toes facing down.
Press your foot into the squishy part of your thigh and pull your thigh into the foot to keep it in place and avoid it sliding down the leg.
Here you can bring your hands together by your heart, or extend your arms overhead. Hold for 30-60 seconds.
Take your foot off the inner thigh, bring the knee to waist height, then place it back on the floor.
You can then switch legs, pulling the opposite foot to your inner thigh, and repeat the movement.
Check the short tree pose video demonstration below.
If you have 12 minutes for a more in-depth tutorial that shows all the technique tips and tricks, we highly recommend watching the following video.
Tips
Before you start the pose, spread your toes and bring awareness to your feet. After all, the feet are the roots and you want to feel a strong base before beginning.
Before you lift the leg and foot into position on your inner thigh, ease yourself into it by first lifting one heel off the ground with the toes still on the ground.
Remember to keep the pelvis tucked in and aligned with your torso. Do not let your buck curl up and arch the lower back.
Gently push yourself into the correct position if the pelvis shifts back or to the side when the foot is pressed into the inner thigh.
Use a wall or place your foot on the lower leg, rather than the top of the inner thigh for support, if you have trouble balancing.
It’s important to root your feet and stand tall in maintaining good balance.
Keep in mind, everyone may not have the same exact form during the tree pose.
If you want more of a challenge, try closing your eyes or looking up at the ceiling to train your balance.
Benefits of Tree Pose Vrksasana
There may not appear to be so many benefits of the tree pose, but we can assure you that there are many worthwhile. Here are the unique benefits of this exercise.
A functional test of balance, coordination and concentration
Challenging indeed, but consequently beneficial, tree pose tests and grows your balance, positional awareness, and concentration. Seldom do basic exercises have you stand on one leg to complete an exercise. Tree pose involved various elements, making you more functional and coordinated.
It’s so beneficial for the aging population who incur injuries from balance issues, in addition to the sports crowd.
One sided
The tree pose is asymmetrical in nature, with the left and right sides performing a different function. This develops proprioception (physical awareness of the body and coordination), unilateral function (training one side at a time), and trains us to perform as humans.
Tree Pose
Posture pose
The tree pose can challenge you to maintain good posture, by standing upright, and consciously focusing on being a tall tree! Today we slouch more than ever, looking down at our devices, and this technique gently helps to reinforce and focus on good body position.
Stretches the full body
We don’t do stretches like this often enough. Lifting the foot and placing it against the inner thigh opens the hips and stretches the groin area, while you’ll also feel it in the quads, and hamstrings via knee and hip flexion. Move up the torso, raise the arms overhead, and the upper chest and latissimus dorsi fibers lengthen, as well as the shoulders and arms.
Keeps you flexible
It takes practice to stretch the groin area if you lack the flexibility to pull your heel into the upper inner thigh region. As school kids, the butterfly stretch hit this area but most of us never did it again. Tree pose is a great way to bring it back into your routine!
Activates the core muscles
Balancing on one leg will naturally recruit your core muscles to do more to stabilize your body. It’s a nice routine for anyone, and especially elderly individuals who need a light, functional activity to help maintain their coordination and stability.
A pelvis exercise
Your pelvis is bones that connect the trunk and legs near the hips. When you stand on one leg, the pelvis is called upon for extra duty where it supports the weight of the upper body, and maintains stability there to keep you in proper posture. From there, you can comfortably perform the moving parts of the pose such as raising the arms overhead.
Builds patience
We live in a very instant world where we can get an immediate dopamine rush without having to wait like we did in the old days. This has caused us to become less patient, more anxious, irritated and yeah you get the point. The tree pose, and yoga, in general, is a form of meditative exercise that can help calm our nerves, reduce anxiety, and teach us that patience creates worthwhile rewards.
Drawbacks of Tree Pose
Take a look at this pose in motion, and it’s easy to see the potential drawbacks. But don’t mistake drawbacks with negatives as practice will change them into positives.
You’ll need some darn good balance!
There’s no way around it, you must have exceptional balance to the do the tree pose. However, we’d assume most people practicing this pose are capable of standing on one leg. But if you’re doing it for the first time and hardly test your balance, it will be difficult.
The good news is that a wall or chair can be used as a progression to a non-supported variation of tree pose.
But you should also take your time with the tree pose, and practice easing yourself onto one leg, and establishing your balance.
Can be frustrating to learn
For beginners especially, it can sometimes be frustrating when you can’t quite nail a pose. Balance, groin flexibility, and are the big annoyances during tree pose.
Common Mistakes While Performing The Tree Pose
While there’s no cookie cutter technique, there are general form cues and recommendations to ensure you stay injury free, maximize the muscles involved, and enjoy the process. Here are some things to avoid.
You can actually place your foot on the lower leg below the knee, if above the knee is too difficult yet. However, we do not recommend placing your foot directly on your knee, which will put unnecessary pressure on this joint. The knee is to meant to bend to the side, but rather back.
Not using the weight bearing/standing leg
If you’re doing nothing with the standing leg, you’re doing the tree pose wrong. You need the counter pressure from the standing weight bearing leg not only to keep the foot from sliding down, but to keep your body straight, which will allow you to have a tall posture and maintain your balance.
Clenching your toes
It’s normal to want to dig your toes into the mat to maintain your balance. But it’s more accurate to relax the toes, so that you can tense the quads and pull them up, to lift the hips in the proper position. Then you’ll have a more efficient tree pose.
Rotating the knees and hips to the side
When the foot is pressed into the upper thigh, there may be a tendency for some people to swing the bent leg and rotate the body. Focus on keeping your body facing one direction and don’t deviate or turn your body. The only thing that should be moving is your arms, whatever you decide to do with them during the pose.
Wandering eyes
Your eyes are also important for maintaining your balance during the tree pose. If you’re looking around, you’ll probably have a difficult time standing on one leg, much less doing anything else. Try to fix your gaze on a spot on the wall and keep it there.
Variations of Tree Pose Vrksasana
A base to other variations, tree pose is a fundamental pose that opens up the door to these similar, but individually unique exercises.
Tree pose with a block
Some people need to ease themselves into a pose, and using a block is a great idea. You can use it to inch your way higher up the leg, while having something to hold your foot up and in position. It will also allow you to focus on engaging the leg muscles and working that flexibility before you go full on tree pose. When you can move beyond this beginner technique, place your foot on the lower leg below the knee.
Steps
Stand tall with your feet roughly hip width apart.
Place a block long ways between your feet.
Find your balance on one leg by rooting down into the four points of your foot.
Bend the other foot and lift your knee up, then place the ball and toes of that foot on the top of the block. Keep your heel close to the ankle bone of the weight bearing leg.
Now focus on keeping your body squared up, with the hips straight, and body nice and tall.
Lift the foot off the block for a few seconds and try to find how you’ll gain balance on the standing leg. Do it a few more times.
Now, switch your legs and repeat.
Windy tree
As the name implies, a windy tree blows the branches from side to side. This can actually challenge your core muscles, stretch your midsection, improve total body stability, balance, focus, and your mind.
Steps
Find your tree pose stance, then raise your arms in the air in the form of a V.
Wave your arms from side to side while rotating your body from left to right.
If you thought tree pose was challenging, bring your feet a little higher on your hips, and try to do the same thing. You’ll also stretch out your abductor muscles on the outer thigh if performed correctly.
Steps
From a standing position, bend your left leg, pull the left foot up, and hold it across the top of your right thigh in the hip crease. Flare your toes and flex your foot. You can hold your foot in place, or let go and try to keep it there.
Stay in this position and try to feel out the movement, and get accustomed to holding your feet there, or bring your arms to a prayer position or raise them overhead.
Arms reaching to sky
There’s nothing like leaning forward and reaching your arms toward the sky to throw off your balance, or rather, force you to maintain it. Try the tree pose with this additional step.
Steps
Get into tree pose stance with one foot pressed into the opposite thigh.
Hinge forward at the hips, rotate your torso toward the bent leg, and lean forward.
Extend the top arm toward the sky, and use the bottom arm to stabilize yourself.
Toe stand pose
You need to be a vrksasana master to get deep down in this sitting pose, and support your entire weight on your toes, while crossing one foot over the opposite thigh. It requires an extreme degree of focus or you can easily be thrown off course.
Steps
Start from a full tree pose with one foot pressed into the opposite inner thigh.
Next grab your foot and pull it into your hip crease. Flare your toes and flex your foot.
Now hinge at the hips, bend your upper body down, extend your arms toward the floor, and slowly drop down on your hands.
Then walk your hands forward, rise up onto the toes of the standing leg, then bend the standing leg and slowly drop your butt down to within a few inches from the floor.
Keep your hands on the floor for support, and instead of sitting all your weight on your calf muscle, focus on pushing into the ground with your toes and lifting yourself up.
Wrapping Up
Balance, coordination, positional awareness, and every functional foundation are vital abilities that we need, yet often fail to maintain. Planting yourself in the tree pose on a weekly basis will help counteract aging’s effects on our balance, while keeping our groins and hips healthier, reinforcing good posture, and easing our minds from the stressful modern culture. Then when you’re ready for something more advanced, you can step into more complex variations that will challenge your body, mind, and spirit on higher levels.
Standing Dumbbell Fly Exercise Guide: How To, Benefits, Muscles Worked, and Variations
Close your eyes and think about an ideal free-weight chest workout. Chances are the training session includes the bench press, dumbbell press, dumbbell fly, and some variation of the incline or decline fly. All these exercises share something in common — they require a bench.
Busy folks that train during rush hours might not have the luxury of waiting for a bench. On the other hand, people that work in their minimal garage gyms might not have access to a bench.
Contrary to what most lifters think, you can train your pecs effectively without a bench with free weights; one of the best exercises to do this is the standing dumbbell fly.
Whether you don’t want to wait for your turn on the bench, don’t have a bench in your home gym, or want to try a new exercise to spark chest growth, the standing dumbbell fly has you covered.
The standing dumbbell fly is a versatile exercise that can be included in your chest, push, upper body, or full-body workouts. This movement demands decent core stability to perform correctly. Furthermore, going too heavy on the standing dumbbell fly can render the exercise ineffective.
You must follow a slow and controlled range of motion while using moderate weights to make the most of the standing dumbbell fly, making it an excellent exercise for beginners. It will also help improve your mind-muscle connection, which will carry over to other lifts.
In this article, we cover everything you need to learn about the standing dumbbell fly to make the most of this lift, including its benefits, the common mistakes, the muscles worked, how to perform correctly, and the best variations and alternatives.
What is a Standing Dumbbell Fly?
Developed pectoral muscles take your physique aesthetics to the next level. They add to your V-taper, draw eyes to your midsection, and improve your overall functionality. However, most lifters leave gains on the table during their chest workout as they chase weights and forget about using a full range of motion and contracting their muscles with each rep. The unique setup of the standing dumbbell fly fixes this. This exercise also improves your stability and balance. Furthermore, the range of motion of the standing dumbbell fly will make you strong enough to lift the love of your life in your arms.
The standing dumbbell fly is a standing low to high cable fly variation. To perform a standing dumbbell fly, assume a hip-width stance while holding a dumbbell in each hand. Maintain an upright torso, push your chest out, and raise your hands to shoulder level while maintaining a slight bend in your elbows.
You could also turn this exercise into a unilateral movement by working one side of your body at a time. Unilateral exercises are incredibly effective at fixing muscle and strength imbalances. While doing the single-arm variation of this lift, keep your other hand on your hip or hold onto a dumbbell for better balance.
Muscles Worked During Standing Dumbbell Fly
The standing dumbbell fly works the following muscles:
Chest
The pectoralis muscle consists of two muscles, the pectoralis major and the pectoralis minor. The pectoralis major is a fan-shaped superficial muscle in the front of your chest wall. On the other hand, the pectoralis minor is triangular and located under the pectoralis major.
The standing dumbbell flys mainly target the pectoralis major, which helps with the adduction, or depression, of the arm and arm rotation forward about the axis of the body.
Shoulders
The standing dumbbell fly is an isolation exercise that restricts movement to the shoulder joint. Since this exercise involves movement in the sagittal plane, it results in anterior deltoid recruitment.
Biceps
This dumbbell fly variation involves maintaining a slight bend in your elbows throughout the range of motion. You might experience a slight biceps engagement during the movement’s concentric (upward) part while performing this exercise, especially while lifting heavy.
Benefits of Standing Dumbbell Fly
Adding the standing dumbbell fly to your exercise arsenal entails the following advantages:
Helps Build Muscle Mass
The standing dumbbell fly is an isolation exercise that can help build muscle mass and improve your conditioning. Perform 3-5 sets and 8-12 reps of this exercise once weekly using appropriate weight to induce hypertrophy. [1]
Beginner-Friendly
This dumbbell fly variation involves lifting light to moderate weights while focusing on your form, making it an excellent exercise for beginners. You must readjust your form if you don’t feel your chest muscles contracting with each rep. Use this exercise as an opportunity to polish your mind-muscle connection.
Variety
Most free-weight chest exercises require lying on a bench. The unique stimulus of the standing dumbbell flies can shock your muscles, sparking new muscle tissue growth. Plus, it is a versatile exercise that can be added as an accessory lift in most training programs. Since it requires only dumbbells, the standing dumbbell fly is incredibly convenient.
How To Do Standing Dumbbell Fly
This is how to perform the standing dumbbell fly with the correct form:
Steps:
Stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance.
Grab a dumbbell in each hand with a supinated (palms facing forward) grip.
Tuck your chin slightly, pull your shoulders back and down, and push out your chest.
Maintain a slight bend in your elbows and lift your arms toward the ceiling until your hands are at shoulder level.
Your hands should move toward the center line of your body during the upward motion and should be next to each other at the top.
Focus on contracting your pecs throughout the range of motion.
Pause and squeeze the life out of your chest at the top.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Standing Dumbbell Fly Tips:
Avoid touching the dumbbells at the top, as it will remove the tension from your chest and put it on your shoulders.
Keep your core and glutes braced throughout the range of motion for optimal stability and balance.
Many lifters make the mistake of extending their elbows at the bottom. Your elbows should be slightly bent throughout the ROM.
Breathe in during the concentric (upward) motion and exhale during the eccentric (downward) motion.
To prevent trapezius muscle activation, refrain from shrugging your shoulders as you lift your arms.
In This Exercise:
Target Muscle Group: Chest
Secondary Muscle Groups: Shoulders and Biceps
Type: Strength
Mechanics: Isolation
Equipment: Dumbbells
Difficulty: Beginner
Best Rep Range: 8-12
Common Mistakes While Performing Standing Dumbbell Fly
Avoid these lapses to make the most of the standing dumbbell fly:
Going Too Heavy
The standing dumbbell fly is an isolation exercise. Using heavier dumbbells than you can handle comfortably can remove tension from your pecs and put it on your shoulders and biceps. For optimal results on this lift, use a moderate weight and focus on contracting your pecs with every rep.
Leaning Forward
Many lifters tend to lean forward while performing this exercise. However, it can result in greater deltoid engagement and remove tension from your chest. You must maintain an upright torso and push your chest out to work your pecs.
Holding the Dumbbells Too Tight
Squeezing the dumbbell handles too hard can fire up your forearms and biceps. Additionally, since you’ll maintain a slight bend in your elbows, it can result in a biceps pump. Use a false (thumbless) grip if you feel excessive forearm engagement while performing this exercise.
Variations and Alternatives of Standing Dumbbell Fly
Add the following standing dumbbell fly variations and alternatives to your training regimen to build a full and round chest:
Standing Low To High Cable Fly
This chest movement is the closest alternative to the standing dumbbell fly exercise. The cables help keep constant tension on your muscles throughout the range of motion.
Steps:
Set the cable pulleys at the lowest setting and hook up a D-handle attachment.
Grab a handle in each hand, walk to the pulley machine’s center, and then take a step forward. The cable should be taut at the starting position.
Your hands should be at the sides of your thighs at the starting position.
While maintaining a slight bend in your elbows, lift your arms until your hands are at shoulder level.
Pause and contract your pecs throughout the range of motion.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Rinse and repeat.
Pro Tip: Slow down the exercise’s eccentric (lowering) motion for optimal pectoral engagement.
Pec Deck Fly
Since the pec deck fly machine follow a fixed movement path, it is a beginner-friendly chest exercise. The fixed movement trajectory allows you to focus on establishing a mind-muscle connection with your pectoral muscles and contracting them throughout the ROM.
Steps:
Set the seat of the pec deck machine at a height so that the machine handles are at shoulder level.
Grab the handles with a neutral (palms facing inward) grip.
Push out your chest slightly.
While maintaining a slight bend in your elbows, bring your hands together.
Pause and contract your pecs at the top.
Slowly return to the start position.
Pro Tip: Keep your shoulder blades pinched throughout the exercise. Rounded shoulders take tension off your pecs.
Check out our complete pec deck fly guide here!
Barbell Fly
Although this exercise requires barbells, it is a bodyweight movement. Besides annihilating your pecs, the barbell fly will engage your core and help improve your balance and stability.
Steps:
Place two barbells together on the floor.
Add a weight plate on the same end of both barbells.
Get into a push position while holding the barbells a few inches below their necks on the weighted sides.
The non-weighted ends of the bars should be between your feet.
Slowly roll out the bars and lower your chest as close to the floor as possible.
Pause at the bottom.
Bring the bars back to the starting position. Pause and contract your pecs at the top.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: Place a weight plate on each side to keep the bars from rolling too far out. The weight plates on the floor will act as guard rails.
Check out our complete barbell fly guide here!
Flat Bench Dumbbell Fly
This is a staple exercise in most chest training routines. It helps develop your inner chest, giving it a fuller appearance.
Steps:
Lie supine on a flat bench while holding a dumbbell in each hand with a neutral grip.
Extend your arms so they are perpendicular to the floor.
While maintaining a slight bend in your elbows, lower your arms to your sides.
Pause at the bottom.
Explode back to the starting position. Contract your pecs at the top.
Rinse and repeat.
Pro Tip: Keep your rhomboids pinched together as if holding a pencil between them. This will improve your chest stimulation.
Check out our complete flat bench dumbbell fly guide here!
Incline Dumbbell Fly
The upper pecs are a lagging muscle group for most lifters. Not only does the incline dumbbell fly improve your upper shelves, but it also enhances your muscle separation.
Steps:
Set the back of an incline bench at a 45-degree angle with the floor.
Lie on the bench holding a dumbbell in each hand using a neutral grip.
Extend your arms so they are perpendicular to the floor.
While maintaining a slight bend in your elbows, slowly lower the bar toward the floor.
Return to the starting position.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: Many lifters make the mistake of holding the dumbbells at an angle, which removes tension from their chest and puts in on their anterior deltoids. Your arms should be at a 90-degree with the floor for optimal chest engagement.
Check out our complete incline dumbbell fly guide here!
Wrapping Up
The standing dumbbell fly is an unorthodox exercise that can spark new growth in your chest. Perform 3-5 sets of 8-12 reps of this exercise with moderate weights to put you in the sweet spot for gaining muscle mass and conditioning.
You must follow a full range of motion to get optimal results. Furthermore, switch this exercise with the alternatives and variations mentioned in this article to target your pectoral muscles from different angles and fast-track your pectoral growth.
References
Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.
Downward Facing Dog (Adho Mukha Svanasana) – How-To, Muscles Worked, Benefits, and Variations
As the name implies, there is a similarity between the downward facing dog and a common habit of our favorite furry sidekicks. Also called Adho Mukha Svanasana in yoga words, this pose is akin to how a dog stretches itself by leaning back onto the legs and lengthening its spine (svana). And this full-body technique will benefit you just the same!
The downward dog is one of the most commonly practiced yoga techniques, cued often in vinyasa yoga, flowing into other poses, but also effective all on its own! But most importantly, the goal isn’t ultimately the downward dog pose, but how it makes us feel and progress in our yoga journey, or life in general.
It’s a tricky one, but follow along with the instructions and tips in this guide, and you’ll get it down pat!
Muscles Worked
A yoga-based pose, downward facing dog still requires various muscles to perform it correctly. Here are brief descriptions of the muscles you’ll use during this technique.
Arms and delts
Anytime your body is being supported by your arms, you’re recruiting the triceps and deltoid muscles. Both muscle groups have a combined three heads, one on the anterior, another laterally, and the third on the posterior or backside of the body.
With the arms extended, your triceps resist elbow flexion, allowing you to support your weight. The front deltoids are engaged when the arms move forward in front of the body.
Trapezius
Traps too have three components – upper, middle, and lower fibers. Individually, they lift the scapula, pull it back, and retract it. The upper fibers are most prominent during a downward facing dog when the arms are in an overhead position.
Core
Finding their role in every total body movement, your core and abdominal muscles stabilize your trunk, and help you to maintain balance, and force efficiency, to keep you in the inverted ‘V’ position.
Leg muscles
Don’t expect much physical gains but the quads, glutes, hamstrings, and calves do bear some of your weight. Not to mention, the calf raise component during a more advanced variation where the toes are dorisflexed which activates the rear lower leg muscles. Then you have the inner thighs or adductor muscles which should be used to keep the lower body in stable and strong position.
How To Do Downward Facing Dog
In this section, we break down the downward facing dog technique with step-by-step instructions. So be sure to follow along closely, and check out the video demonstration below to hear all the important form ques.
Steps
Note: The following instructions and demonstration are the quick and easy steps to get into a downward facing dog position. If you plan to progress in your yoga journey, we recommend learning additional pre-pose techniques. This will make your yoga practice more enjoyable, productive, and sustainable.
Get down on your hands and knees in a tabletop position. Your hands should be roughly shoulder width apart, shoulders slightly forward past the wrists, with arms fully extended, knees directly under the hips, and back neutral. Turn your hands slightly outward so your elbows are pointing straight behind you, not completely out to the sides.
While you’re in this position, you may feel the natural need to do a cat-cow pose, to stretch your back and abdomen. It’s a great choice before hopping into the downward dog. We’ve included a video example of cat-cow below.
From your hands and knees, squeeze your hands together, without physically moving them inward, to activate your chest.
Now curl your toes under and press your feet into the ground bringing your knees into full extension, while lifting your hips up and back. In this position, your arms should be aligned with your torso in a straight line from your hands to your butt. Bring your gaze down so you’re looking down at the floor, or at the back of the room through your legs.
Accentuate the extension through your spine by lifting up through the pelvis and pressing the full hands into the floor. Externally rotate your arms, to create space between the shoulder blades. Lift the heels, and pretend to squeeze the inner thighs together.
Congrats! You just did the downward facing dog!
Here’s a short video demonstration of cat-cow pose.
Tips
Take some time and find the right knee and foot position to ensure you are doing the downward facing dog with the correct technique.
One way people find the optimal feet to hands distance is to get into a plank.
You should be able to transition between a plank and downward facing dog without moving your hands and feet.
If you cannot keep your spine straight during the downward facing dog, do it with your knees bent until you gain more flexibility.
Your heels do not need to be touching the ground.
Do a few reps of a cat-cow pose to warm up the spine before the downward dog.
Consider easing into the downward dog by incorporating pre-movement techniques beforehand.
You need a comfortable and non-slip surface to do this technique safely and effectively.
Press down into the floor with the entire hands (palms and fingers) to get the most efficiency from the movement.
Benefits of Downward Facing Dog
The advantages of learning this technique surely outweigh any potential negatives. It does a whole lot of good for the body and mind, and it’s also challenging and a good transition pose to other yoga practices.
Get a lovely stretch!
If done right, the downward facing dog should stretch your back first and foremost, followed by everything from your wrists to your shoulders, abs, and leg muscles. However, the back should be the focal point. The goal should not be to force a stretch in your legs.
Stretching has many benefits including healthier muscles, increased range of motion and flexibility, more blood flow to the area, reduced muscle soreness, and even stress relief. During downward facing dog you’re also strengthening the aformentioned muscles.
Strengthen all your muscles
The downward dog involves your push muscles, back, abdominals and obliques, hips, legs, and feet. There’s literally no muscle sitting out. While there is some muscular strengthening from movement (isotonic), you also benefit from static strengthening, where the muscles are not contracting, but support your weight in a contracted state.
Learn about the differences and benefits of isotonic vs isometric training here.
Form of inversion
Most exercises don’t involve hanging the head down, somewhat upside down. But what this does is increase blood flow and circulation to the brain possibly enhancing mental performance, while decompressing the spine and creating more space between the vertebra which may allow better disk hydration and hence greater spine mobility and reduced risk of injury.
Many experts also believe that inversion supports the lymphatic system, which helps the body cleanse itself. And this is said to only be able to occur via the movement of muscles, and breathing. Some other supposed benefits include improving back pain, and increasing torso strength and mobility too.
It’s important to note, however, that studies are limited and not conclusive on the potential benefits of inversion.
Ease your mind
Yoga has long been practiced for its stress-relieving effects. Most of us live every day without releasing the tension that we build up in our muscles due to mental stress, physical stress, lack of activity, and high intensity exercise. Bringing flexibility, and stretch into our daily routines can have a great effect on us. Not to mention, yoga technique are therapeutic alone.
May support better digestion
For the same reason the brain and spine may benefit from downward facing dog, so too may your digestive system. In normal conditions, the belly has to work a little to digest food against gravitational forces. Well, the increased blood driven to the stomach could possibly stimulate a healthier process.
Burn calories
Moving your body and using your muscles to resist your body weight is one way to burn calories. During this process, your body uses energy from stored food for fuel, and if you expend more energy than you consume, you’ll lose fat. Yoga is one way to contribute to the weight loss process if you’re not eating too much every day.
Try our yoga calories burned calculator to see how much energy you’re using during your sessions.
This Exercise:
Target Muscle Group: Arms, delts, core, quads, glutes, hamstrings, calves
Type: Yoga
Mechanics: Compound
Equipment: Cushioned surface, exercise mat
Difficulty: Intermediate
Drawbacks of Downward Facing Dog
If you want to try the downward facing dog, you could experience some of these negatives.
Not as easy as it looks
If you’re not decently flexible or fit, you may be in for a nice surprise. It’s harder than it looks both on video, and in your head. But… if you use a suitable surface, wear the right clothing, and follow the form instructions, you’ll have the best chance at nailing this technique. The good news is, if you can’t yet, you’re totally allowed to bend your knees. So keep practicing and you’ll master this staple pose!
Bad form is common and good form ignored
Without a proper understanding of basic exercise technique mechanics, or yoga experience, it’s too easy to do this exercise wrong. Not that its the worst thing you could do, but people try to force their heels down when they shouldn’t, or they don’t realize they have bad form. The downward dog should be a beautiful exercise that feels good, and encourages you do it more.
Common Mistakes When Performing Downward Facing Dog
If you want to get the most out of the downward facing dog, try to keep these bad habits out of your checklist.
Tucking in the tailbone
You want to lift the tailbone, not tuck it in. The latter will move the pelvis rearward and round the back in a convex shape which you don’t want. Rather bend the knees to bring the back into a better and safer alignment.
Forcing the heels down
We’re not all physically constructed the same, hence different heights, proportions, movement, etc. If your heels don’t naturally touch the floor, don’t force them. As you stretch, you’ll learn if it’s tight calves and hamstrings. But it could also be a shorter achilles tendon, or someone’s bone structure, and that’s fine, there’s nothing to do there. After all, the goal is not to stretch the calves, it’s to target the back.
Bad shoulder position
Slouching over and letting your head into your shoulders is the wrong way. The delts and scapular area should be set properly with proper arm placement and involved to make the exercise most efficient.
Wrong hand positioning
When pushing your hands into the floor, you should focus on shifting the weight onto your thumbs, index and middle fingers, not the pinkies or palms only. This will create a better position for your shoulders and it’s more efficient.
Not bending the knees
While you will need to lengthen the legs to lift the tailbone and stretch the back, you are free to keep the knees slightly bent.
Internal shoulder rotation
Remember that these three words are something you seldom ever wanted to do during any exercise. Turning the shoulders inward toward the chest can cause impingement issues, and it doesn’t make for efficient technique. Instead, turn your biceps slightly out to open up the delts and create a safer position.
Feet too close or wide
Your feet should be roughly the same distance apart that they are in a plank. That’s why it’s good to start the movement from a plank, especially if you’re a beginner. But, you may find the need to adjust your footing slightly.
Variations of Downward Facing Dog
You can find so many different variations of the downward facing dog. Unfortunately, there are too many to list here, however, we picked some favorites for you to try!
Single leg downward facing dog
Also called Eka Pada Adho Mukha Svanasana, this single leg downward facing dog variation stretches the hamstrings, engages more core muscles, and trains your balance.
Steps
Assume the basic downward facing dog as shown in the primary example in this guide. Your feet should be fully planted on the mat.
Press down into the left foot, and lift the right heel as high as you can while keeping it fully extended. Point the toes straight down. You should feel a nice stretch in the left hamstring. Keep your gaze down toward the floor, or back toward your feet.
Hold then switch legs and repeat.
Tips
Inhale as you lift the leg and exhale as you drop it down.
Keep your shoulders and hips square, avoiding allowing the body to rotate in either direction.
For a more advanced technique, great for training balance, lift one leg, and the opposite arm.
Knee to elbow
If you want to take the previous variation a step further, hence increasing the benefits, you can introduce more movement.
Steps
From the three legged, or single leg downward facing dog with one leg extended in the air, bend the knee and bring it into the same side elbow. Keep your core tense and spine neutral.
Lift the same leg back up into extension or the three legged dog, now pull the knee into your opposite elbow.
Do several reps, then switch legs.
Twisted dog
Here’s a simple, but challenging variation you should also try. It will wake up your obliques, and give you a releasing stretching in the waist.
Steps
From the basic downward facing dog position, move your feet closer to your arms and simply reach one hand back and grab the opposite ankle. Rotate your upper body to face the same side as the leg you’re grabbing. Return to the starting position, then reach with the opposite hand to the other ankle.
Make sure to keep your spine lengthened.
Bent knee dog
From the inverted downward dog position, bend one knee so that your toes are pointed at the ceiling. Reset, and repeat with the other leg.
Downward facing dog on blocks
Prop your feet or hands up on some blocks to vary the angle and lessen the difficulty of the downward facing dog. Elevating the hands, for example, creates more space in the upper body like shoulders, back and neck. It also helps maximize space on the mat during vinyasa flow!
Steps
Prop your hands up on blocks and find your downward dog.
Keeping your toes on the mat, lift your heels high, and extend your spine by raising your hips up above your shoulders.
Now exhale, bend your knees, tighten your core, press into the blocks and hop your feet forward in between your hands. As you jump, keep the hips higher than the shoulders.
Inhale, stand halfway up keeping your hands on the blocks, exhale, fold your upper body into your lower body, then inhale, and stand all the way up reaching your arms overhead with hands together.
Finally, exhale and bring your hands to your heart.
FAQs
Below we included a few common questions and answers regarding the downward facing dog pose.
Who is the downward facing dog not good for? Due to the nature of this exercise, it’s best avoided by people with wrist problems such as carpal tunnel, or those with back issues, vertigo, high blood pressure, or eye conditions that affect vision. We also don’t recommend it for women who are pregnant.
What should be the primary goal of the downward facing dog?Stretching the back, activating the core, and really becoming more in tune with your body. There are many benefits of downward facing dog that can enhance your physical, mental, and yoga progression.
Wrapping Up
Congrats on mastering the downward facing dog pose! But if you haven’t yet, don’t worry you’re not alone, it’s by no means an easy exercise for most people. But this common yoga class pose should be learned as it’s a fundamental technique and you’ll probably be called to do it. The tips, tricks and variations in this guide are going to help you utilize the downward dog effectively, build more confidence in your yoga journey, and enhance your life!
CrossFit Cluster Exercise Guide: How To, Benefits, Muscles Worked, and Variations
CrossFit is a unique sport. It involves beginner-friendly simple movements like the air squat, shoulder press, and kettlebell swings. On the flip side, it also incorporates demanding exercises such as rope climbs, pig flips, and Olympic lifts (clean and jerk and snatch) that get elite athletes on their knees.
Most CrossFit WODs (workout of the day) consist of circuits that combine two or more movements. The CrossFit cluster takes this a step further, merging the thruster with the clean into a single exercise.
Interestingly, the thruster is a combination of two exercises — the front squat and the push press. Adding the clean to the mix makes the cluster a blend of three compound (multi-joint) movements.
CrossFit has set itself apart by requiring its athletes to perform unique and challenging compound exercises that help you work your entire body in a short time. The cluster fits the bill perfectly.
In this article, we go over the fundamentals of the CrossFit cluster, and everything you need to know about it to master the movement, including its benefits, correct form, common mistakes, variations, and the muscles worked during this exercise.
What is a CrossFit Cluster?
A CrossFit cluster combines two exercises — the clean and the thruster. The compound exercise works your entire body. Most WODs have just the right amount of clusters as chippers or in a circuit to destroy you by the end of the workout.
Each cluster begins from the ground. You must lift the bar to your hip height and catch it in the front rack position at the bottom of a squat. The rest of the movement is the same as the thruster. From the bottom of the front squat, stand up by extending your knees and driving through your midfoot. As you’re about to achieve full knee extension, use the momentum to drive the bar overhead and lock out your elbows. Return the bar to the front rack position.
In the thruster, you would go right into a squat after catching the bar and repeat for the recommended reps. However, you will return the bar to the floor with each rep while doing the cluster. Adding the cleans makes the cluster much more demanding than the thrusters.
You must follow the perfect form while performing the cluster to avoid unnecessary strain on your lower back. Lifting with a rounded back is one of the most common mistakes while doing this exercise.
Muscles Worked During CrossFit Cluster
The CrossFit cluster is a full-body exercise, recruiting almost every muscle fiber in your body. It is such an effective compound exercise that we think this section should be titled “Muscles not worked in a CrossFit Cluster.” Nonetheless, here are the muscles stimulated in this exercise:
Legs
The cluster works your quads during the initial lift off the floor; your glutes and hamstrings are activated as you get into the squat after catching the bar. This exercise is a complete leg builder that will help you add strength and size to your lower body.
Back
While performing the cluster, you’ll experience latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, teres major and minor, and trapezius muscle engagement. Since this is a hip-hinge movement, you’ll also feel lower back stimulation.
Shoulders
From pulling the bar off the floor and pressing it overhead, you’ll experience shoulder engagement. Cycle through the cluster reps, and you’ll feel a sick anterior and lateral deltoid pump.
Arms
The first half of the movement involves pulling the bar to the front rack, resulting in biceps engagement. The second half requires you to press the bar overhead, which will fire up your triceps.
Core
Performing a clean, especially while lifting heavier, requires a strong core. Your midriff and stabilizers will also be in action as you press the bar overhead and complete a lockout. Folks that lack a solid core will have trouble completing a heavy overhead lockout.
Benefits of CrossFit Cluster
Adding the cluster to your exercise arsenal entails the following benefits:
Boosts Your Skills
CrossFit involves a lot of skills. Most WODs involve a healthy chunk of high-skill weightlifting moves such as the Olympic lifts and gymnastics moves like handstand walks and ring muscle-ups.
The cluster helps you improve at Olympic lifts by incorporating the clean, front squat, and overhead press into a single movement. It will aid in improving your technique and get you better results faster.
Full-Body Exercise
The cluster is a full-body exercise that will help you build overall strength and muscle mass. This compound exercise will improve your functionality, making you better at other exercises and day-to-day activities.
The cluster will also improve your metabolic conditioning, boosting your performance in demanding workouts.
Helps Build Strength and Muscle Mass
The compound exercise will boost your strength and muscle mass. You must, however, program your workouts accordingly. Stay in the 1-5 rep range to focus on strength. On the other hand, the 8-12 range is optimal for hypertrophy. [1]
Enhances Endurance and Stamina
Perform high-rep sets of clusters, and you’d be gasping for breath. Adding cluster ladders to your WODs will help you build stamina and endurance, translating to better performance in demanding workouts.
Improves Coordination
There are several moving parts in the cluster. You need to clean the barbell off the floor, perform a squat, and then do an overhead press. Doing this exercise regularly will help improve your hand-eye coordination.
How To Do a CrossFit Cluster
The CrossFit cluster is a complex lift. You must dial in your technique to get the best bang for your buck. There will be a lot of tips and tricks, so pay close attention. Here is how to perform the cluster with the perfect form:
Steps:
Place a barbell against your shins and stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance.
Grab the bar using a shoulder-wide hook grip. Your hip crease should be below your knees crease. This will help you use your quads in the initial phase of the lift.
Your chest should be open, and you should look straight ahead while at the bottom of the lift.
Pull the bar to your hip level while keeping it close to your body by driving through your midfoot.
Pull the bar faster as it crosses your knees, and you stand upright by extending your knees.
The bar should make contact with your hips. At this point, lean back slightly, generate momentum by getting on your heels, and pull the bar toward your shoulders.
In one motion, jump your feet wide and get under the bar to catch it in the front rack position at the bottom of the squat.
Get out of the hole explosively by driving through your midfoot.
Press the bar overhead as you reach the top of the movement.
Move your head through your arms to achieve a lockout.
Lower the bar to a front rack position.
Repeat for reps.
CrossFit Cluster Tips
Pull the slack out of the bar at the bottom by pulling the bar slightly off the floor. This will help ensure a smooth upward movement.
You can skip jumping your feet out if you are comfortable with your initial stance and can use it to push the weight overhead.
Your elbows should trace over the bar in the initial part of the lift and drop below the bar as you catch it in a squat. This will help you keep control of the barbell.
Avoid rounding your back or looking down in the initial phase of the cluster, as it can put unnecessary strain on your neck.
Driving through your heels or toes will throw you off balance. Drive through your midfoot to maintain your center of gravity.
This Exercise:
Target Muscle Groups: Back, Legs, Shoulders, Arms, and Core
Type: Strength
Mechanics: Compound
Equipment: Barbell
Difficulty: Intermediate
Best Rep Range: 8-12 Reps
Common Mistakes While Performing a CrossFit Cluster
Stay clear of the following cluster errors for optimal gains and to avoid injuries:
Improper Form
Like all the other exercises, you only get better at the cluster with practice. Since this is a compound movement, lifters tend to make several mistakes initially. You must not yank the bar off the floor in the first half of the lift, as it can throw you off balance.
Keep your chin tucked and your eyes locked straight ahead throughout the exercise. Tilting your head toward the ceiling or the floor will again make the lift unstable. Plus, many lifters get on their toes too soon. You must wait for the bar to reach your hip level before using your feet to generate extra momentum.
Not Warming Up
The cluster is a full-body exercise, meaning a lot can go wrong while performing this exercise. Many people increase their odds of injury by not warming up before a workout. You must spend 10-15 minutes warming up before a training session for optimal performance.
Furthermore, compound lifts like the cluster require a decent amount of mobility. You must work on improving your flexibility and mobility to get better at the Olympic lifts.
Going Too Heavy
This is one of the most common mistakes lifters make while doing the cluster. Since this exercise is a combination of three lifts, many people load the bar with more weight than they can handle, assuming that they can muscle through the lift. However, letting your ego get the better of you jeopardizes your form and puts you at a greater risk of injury.
Variations and Alternatives of CrossFit Cluster
Use the following cluster variations and alternatives to add variety to your training regimen:
Dumbbell Cluster
This cluster variation uses dumbbells instead of a barbell. Although many lifters might think it is easier than the conventional cluster, it is not the case. The dumbbell cluster requires a different skill.
Steps:
Grab a dumbbell in each hand and stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance.
Push your hips back, hinge at your hips, and bend your knees to lower the dumbbells to your floor. Place the dumbbells on the outside of your feet at the starting position.
Lift the dumbbell to your knees by driving through your quads and midfoot.
Drive your hips forward and extend your knees as the dumbbells cross the knees.
Generate momentum by lifting your heels off the floor when the dumbbells reach your hip level.
Drop under the dumbbells and catch them over your shoulders.
Explode out of the hole and push the dumbbells overhead as you complete the movement.
Pro Tip: Ensure you’re using your quads to power off the floor by getting your hip crease below your knee crease at the bottom of the movement.
Thruster
The thruster is a great exercise to forge a more robust cluster. It is just like the cluster, minus the cleans while doing multiple reps.
Steps:
Take a shoulder-width stance and stand upright with a barbell against your shins.
Grab the bar at shoulder-width using a hook grip.
Clean the bar into a front rack and get into a squat.
Explode out of the hole by driving through your midfoot.
Press the bar overhead as you extend your knees.
Lower the bar into a front rack.
Perform a squat.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Hold the bar in the front rack position using a full grip. Balancing the bar using only your fingers can make the lift unstable.
Clean
The clean is an Olympic lift, which needs a lot of practice to master. However, sticking with this exercise will make you better at most other CrossFit compound lifts, as it will help develop a stronger base.
Steps:
Stand with a shoulder-wide stance with a barbell placed against your shins.
Grab the bar with a hook grip.
Maintaining an open chest and flat back, pull the bar to your knees using your quads.
Drive your hips forward and extend your knees to bring the bar to your hip level.
From here, lift your heels off the floor to pull the bar toward the ceiling.
Get under the bar and catch the bar in a front rack position while jumping your feet out.
Stand upright.
Pro Tip: Drive your knees outward during the initial phase of the lift, as it will help engage your legs to generate power.
Front Squat
The next two exercises on the list are among the nine basic movements of CrossFit. The front squat is a compound exercise that primarily works your quads.
Steps:
Start with the bar in a front rack position with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
Use a shoulder-wide stance and turn your toes slightly outward.
While maintaining an upright torso, lower into a squat and go as deep as possible.
Return to the starting position.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: You must have decent upper body, overhead, hip, and lower body mobility to perform a front squat with an upright torso.
Push Press
The push press is a basic CrossFit movement that will help you build upper body strength and explosiveness.
Steps:
Start in the front rack position and a shoulder-width stance.
Drop into a shallow stance.
Extend your knees rapidly and push the barbell overhead while raising your heels off the floor.
Lock out your elbows at the top and drive your head through your arms.
Lower the bar to the front rack position.
Repeat.
Pro Tip: Your elbows should be under the bar at the starting position, as it will help you generate power.
Wrapping Up
CrossFit is a high-intensity sport that combines weightlifting, gymnastics, and cardio. Olympic weightlifting exercises form the basis of the CrossFit resistance training WODs and help work your entire body in a short time.
The CrossFit cluster is one of the most effective functional exercises to help you build strength, muscle, endurance, and balance. Use the cluster alternatives and variations listed in this article to take your WODs to the next level. Best of luck!
References
Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.